Project Plowshare

Operation Plowshare, better known as Project Plowshare, not to be confused with the anti-nuclear Plowshares Movement, was the overall United States term for the development of techniques to use nuclear explosives for peaceful construction purposes. The phrase was coined in 1961, taken from Micah 4:3 ("And he shall judge among the nations, and shall rebuke many people: and they shall beat their swords into plowshares, and their spears into pruning hooks: nation shall not lift up sword against nation, neither shall they learn war any more"). It was the U.S. portion of what are called Peaceful Nuclear Explosions (PNE). The Soviet Union had a similar program of testing as well for many years.[1] The Soviet program was titled Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy.
Suggested usage
Proposed uses included widening the Panama Canal, constructing a new sea-level waterway through Nicaragua nicknamed the Pan-Atomic Canal, cutting paths through mountainous areas for highways, and for connecting inland river systems. Other proposals involved blasting underground caverns for water, natural gas, and petroleum storage. Serious consideration was also given to using these explosives for various mining operations. One proposal suggested using nuclear blasts to connect underground aquifers in Arizona. Another plan involved surface blasting on the western slope of California's Sacramento Valley for a water transport project. Project Carryall[2], proposed in 1963 by the Atomic Energy Commission, the California Division of Highways (now Caltrans), and the Santa Fe Railway, would have used 22 nuclear explosions to excavate a massive roadcut through the Bristol Mountains in the Mojave Desert, to accommodate construction of Interstate 40 and a new rail line. At the end of the program, a major objective was to develop nuclear explosives, and blast techniques, for stimulating the flow of natural gas in "tight" underground reservoir formations. In the 1960s, a proposal was suggested for a modified in situ shale oil extraction process which involved creation of a rubble chimney (a zone in the oil shale formation created by breaking the rock into fragments) using a nuclear explosive.[3] However, this approach was abandoned for a number of technical reasons.
Nuclear explosives have never been used for commercial engineering purposes in the United States, but the concept has been tested.
Plowshare testing
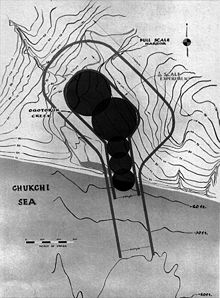
One of the first plowshare nuclear blast cratering proposals that came close to being carried out was Project Chariot, which would have used several hydrogen bombs to create an artificial harbor at Cape Thompson, Alaska. It was never carried out due to concerns for the native populations and the fact that there was little potential use for the harbor to justify its risk and expense. After the project was terminated, a proof-of-concept 104 kiloton (435 terajoule) cratering blast was conducted on July 6, 1962 at the north end of Yucca Flats, within the Atomic Energy Commission's Nevada Test Site (NTS) in southern Nevada. The shot, "Sedan", displaced more than 12 million short tons (11 teragrams) of soil and resulted in a radioactive cloud that rose to an altitude of 12,000 ft (3.7 km). The radioactive dust plume headed northeast and then east towards the Mississippi River.
The first PNE blast was Project Gnome, conducted on December 10, 1961 in a salt bed 24 mi (39 km) southeast of Carlsbad, New Mexico. The explosion released 3.1 kilotons (13 TJ) of energy yield at a depth of 361 meters (1,184 ft) which resulted in the formation of a 170 ft (52 m) diameter, 80 ft (24 m) high (52 by 25 m) cavity. The test had many objectives. The most public of these involved the generation of steam which could then be used to generate electricity. Another objective was the production of useful radioisotopes and their recovery. Another experiment involved neutron time-of-flight physics. A fourth experiment involved geophysical studies based upon the timed seismic source. Only the last objective was considered a complete success. The blast unintentionally vented radioactive steam while the press watched. The partly developed Project Coach detonation experiment that was to follow adjacent to the Gnome test was then canceled.
Over the next 11 years 26 more nuclear explosion tests were conducted under the U.S. PNE program. Funding quietly ended in 1977. Costs for the program have been estimated at more than (US) $770 million.
Natural gas stimulation experiment
The final PNE blast took place on 17 May 1973, under Fawn Creek, 76.4 km north of Grand Junction, Colorado. Three 30 kiloton detonations took place simultaneously at depths of 1,758, 1,875, and 2,015 meters. It was the third nuclear explosion experiment intended to stimulate the flow of natural gas from "tight" formation gas fields. Industrial participants included the El Paso Natural Gas Company for the Gasbuggy test; Austral Oil Company; CER Geonuclear Corporation for the Rulison test; and CER Geonuclear Corporation for the Rio Blanco test.
If it was successful, plans called for the use of hundreds of specialized nuclear explosives in the western Rockies gas fields. The previous two tests had indicated that the produced natural gas would be too radioactive for safe use. After the test it was found that the blast cavities had not connected as hoped, and the resulting gas still contained unacceptable levels of radionuclides.[4]
By 1974, approximately $82 million had been invested in the nuclear gas stimulation technology program. It was estimated that even after 25 years of gas production of all the natural gas deemed recoverable, that only 15 to 40 percent of the investment could be recovered.
Also, the concept that stove burners in California might soon emit trace amounts of blast radionuclides into family homes did not sit well with the general public. The contaminated well gas was never channeled into commercial supply lines.
The radioactive blast debris from 839 U.S. underground nuclear test explosions remains buried in-place and has been judged impractical to remove by the DOE's Nevada Site Office.
