Anocutaneous line
(Redirected from Intersphincteric groove)
| Anocutaneous line | |
|---|---|
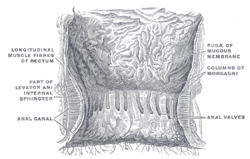 The interior of the anal canal and lower part of the rectum. (Line not shown but region is visible.) | |
| Details | |
| System | Alimentary system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | linea anocutanea |
| TA98 | A05.7.05.012 |
| TA2 | 3019 |
| FMA | 15715 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anocutaneous line, also called the Hilton white line or intersphincteric groove, is a boundary in the anal canal.[1]
Below the anocutaneous line, lymphatic drainage is to the superficial inguinal nodes.[2]
The anocutaneous line is slightly below the pectinate line and a landmark for the intermuscular border between internal and external anal sphincter muscles.
The anocutaneous line represents the transition point from non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the anal canal to keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the anus and perianal skin.[3]
In live persons, the color of the line is white, hence the alternative name. It is named for John Hilton.[4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Ewing MR (July 1954). "The white line of Hilton". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 47 (7): 525–30. doi:10.1177/003591575404700706. PMC 1918929. PMID 13185975.
- ^ "Pelvis". Archived from the original on 2007-10-21. Retrieved 2007-12-09.
- ^ "The Digestive System". Retrieved 2009-01-14.
- ^ synd/3030 at Who Named It?
