Longisquama
| Longisquama Temporal range: Middle or Late Triassic,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Cast of the type specimen | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Neodiapsida |
| Genus: | †Longisquama Sharov, 1970 |
| Species: | †L. insignis
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Longisquama insignis Sharov, 1970
| |
Longisquama is a genus of extinct reptile. There is only one species, Longisquama insignis, known from a poorly preserved skeleton and several incomplete fossil impressions from the Middle to Late Triassic Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan. It is known from a type fossil specimen; slab and counterslab (PIN 2548/4 and PIN 2584/5), and five referred specimens of possible integumentary appendages (PIN 2584/7 through 9). All specimens are in the collection of the Paleontological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow.
Longisquama means "long scales"; the specific name insignis refers to its small size. The Longisquama holotype is notable for a number of long structures that appear to grow from its skin. The current opinion is that Longisquama is an ambiguous diapsid and has no bearing on the origin of birds.
Description
Integumentary structures

Longisquama is characterized by distinctive integumentary structures along its back. The holotype (specimen PIN 2584/4) is the only known fossil preserving these appendages projecting from the back of an associated skeleton. It has 7 appendages radiating in a fan-like pattern, but their tips are not preserved. PIN 2584/9 preserves five complete appendages spaced close together. PIN 2584/6 preserves two long, curved appendage running side by side. Other specimens, such as PIN 2585/7 and FG 596/V/1 preserve only one appendage. These structures are long and narrow throughout most of their length, and angle backward near the tip to give the appearance of a hockey stick. The proximal straight section is divided into three longitudinal lobes: a smooth lobe on either side and a transversely ridged lobe running between them. The middle ridged lobe is made up of raised "rugae" and deep "interstices," which Sharov compared to rosary beads. The distal section is thought to be an extension of the middle and anterior lobes of the proximal section. While the anterior lobe widens in the distal section, the posterior lobe of the proximal section narrows until it ends at the base of the distal section. In addition, an "anterior flange" appears about two-thirds the way up the proximal section and continues to the tip of the distal section. Both lobes in the distal section are ridged and separated by a grooved axis. In some specimens, the rugae of either lobe in the distal section line up with each other, while in other specimens they do not. Some specimens have straight rugae projecting perpendicular to the axis, while others have rugae that curve in an S-shape. One specimen of Longisquama, PIN 2584/5, has small spines projecting from the axis of the distal section.[1]
The holotype skeleton shows each structure attaching to a vertebral spine. These anchorage points are visible as raised knobs. The base of each appendage is slightly convex, unlike the flattened shape of the rest of the structure. The convex shape may be evidence that the base of each structure was tubular in life, anchoring like other integumentary structures such as Mammalian hair or Avian feathers into a follicle. Moreover, the proximity of each structure to its corresponding vertebra suggests that a thick layer of soft tissue, possibly including a follicle, surrounded each base.[1]
History
Interpretation

Haubold and Buffetaut believed that the structures were long, modified scales attached in pairs to the lateral walls of the body, like paired gliding membranes.[2] They published a reconstruction of Longisquama with plumes in a pattern akin to gliding lizards like Draco species and Kuehneosaurus, allowing it to glide, or at least parachute. Though this is now thought to be inaccurate, versions of this reconstruction are still often seen on the Internet and elsewhere.
Other researchers place the scales differently. Unwin and Benton interpreted them as a single, unpaired, row of modified scales that run along the dorsal midline.[3] Jones et al. interpreted them as two paired rows of structures that are anatomically very much like feathers, and which are in positions like those of birds' spinal feather tracts.[4] Feather development expert Richard Prum and also Reisz and Sues see the structures as anatomically very different from feathers, and think they are elongate, ribbon-like scales.[5][6]
Still other observers (e.g. Fraser in 2006) believe that the structures are not part of Longisquama at all; they are simply plant fronds which were preserved along with the reptile and misinterpreted.[7] Buchwitz & Voigt (2012) argue that the structures of Longisquama are not plant remains because all of the structures except for the last in the holotype PIN 2584/4 are arranged regularly, and that they are not preserved as carbon films, the usual mode of preservation for plants in the Madygen Formation.[1] The only plant from Madygen with similarities to the Longisquama structures is Mesenteriophyllum kotschnevii, but its leaves do not have the distinct hockey-stick shape of the structures attributed to Longisquama.[1]
Classification
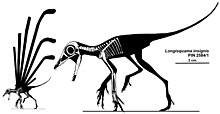
Like the 'long scales', the skeletal features of Longisquama are equally difficult to diagnose. As a result, Longisquama has been related by scientists to many different Sauropsid groups.
Sharov determined that it was a "pseudosuchian" (a "primitive" archosaur, but as an archosaur a relatively derived reptile) on the basis of two features - a mandibular fenestra and an antorbital fenestra.[8] Sharov's original description also includes an elongate scapula. Jones et al. see Longisquama as an archosaur, adding to Sharov's two characters a furcula.[4] Olshevsky believes that Longisquama is an archosaur and, moreover, an early dinosaur[9] - a possibility which could actually dispense with almost all of the debate about bird origins, were it true.
Unwin & Benton didn't think it was possible to diagnose the crucial fenestrae; the holes could simply be damage to the fossil.[3] They agreed with Sharov that Longisquama has acrodont teeth and an interclavicle, but instead of a furcula they saw paired clavicles. These features would be more typical of a member of Lepidosauromorpha, meaning that Longisquama is not an archosaur and thus not closely related to birds. According to a cladistic study by Phil Senter in 2004, Longisquama would be an even more basal diapsid and a member of Avicephala, more closely related to Coelurosauravus.[10]
A 2012 re-examination of the fossil found that the presence of fenestrae in the skull crucial to classification as an archosaur could not be confirmed; in fact, a section of the skull in one of the fossil slabs that had previously been used to justify the presence of antorbital fenestrae does not contain any actual bone. This study concluded that none of the proposed classifications of Longisquama could be confirmed or refuted using the available evidence. The authors of the study tentatively placed Longisquama among the Archosauromorpha due to their hypothesis of developmental "deep homology" between its plumes, bird feathers, crocodile scales, and pterosaur pycnofibres.[1]
Debate over bird origins

