Interosseous membrane of leg
| Interosseous membrane of leg | |
|---|---|
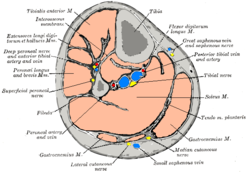 Cross-section through middle of left leg. (Interosseus membrane labeled at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Membrana interossea cruris, ligamentum tibiofibulare medium |
| TA98 | A03.6.05.002 |
| TA2 | 1867 |
| FMA | 35187 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The interosseous membrane of the leg (middle tibiofibular ligament) extends between the interosseous crests of the tibia and fibula, helps stabilize the Tib-Fib relationship and separates the muscles on the front from those on the back of the leg.
It consists of a thin, aponeurotic lamina composed of oblique fibers, which for the most part run downward and lateralward; some few fibers, however, pass in the opposite direction.
It is broader above than below. Its upper margin does not quite reach the tibiofibular joint, but presents a free concave border, above which is a large, oval aperture for the passage of the anterior tibial vessels to the front of the leg.
In its lower part is an opening for the passage of the anterior peroneal vessels.
It is continuous below with the interosseous ligament of the tibiofibular syndesmosis, and presents numerous perforations for the passage of small vessels.
It is in relation, in front, with the Tibialis anterior, Extensor digitorum longus, Extensor hallucis proprius, Peronæus tertius, and the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve; behind, with the Tibialis posterior and Flexor hallucis longus.
Additional images
-
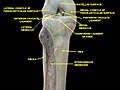
Bones of the right leg. Anterior surface.
-
Right knee-joint. Posterior view.
-
The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries.
-
Knee and tibiofibular joint.Deep dissection. Anterior view.
-
Knee and tibiofibular joint.Deep dissection. Anterior view.
-
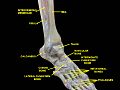
Knee, tibiofibular and ankle joints.Deep dissection. Anterolateral view.
-
Knee, tibiofibular and ankle joints.Deep dissection. Anterolateral view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 348 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 348 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)