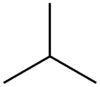
Isobutane
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Methylpropane
2-Methylpropane | |||
| Other names
Isobutane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
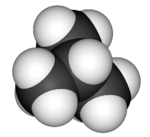
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.780 | ||
| E number | E943b (glazing agents, ...) | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H10 | |||
| Molar mass | 58.124 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 2.51 kg/m3, gas (15 °C, 1 atm) 593.4 kg/m3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −159.6 °C (−255.3 °F; 113.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −11.7 °C (10.9 °F; 261.4 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | flammable gas | ||
| Explosive limits | 1.8–8.4% | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Isobutane (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Isobutane, also known as methylpropane or 2-methylpropane, is an alkane, isomeric with butane. Recent concerns with depletion of the ozone layer by freon gases have led to increased use of isobutane as a gas for refrigeration systems, especially in domestic refrigerators and freezers, and as a propellant in aerosol sprays. When used as a refrigerant or a propellant, isobutane is also known as R-600a. Some portable camp stoves use a mixture of isobutane with propane, usually 80:20. Isobutane is used as a feedstock in the petrochemical industry, for example in the synthesis of isooctane.[1]
Its UN number (for hazardous substances see shipping) is UN 1969.
Isobutane is the R group for the amino acid leucine.
Nomenclature

Isobutane is the trivial name retained by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in its 1993 Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry.[2]
Methylpropane is the systematic name. The substituent number (2-) is unnecessary because there is no isomer of this molecule with methylpropane as part of its name.
Uses
- As a refrigerant.
- As a propellant for aerosol cans and foam products, such as reddi wip.
References
- ^ Patent Watch, July 31, 2006.
- ^ Panico, R.; & Powell, W. H. (Eds.) (1994). A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds 1993. Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-03488-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) http://www.acdlabs.com/iupac/nomenclature/93/r93_679.htm
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0901
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry (online version of the "Blue Book")
- Data from Air Liquide