The situation remained so for the next three decades, however, a resurgence in Colorado Western slope natural gas drilling has brought resource development closer and closer to the original underground detonations. As of summer 2009, 84 drilling permits have been issued within a 3-mile radius, with 11 permits within one mile of the site. [5]
Table of Plowshare tests
The U.S. conducted twenty-seven PNE shots in conjunction with other, weapons-related, test series.
| Test Name | Date | Location | Yield | Test Series |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gnome | 10 December 1961 | Carlsbad, New Mexico | 3 kilotons | Nougat |
| Sedan | 6 July 1962 | Nevada Test Site | 104 kilotons | Storax |
| Anacostia | 27 November 1962 | Nevada Test Site | 5.2 kilotons | Dominic I and II |
| Kaweah | 21 February 1963 | Nevada Test Site | 3 kilotons | Dominic I and II |
| Tornillo | 11 October 1963 | Nevada Test Site | 0.38 kilotons | Niblick |
| Klickitat | 20 February 1964 | Nevada Test Site | 70 kilotons | Niblick |
| Ace | 11 June 1964 | Nevada Test Site | 3 kilotons | Niblick |
| Dub | 30 June 1964 | Nevada Test Site | 11.7 kilotons | Niblick |
| Par | 9 October 1964 | Nevada Test Site | 38 kilotons | Whetstone |
| Handcar | 5 November 1964 | Nevada Test Site | 12 kilotons | Whetstone |
| Sulky | 5 November 1964 | Nevada Test Site | 0.9 kilotons | Whetstone |
| Palanquin | 14 April 1965 | Nevada Test Site | 4.3 kilotons | Whetstone |
| Templar | 24 March 1966 | Nevada Test Site | 0.37 kilotons | Flintlock |
| Vulcan | 25 June 1966 | Nevada Test Site | 25 kilotons | Flintlock |
| Saxon | 11 July 1966 | Nevada Test Site | 1.2 kilotons | Latchkey |
| Simms | 6 November 1966 | Nevada Test Site | 2.3 kilotons | Latchkey |
| Switch | 22 June 1967 | Nevada Test Site | 3.1 kilotons | Latchkey |
| Marvel | 21 September 1967 | Nevada Test Site | 2.2 kilotons | Crosstie |
| Gasbuggy | 10 December 1967 | Farmington, New Mexico | 29 kilotons | Crosstie |
| Cabriolet | 26 January 1968 | Nevada Test Site | 2.3 kilotons | Crosstie |
| Buggy | 12 March 1968 | Nevada Test Site | 5 at 1.1 kilotons each | Crosstie |
| Stoddard | 17 September 1968 | Nevada Test Site | 31 kilotons | Bowline |
| Schooner | 8 December 1968 | Nevada Test Site | 30 kilotons | Bowline |
| Rulison | 10 September 1969 | Grand Valley, Colorado | 43 kilotons | Mandrel |
| Flask | 26 May 1970 | Nevada Test Site | 105 kilotons | Mandrel |
| Miniata | 8 July 1971 | Nevada Test Site | 83 kilotons | Grommet |
| Rio Blanco | 17 May 1973 | Rifle, Colorado | 3 at 33 kilotons each | Toggle |
See also
- Plowshares Movement
- Atoms for Peace
- Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy: Soviet Plowshare-type program
References
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "Preliminary Design Studies In A Nuclear Excavation - Project Carryall". Highway Research Board. 1964. pp. 32–39. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ^ Lombard, D.B.; Carpenter, H.C. (1967). "Recovering Oil by Retorting a Nuclear Chimney in Oil Shale". Journal of Petroleum Technology (19). Society of Petroleum Engineers: 727–734.
- ^ Project Dubious
- ^ Jaffe, Mark (07/02/2009). "Colorado drilling rigs closing in on '60s nuke site". The Denver Post. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
External links
- U.S. Department of Energy Nevada Operations Office (2000). "United States Nuclear Tests, July 1945 through September 1992 (DOE/NV--209-REV15)" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Plowshare Program
- Bruce A. Bolt, "Nuclear Explosions and Earthquakes: The Parted Veil" (San Francisco, CA: W. H. Freeman and Company, 1976). ISBN 0-7167-0276-2
- Richard L. Miller, Under the Cloud: The Decades of Nuclear Testing (Woodlands, TX: Two Sixty Press, 1999). ISBN 1-881043-05-3
- Chuck Hansen, U.S. Nuclear Weapons: The Secret History (Arlington, TX: Aerofax, Inc., 1988). ISBN 0-517-56740-7
- Chuck Hansen, The Swords of Armageddon: U.S. Nuclear Weapons Development Since 1945 (CD-ROM).
- Scott Kirsch, Proving Grounds: Project Plowshare and the Unrealized Dream of Nuclear Earthmoving. (New Brunswick, NJ and London: Rutgers University Press, 2005)
- National Cancer Institute / Radioactive I-131 from Fallout website. See "Background" link.
- "Estimated Exposures and Thyroid Doses Received by the American People from Iodine-131 in Fallout Following Nevada Atmospheric Nuclear Bomb Tests", A Report from the National Cancer Institute. Contained in the Executive Summary is the map Figure 1 - Per capita thyroid doses resulting from all exposure routes from all test.
- Stephen I. Schwartz, ed., Atomic Audit: The Costs and Consequences of U.S. Nuclear Weapons Since 1940, (Washington, D.C.: Brookings Institution Press, 1998). ISBN 0-8157-7773-6
- "Focused Evaluation of Selected Remedial Alternatives for the Underground Test Area" (DOE/NV-465), April 1997, Environmental Restoration Division, Nevada Operations Office, U.S. Department of Energy.
- Declassification of the yields of 11 nuclear tests conducted as part os the plowshare ... program
- A chronology of Plowshare Program milestones, including proposed tests and projects conducted
- 2-part documentation about Project Plowshare from Prelinger Archives: Part 1, Part 2
