1893 Atlantic hurricane season
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2020) |
| 1893 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
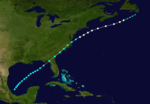
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | June 12, 1893 |
| Last system dissipated | November 9, 1893 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | "Cheniere Caminada" |
| • Maximum winds | 130 mph (215 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 948 mbar (hPa; 27.99 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 12 |
| Total storms | 12 |
| Hurricanes | 10 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 5 |
| Total fatalities | ~4,028 |
| Total damage | At least $6 million (1893 USD) |
| Related article | |
The 1893 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1893. The 1893 season was fairly active, with 12 tropical storms forming, 10 of which became hurricanes. Of those, five became major hurricanes. This season proved to be a very deadly season, with two different hurricanes each causing over 2,000 deaths in the United States; at the time, the season was the deadliest in U.S. history. The season was one of two seasons on record to see four Atlantic hurricanes active simultaneously, along with the 1998 Atlantic hurricane season. Additionally, August 15, 1893 was the only time since the advent of modern record keeping that three storms have formed on the same day (Hurricanes Four, Five, and Six) until 2020 saw Wilfred, Alpha, and Beta forming on the same day; and for the first time, there were two high-intensity hurricanes simultaneously in one month of August, and this was not repeated until the year 2023.[clarify]
Timeline
[edit]
Systems
[edit]Hurricane One
[edit]| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 10 – June 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min); 990 mbar (hPa) |
Observations from ships indicated the presence of a tropical storm in the Bay of Campeche on June 12.[1] The storm moved northeastward across the Gulf of Mexico and intensified into a strong tropical storm. Around 23:00 UTC on June 15, the system made landfall southwest of Perry, Florida, with winds of 70 mph (110 km/h). The cyclone weakened somewhat while moving over Florida and coastal portions of Georgia and the Carolinas. After emerging into the Atlantic near the North Carolina–Virginia state line early on June 17, the storm strengthened, reaching hurricane intensity later that day.[2] On June 19, a ship located in the vicinity of the storm recorded a barometric pressure around 999 mbar (29.5 inHg) - the lowest in relation to the cyclone.[1] However, the system then became losing tropical characteristics and transitioned into an extratropical cyclone about 155 mi (250 km) south of Saint Pierre and Miquelon by 00:00 UTC on June 20.[2]
Several locations in the Southeastern United States observed tropical storm-force winds, with the strongest recorded sustained wind speed being 56 mph (90 km/h) in Charleston, South Carolina.[1]
Hurricane Two
[edit]| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 4 – July 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); |
Observations of this storm began as early as July 4 in the southwestern Caribbean Sea,[1] with a ship encountering the cyclone about 130 mi (210 km) north-northeast of Colón, Panama. The system intensified steadily while moving northwestward, becoming a hurricane around 12:00 UTC on the following day. About six hours later, the storm intensified into a Category 2 hurricane and peaked with winds of 100 mph (155 km/h). The hurricane then made landfall near the Nicaragua–Honduras border. The cyclone weakened back to a Category 1 before re-emerging into the Caribbean off the north coast of Honduras early on July 6. Continuing northwestward, the system then re-strengthened slightly, reaching winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) prior to making landfall in northern Belize around 00:00 UTC on July 7. The cyclone weakened rapidly over the Yucatán Peninsula and dissipated just offshore Tabasco several hours later.[2]
The storm sank several ships, including many steamers loaded with fruit in Honduras. About 6,000 bunches of bananas awaiting shipment were washed away at Bonito, while fruit plantations also experienced extensive damage. A number of homes on Roatán were also severely damaged.[3] The hurricane reportedly caused a large loss of life.[1] It has been paleotempestologically traced in sediment near Gales Point in Belize.[4]
Hurricane Three
[edit]| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 13 – August 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min); 956 mbar (hPa) |
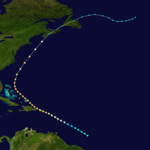
Hurricane San Roque of 1893