The question of what kind of reptile Longisquama is, and what exactly the 'long scales' are, relates to a wider debate about the origin of birds, and whether or not they are descended from dinosaurs.
Background
A consensus of paleontologists agree that birds evolved from theropod dinosaurs. The scenario for this hypothesis is that early theropod dinosaurs were endothermic, and evolved simple filamentous feathers for insulation. These feathers later increased in size and complexity and then adapted to aerodynamic uses. Ample evidence for this hypothesis has been found in the fossil record, specifically such dinosaurs as Kulindadromeus, Sinosauropteryx, Caudipteryx, Microraptor, and many others. Longisquama is thus regarded as a diapsid with strange scales, ambiguous skeletal features, and no real significance to bird evolution.
A group of fringe scientists prefer the hypothesis that birds evolved from small, arboreal archosaurs like Longisquama. They see these as ectothermic animals that adapted to gliding by developing elongated scales and then pennaceous feathers. This hypothesis, however, is not supported by cladistic analysis. [11]
References
- ^ a b c d e Buchwitz, M.; Voigt, S. (2012). "The dorsal appendages of the Triassic reptile Longisquama insignis: reconsideration of a controversial integument type". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 86 (3): 313–331. doi:10.1007/s12542-012-0135-3.
- ^ Haubold, H. & Buffetaut, E. (1987). "Une novelle interprétation de Longisquama insignis, reptile énigmatique du Trias supérieur d'Asie centrale [A new interpretation of Longisquama insignis, an enigmatic reptile from the Upper Triassic of Central Asia]". Comptes Rendus Académie des Sciences du Paris. 305 (serie II): 65–70.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Prum, R. O./Unwin, D.M., Benton, M.J./Response; Jones, T.D., Ruben, J.A., Maderson, P.F.A., Martin, L.D. (9 March 2001). "Longisquama Fossil and Feather Morphology". Science. 291 (5510): 1899–1902. doi:10.1126/science.291.5510.1899c. PMID 11245191.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Jones, T.D., Ruben, J.A., Martin, L.D., Kurochkin, E., Feduccia, A., Maderson, P.F.A., Hillenius, W.J., Geist, N.R., Alifanov, V. (23 June 2000). "Nonavian Feathers in a Late Triassic Archosaur". Science. 288 (5474): 2202–2205. doi:10.1126/science.288.5474.2202. PMID 10864867.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Prum, R.O. (2002). "Are current critiques of the theropod origin of birds science? Rebuttal to Feduccia". The Auk. 120 (2): 550–561. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2003)120[0550:ACCOTT]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0004-8038.
- ^ Reisz, R.R., Sues, H.-D. (23 November 2000). "The "Feathers" of Longisquama". Nature. 408 (6811): 428. doi:10.1038/35044204. PMID 11100716.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fraser, N. (2006). Dawn of The Dinosaurs: Life in the Triassic. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-025-334-3.
- ^ Sharov, A.G. (1970). "A peculiar reptile from the lower Triassic of Fergana". Paleontologiceskii Zhurnal (1): 127–130.
- ^ Olshevsky, G. 1991. A Revision of the Parainfraclass Archosauria Cope, 1869, Excluding the Advanced Crocodylia. Mesozoic Meanderings, 2: 196 pp.
- ^ Senter, P. (2004). "Phylogeny of the Drepanosauridae (Reptilia: Diapsida)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 2 (3): 257–268. doi:10.1017/S1477201904001427.
- ^ Padian, Kevin. (2004). "Basal Avialae". In Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; & Osmólska, Halszka (eds.) (ed.). The Dinosauria (Second ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 210–231. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link)
Further reading
- Feduccia, A., Lingham-Soliar, T., and Hinchliffe, J.R. (2005). "Do feathered dinosaurs exist? Testing the hypothesis on neontological and paleontological evidence". Journal of Morphology. 266 (2): 125–66. doi:10.1002/jmor.10382. PMID 16217748.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Martin, L. D. (2008). "Origin of avian flight- a new perspective". Oryctos. 7: 45–54.
- Peters, D. (2000). "A Redescription of Four Prolacertiform Genera and Implications for Pterosaur Phylogenesis". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 106 (3): 293–336.
- Peters, D. (2002). "A New Model for the Evolution of the Pterosaur Wing – with a twist". Historical Biology. 15 (4): 277–301. doi:10.1080/08912960127805.
- Stokstad E. (23 June 2000). "Feathers, or flight of fancy?". Science. 288 (5474): 2124–2125. doi:10.1126/science.288.5474.2124. PMID 10896578.
- Sebastian Voigt & Michael Buchwitz & Jan Fischer & Daniel Krause & Robert Georgi (2009). "Feather-like development of Triassic diapsid skin appendages". Naturwissenschaften. 96 (1): 81–86. doi:10.1007/s00114-008-0453-1. PMID 18836696.
