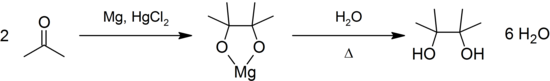Pinacol
Appearance

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3-dimethyl-2,3-butanediol
| |
| Other names
tetramethylethylene glycol, 1,1,2,2-tetramethylethylene glycol, pinacone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.849 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 118.174 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | solid |
| Melting point | 40–43 °C |
| Boiling point | 171–173 °C (444–445 K) |
| ? g/100 ml (?°C) | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 77 °C |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pinacol is a white solid organic compound. It is an alcohol that has -OH groups on adjacent carbon atoms on the same side. (i.e., same spatial arrangement).
Preparation
It may be produced by the pinacol coupling reaction from acetone:[1]
Reactions
As a vicinal-diol, it can rearrange to pinacolone by the pinacol rearrangement, e.g. by heating with sulfuric acid:[2]
Pinacol can be use with borane and boron trichloride to produce useful synthetic intermediate such as pinacolborane, bis(pinacolato)diboron,[3] and pinacolchloroborane.
See also
References
- ^ Roger Adams and E. W. Adams. "Pinacol Hydrate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 459.
- ^ G. A. Hill and E. W. Flosdorf (1941). "Pinacolone". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 462.
- ^ Tatsuo Ishiyama, Miki Murata, Taka-aki Ahiko, and Norio Miyaura (2004). "Bis(pinacolato)diboron". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 10, p. 115.