The third storm of the season formed on August 13 east of the Lesser Antilles. It steadily strengthened to a hurricane while moving over the Leeward Islands. While approaching Puerto Rico on August 16, its winds increased to major hurricane status before landfall at Patillas. It crossed the island and exited near Isabela.[5] There were heavy rains over the island of Puerto Rico and damages to the agricultural crops, especially coffee. In San Juan 2.36 inches of rain were reported.[5] The eye remained over Puerto Rico for a period of seven hours. The lowest barometric pressure reading recorded in San Juan was 29.17 inches. Four deaths were reported. This was the first hurricane in Puerto Rico where flags were used to alert the public about the danger of an approaching hurricane; they were flown from government buildings.[5][6]
Although landfall weakened the storm, the storm regained major hurricane status as it approached the Bahamas. It then re curved northward and on August 22, made landfall in St. Margaret's Bay near Halifax, Nova Scotia as a non-tropical category 1. The storm was known in Nova Scotia as "the second Great August Gale" and claimed 25 lives, including the sinking of the vessels "Dorcas" and "Etta Stewart."[7]
This hurricane was one of four active hurricanes on August 22.[citation needed]
Hurricane Four
[edit]| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 15 – August 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min); 952 mbar (hPa) |
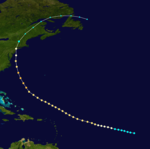
The New York Hurricane of 1893
This storm was first observed over the southeastern Atlantic on August 15,[1] with the official track beginning about 790 mi (1,270 km) of the Cabo Verde Islands. Initially a tropical storm, the cyclone is estimated to have intensified into a hurricane by Agust 15 as it moved west-northwestward. The storm gradually moved more northwestward for the next several days, until turning north-northwestward on August 22. That day, the system strengthened into a major Category 3 hurricane with winds of 115 mph (185 km/h),[2] based on the bark Glencoyn observing an atmospheric pressure of 952 mbar (28.1 inHg) early on August 23.[1] Thereafter, the cyclone weakened as it moved generally northward. Shortly before 12:00 UTC on August 24, the storm made landfall in New York City as a Category 1 hurricane with winds of 85 mph (140 km/h). Curving north-northeastward, the system weakened to a tropical storm and then transitioned into an extratropical cyclone later that day over Quebec. The extratropical remnants dissipated east of Newfoundland on August 26.[2]
Strong winds occurred in North Carolina, including gusts of 70 mph (110 km/h) in Kitty Hawk and 60 mph (95 km/h) in Hatteras.[8] Despite the storm's close proximity to New Jersey, the state likely did not experience hurricane force-winds because of the system's motion and asymmetrical wind field.[9] Nonetheless, Jersey City experienced its worst storm in several years. The hurricane capsized or beached numerous boats and vessels in the vicinity of New York City, leading to 34 deaths, 17 from the tugboat Panther alone.[1] At Coney Island, the storm demolished a number of buildings, walkways, piers, and resorts, while many homes were destroyed in Brooklyn. Hundreds of thousands of dollars in damage occurred in New York City.[10] Meteorologists Gordon E. Dunn and Banner I. Miller noted in 1960 that major damage occurred in Connecticut and Rhode Island.[1] In New Haven, Connecticut, the storm toppled about 1,000 elm and maple trees, blocking many streets. Surrounding communities reported unroofed homes and barns and downed fences and trees. Additionally, The Boston Globe noted that "Crops of all kinds are a total loss."[11] In western Massachusetts, the storm downed many wires and badly damaged corn and tobacco crops.[12]
Hurricane Five
[edit]| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 15 – August 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); |
The 5th storm of the season formed east of Bermuda on August 15. After moving northwestward for a day, it moved northeastward and strengthened to a Category 2 hurricane. The storm crossed over Sable Island at peak intensity, before making landfall in the Burin Peninsula of Newfoundland on August 18 as a 90 mph (145 km/h) hurricane. The storm dissipated on August 19.[citation needed] Climate researcher Michael Chenoweth proposed the removal of this system from HURDAT, finding "No convincing evidence for a tropical system" and arguing that data instead favored an extratropical cyclone.[13]
Hurricane Six
[edit]| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 15 – August 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min); 954 mbar (hPa) |
The Sea Islands Hurricane of 1893
Although no observations for this storm could be found prior to August 22, José Fernández-Partagás and Henry F. Diaz and the Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project retained C. J. Neumann's 1993 review of the system, which began the track on August 15.[14][2] Located near the west coast of Africa, the tropical storm initially moved west-southwestward, passing through the Cabo Verde Islands on August 16 and August 17. By the following day, the system curved west-northward, and on August 19, intensified into a hurricane. The storm became a Category 3 early on August 23. Three days later, the hurricane curved northwestward while passing through the northern Bahamas, crossing or passing near Eleuthera, the Abaco Islands, and Grand Bahama. Curving north-northwestward on August 27, the cyclone remained just offshore Florida, and made landfall near Ossabaw Island, Georgia, early on August 28. Based on Savannah recording a barometric pressure of 954 mbar (28.2 inHg), the storm is estimated to have peaked with winds of 120 mph (195 km/h). The system weakened to a tropical storm as it curved northeastward over the Carolinas on August 29. After crossing the Mid-Atlantic, New England, and New Brunswick, the storm became extratropical over eastern Quebec by the following day. On September 2, the remnants were last noted over the far north Atlantic.[2]
In the Bahamas, significant impacts were reported on the Abaco Islands, particularly at Marsh Harbour, with damage being "very large to houses, wharves, fences, boats, fields and in fact everything", according to The Nassau Guardian.[15] Several sponging vessels sank at the Abaco Islands. The captain of the ship Sarah Emma reported flooding on Grand Bahama, which destroyed crops.[16] In Florida, the storm downed hundreds of trees and partially or fully deroofed dozens of buildings, some as far as 50 mi (80 km) inland. Storm surge and abnormally high tides also caused damage, especially along the First Coast.[17] Farther north, strong winds unroofed hundreds of buildings in Savannah, Georgia, where the hurricane was compared to a storm in 1881.[18] However, the elevation and distance from the coast of the city left it relatively unscathed compared to the Sea Islands. Storm surge and abnormally high tides in South Carolina extensively flooded the islands and the cities of Beaufort, Charleston, and Port Royal,[1] which reportedly had no structures elevated more than 2 ft (0.61 m) above ground.[19] The National Hurricane Center places the death toll between 1,000–2,000, mostly in the Sea Islands,[20] while the Red Cross estimated that approximately 30,000 survivors in the region became destitute.[21] In North Carolina, high tides wrecked a number of vessels along the coast or just offshore. High winds caused severe impacts in Kernersville, including one death and the destruction of about 100 homes.[8]
Hurricane Seven
[edit]| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 20 – August 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); |
The official track for this storm begins on August 20 to the southwest of the Cabo Verde Islands,[2] similar to the paths created by Charles Mitchell in 1924 and C. J. Neumann in 1993. Although very little information could be found in relation to the storm,[14] it moved west-northwestward and is estimated to have intensified into a hurricane on August 22. By the following day, the system strengthened into a Category 2 hurricane with winds of 100 mph (155 km/h). Turning northeastward on August 26, the hurricane crossed the Azores, moving near Faial Island. The cyclone weakened to a tropical storm early on August 29 and was last noted northeast of the Azores several hours later.[2]
The hurricane destroyed 14 homes on Faial Island and 28 others on Terceira Island and ruined crops.[14][22] Three ships in the vicinity of the Azores were lost, while two remained missing by September 2. At least five people died in the archipelago.[22]
Hurricane Eight
[edit]| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 4 – September 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); 973 mbar (hPa) |
The 8th storm of the season formed in the western Caribbean Sea on September 4. After hitting the Yucatán Peninsula, it strengthened in the Gulf of Mexico to a 95 mph (153 km/h) hurricane. It hit the southern coast of Louisiana on September 7, and dissipated over northeastern Alabama.[citation needed]
Heavy rains fell over southern Louisiana, including a peak total of 15.2 in (390 mm) in Franklin, while Donaldsonville, Emilie, and Wallace broke 24-hour precipitation records for the month of September. Extensive losses to cotton, rice, and sugar occurred in St. Martin and St. Mary parishes, while East Feliciana Parish reported severe damage to oranges.[23] In Lockport, a tornado killed five people, injured seventeen others, and inflicted about $40,000 in damage. The storm also dropped heavy rain in Mobile, Alabama, and Pensacola, Florida.[24]
Hurricane Nine
[edit]| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 25 – October 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min); 955 mbar (hPa) |
The Great Charleston Hurricane of 1893
The ninth known tropical cyclone of the season formed southwest of Cape Verde on September 25. It moved westward and intensified into a hurricane on September 28, before turning northwestward on October 2. By then, the system strengthened into a Category 3 hurricane and likely peaked with maximum sustained winds of 120 mph (195 km/h). The hurricane then moved west-northwestward for several days, beginning on October 6. After passing just north of the Abaco Islands on October 12, the storm curved northwestward and then north-northwestward, remaining closely offshore Florida and Georgia. The hurricane then turned northeastward and at around 13:00 UTC on October 13, it made landfall near McClellanville, South Carolina, winds of 120 mph (195 km/h) and a barometric pressure of 955 mbar (28.2 inHg). Moved rapidly northward through North Carolina and the Appalachian Mountains, the cyclone was still a Category 1 hurricane as it passed 60 mi (95 km) west of Washington, D.C. The storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over far southern Quebec on October 14 after crossing Lake Ontario and continued northeastward until dissipating over the northeastern portions of the province on the following day.[2]
In the Bahamas, abnormally high tides inundated some streets on New Providence and nearby Hog Island, sweeping away the home of the assistant lighthouse keeper. The storm severely damaged pineapple cultivation facilities on Eleuthera and plantations on the Abaco Islands, where many other buildings were destroyed.[14] In Florida, storm surge reached several feet above ground between Palm Beach and Jacksonville, while heavy rains fell, leading to flooding in a number of coastal communities.[25] Storm surge and abnormally high tides in Georgetown, South Carolina, exceeded the heights of those measured in the August hurricane. An estimated 15 deaths occurred in the state,[26] while the National Hurricane Center lists the combined toll for Florida and South Carolina at 28.[20] Waves reached the then-record highest height in Wilmington, North Carolina, causing about $150,000 in damage to the waterfront. The state also suffered "great destruction ... to forests, crops and property, and to shipping.", according to a 2000 report by National Weather Service meteorologist James E. Hudgins. A total of 22 fatalities were reported in North Carolina.[8]
Strong winds in Virginia partially deroofed homes and downed several trees in Richmond, while the storm destroyed barns and outhouses and toppled many electrical lines in Petersburg. The Roanoke River rose significantly at Roanoke, causing washouts along the Norfolk and Western Railway. The river also overflowed into Elliston, washing away residences. High tides destroyed the wharves at Alexandria, causing about $25,000 in damage, and capsized the Edward Ewing. Gale-force winds downed trees, limbs, and a church wall in Washington, D. C. Four vessels suffered damage or capsized. In Maryland, the electric light plant burned down in Baltimore, while winds downed fences and partly deroofed some residences in Bladensburg.[27] Two prisoners died after the fire spread to the jail. Several Pennsylvania towns reported downed trees, unroofed dwellings, disrupted telegraph service, and delayed traffic on railroads. In New Jersey, the storm washed out several parts of the West Jersey Railroad, downed many telegraph wires, and beached several vessels.[26] Strong winds over western New York downed many lines, unroofed a number of structures, and destroyed four cottages and a railroad depot in Buffalo, causing three deaths. The center crossed Lake Ontario, sinking 10 ships and stranding 29 others, leading to the loss of 54 lives. Another person died after being blown into the Niagara River.[28] Winds also downed some trees and wires in New England.[26]
Hurricane Ten
[edit]| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 27 – October 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 mph (215 km/h) (1-min); 948 mbar (hPa) |
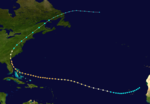
The Cheniere Caminada Hurricane
Although meteorologist José Fernández Partagás noted a "lack of suitable information" prior to October 1,[14] the official track for this system begins on September 27 to the northeast of Honduras. The storm headed northwestward and intensified into a hurricane on the next day. Thereafter, the cyclone brushed Cozumel and then made landfall in Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula near Puerto Morelos as a Category 2 hurricane early on September 29. The storm continued northwestward until late on October 1, at which time a northeasterly motion commenced. While nearing the Gulf Coast of the United States, the system intensified significantly, peaking as a Category 4 hurricane with winds of 130 mph (215 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 948 mbar (28.0 inHg) at 06:00 UTC on October 2. Two hours later, the hurricane struck near Cheniere Caminada, Louisiana, at the same intensity and then another made landfall eight hours thereafter near Ocean Springs, Mississippi, as a strong Category 2 hurricane. The cyclone weakened to a tropical storm over Alabama early on October 3. Retaining tropical storm intensity while crossing the Southeastern United States, the storm emerged into the Atlantic from the Outer Banks of North Carolina on October 4 but likely dissipated on the following day.[2]
Strong winds and storm surge left extensive effects in southeastern Louisiana, with towns between New Orleans and Port Eads suffering major damage, while other communities such Cheniere Caminada and Grand Isle also experienced extreme impacts. Some bays along the south coast observed storm surge reaching 15 ft (4.6 m), while the Chandeleur Islands recorded a storm surge of 16 ft (4.9 m).[23] The Thibodaux Sentinel noted that Cheniere Caminada had been "swept out of existence.", with few homes remaining standing and 779 residents being killed.[29] At nearby Grand Isle, none of the summer homes and hotels survived the storm due to storm surge and tides inundating the area with water 9 ft (2.7 m) above ground.[14][23] Extensive crop damage also occurred along both sides of the lower Mississippi River. The hurricane destroyed at least four churches across the state and caused about $5 million in damage to property alone. Approximately 2,000 deaths occurred as a result of the storm.[23] In coastal Mississippi, storm surge washed hundreds of feet of a railroad bridge between Biloxi and Ocean Springs into several buildings. The storm also damaged a saw mill, a ship yard, several canning facilities, many wharves, bathhouses, and some homes.[30] Abnormally high tides and storm surge in Alabama caused damage, especially in the Mobile area, with the commerce district submerged with 4 ft (1.2 m) of water. Seven deaths occurred in the state. In Florida, The New York Times noted that "on every street, uprooted trees, broken fences and roofless buildings testify of the storm's force" in Pensacola. Storm surge caused washouts that disrupted rail service and shipping. Several other places in the Southeastern United States reported heavy rainfall.[14]
Tropical Storm Eleven
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 20 – October 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min); |
The 11th storm of the season formed just south of the Isla de la Juventud on October 20. After moving through Cuba, it strengthened to a 60 mph (97 km/h) storm before it hit the Delmarva Peninsula on October 23.[citation needed] Chenoweth proposed removing the cyclone from HURDAT, noting that it was "most likely an extratropical system".[13]
Tropical Storm Twelve
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 5 – November 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min); |
A low-pressure became a tropical storm on November 5,[14] situated about 385 mi (620 km) east of Marsh Harbour in the Bahamas,[2] though Partagás noted the possibility of the system having subtropical characteristics.[14] The storm gradually turned west-northward and then northward. On November 8, the cyclone passed within 50 mi (80 km) of the Outer Banks of North Carolina with winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) but curved northeastward and remained offshore. The system then shifted east-northeastward on November 9 and transitioned into an extratropical storm that day. The extratropical remnants dissipated near the Azores on November 12.[2] The 2014 study by Chenoweth suggested the removal this system from HURDAT, noting "Daily weather maps indicate that this is most likely an extratropical system".[13]
In North Carolina, the town of Kitty Hawk observed sustained winds of 58 mph (93 km/h). Offshore the Mid-Atlantic and New England, 14 coal barges encountered rough seas generated by the storm, several of which later sank. An unidentified steamship near the Delaware Breakwater also became disabled but was towed to safety by the bark Clan Ferguson.[14]
Other storms
[edit]Chenoweth proposed four other storms not currently listed in HURDAT:[13]
- August 22 to August 23, peaked as a tropical storm
- August 25 to September 4, peaked as a Category 1 hurricane
- September 5 to September 13, peaked as a Category 1 hurricane
- September 15 to September 17, peaked as a tropical storm
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Jose Fernandez-Partagas (1996). Year 1893 (PDF). Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved August 23, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Storm in Honduras". Evening Messenger. July 15, 1893. p. 2. Retrieved August 26, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ McCloskey, T. A.; Keller, G. (2009). "5000 year sedimentary record of hurricane strikes on the central coast of Belize". Quaternary International. 195 (1–2): 53–68. Bibcode:2009QuInt.195...53M. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2008.03.003.
- ^ a b c Mújica-Baker, Frank. Huracanes y Tormentas que han afectadi a Puerto Rico (PDF). Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, Agencia Estatal para el manejo de Emergencias y Administracion de Desastres. p. 10. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 24, 2015. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
- ^ "Hurricanes and Tropical Storms in Puerto Rico from 1500 to 1899". Retrieved December 29, 2010.
- ^ Bowyer, Peter. "Hurricane Juan Storm Summary". ec.gc.ca. Environment Canada. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- ^ a b c Hudgins, James E. (2000). Tropical cyclones affecting North Carolina since 1586: an historical perspective (Report). Blacksburg, Virginia: National Weather Service. p. 20. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ Landsea, Christopher W.; et al. (May 2015). Documentation of Atlantic Tropical Cyclones Changes in HURDAT. Hurricane Research Division (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ "