Japp–Klingemann reaction
| Japp–Klingemann reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Francis Robert Japp Felix Klingemann |
| Reaction type | Coupling reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000158 |
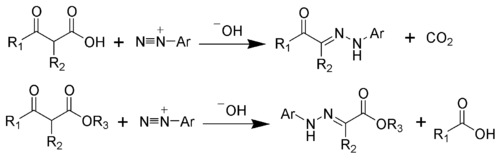
The Japp–Klingemann reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize hydrazones from β-keto-acids (or β-keto-esters) and aryl diazonium salts.[1][2][3][4][5][6] The Reaction is named after the chemists Francis Robert Japp and Felix Klingemann.
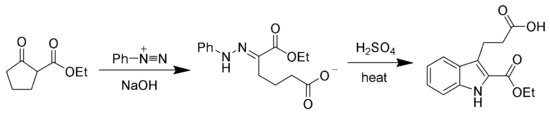
The hydrazone products of the Japp–Klingemann reaction are most often used as intermediates in syntheses of more complex organic molecules. For example, a phenylhydrazone product can be heated in the presence of strong acid to produce an indole via the Fischer indole synthesis.[7][8]
Reaction mechanism
To illustrate the mechanism, the Japp-Klingemann ester variation will be considered. The first step is the deprotonation of the β-keto-ester. The nucleophilic addition of the enolate anion 2 to the diazonium salt produces the azo compound 3. Intermediate 3 has been isolated in rare cases. However, in most cases, the hydrolysis of intermediate 3 produces a tetrahedral intermediate 4, which quickly decomposes to release the carboxylic acid 6. After hydrogen exchange, the final hydrazone 7 is produced.

References
- ^ Francis Robert Japp, Felix Klingemann (1887). "Ueber Benzolazo- und Benzolhydrazofettsäuren". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 20 (2): 2942–2944. doi:10.1002/cber.188702002165.
- ^ F. R. Japp; F. Klingemann (1887). "Zur Kenntniss der Benzolazo- und Benzolhydrazopropionsäuren (p 3284-3286)". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 20 (2): 3284–3286. doi:10.1002/cber.188702002234.
- ^ F. R. Japp; F. Klingemann (1887). "Ueber sogenannte »gemischte Azoverbindungen". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 20 (2): 3398–3401. doi:10.1002/cber.188702002268.
- ^ F. R. Japp; F. Klingemann (1888). "Ueber die Constitution einiger sogenannten gemischten Azoverbindungen". Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 247 (2): 190–225. doi:10.1002/jlac.18882470208.
- ^ Phillips, R. R. Org. React. 1959, 10, 143.
- ^ Reynolds, G. A.; VanAllan, J. A. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol. 4, p.633 (1963); Vol. 32, p.84 (1952). (Article Archived 2012-07-16 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Bowman, R. E.; Goodburn, T. G.; Reynolds, A. A. (1972). "1,3,4,5-Tetrahydrobenz[cd]indoles and related compounds. Part I. A new synthesis of 3,4-dihydrobenz[cd]indol-5(1H)-one (Uhle's ketone)". J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1: 1121. doi:10.1039/P19720001121.
- ^ Meyer, M. D.; Kruse, L. I. (1984). "Ergoline synthons: Synthesis of 3,4-dihydro-6-methoxybenz[cd]indol-5(1H)-one (6-methoxy-Uhle's ketone) and 3,4-dihydrobenz[cd]indol-5(1H)-one (Uhle's ketone) via a novel decarboxylation of indole-2-carboxylates". J. Org. Chem. 49 (17): 3195–3199. doi:10.1021/jo00191a028.
