Posterior clinoid processes
Appearance
| Posterior clinoid processes | |
|---|---|
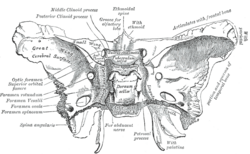 Sphenoid bone. Superior view. (Posterior clinoid process labeled at upper left.) | |
 Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Caption for posterior clinoid process visible at center left. Sphenoid bone is yellow.)) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Processus clinoideus posterior |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.011 |
| TA2 | 595 |
| FMA | 54696 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In the sphenoid bone, the anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the anterior clinoid processes, while the posterior boundary is formed by a square-shaped plate of bone, the dorsum sellæ, ending at its superior angles in two tubercles, the posterior clinoid processes, the size and form of which vary considerably in different individuals. The posterior clinoid processes deepen the sella turcica, and give attachment to the tentorium cerebelli.

Etymology
Clinoid likely comes from the Greek root klinein or the Latin clinare, both meaning "sloped" as in "inclined."
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 147 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 147 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Anatomy figure: 22:5b-06 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
