Rhizopus
| Rhizopus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Schematic diagram of Rhizopus spp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Rhizopus Ehrenb. (1820)
|
| Type species | |
| Rhizopus nigricans Ehrenb. (1820)
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found on a wide variety of organic substrates, including "mature fruits and vegetables",[2] jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic agents of human zygomycosis (fungal infection) and can be fatal. Rhizopus infections may also be a complication of diabetic ketoacidosis.[3] This widespread genus includes at least eight species.[4][5]
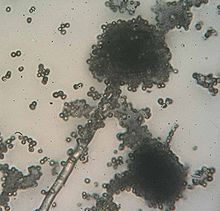
Rhizopus species grow as filamentous, branching hyphae that generally lack cross-walls (i.e., they are coenocytic). They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, sporangiospores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, the sporangiophore. Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, a zygospore produces colonies that are genetically different from either parent.
- R. microsporus var. oligosporus is used to make tempeh, a fermented food derived from soybeans.
- R. oryzae is used in the production of alcoholic beverages in parts of Asia and Africa.
- Rhizopus stolonifer (black bread mold) causes fruit rot on strawberry, tomato, and sweet potato and used in commercial production of fumaric acid and cortisone.
Various species, including R. stolonifer, may cause soft rot in sweet potatoes and Narcissus.
Species
See also
References
- ^ "Rhizopus Ehrenb. 1820". MycoBank. International Mycological Association. Retrieved 2011-02-05.
- ^ Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA (2008). Dictionary of the Fungi (10th ed.). Wallingford, UK: CABI. p. 599. ISBN 978-0-85199-826-8.
- ^ Chinn RY, Diamond RD (1982). "Generation of chemotactic factors by Rhizopus oryzae in the presence and absence of serum: relationship to hyphal damage mediated by human neutrophils and effects of hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis". Infection and Immunity. 38 (3): 1123–29.
- ^ Zheng RY, Chen GQ, Huang H, Liu XY (2007). "A monograph of Rhizopus". Sydowia. 59 (2): 273–372.
- ^ Abe A, Asano K, Sone T (2010). "A Molecular Phylogeny-Based Taxonomy of the Genus Rhizopus". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 74 (7): 1325–1331.
External links
- Rhizopus at Zygomycetes.org
- Photos of Rhizopus spp. used for tempeh-making at www.tempeh.idv.tw
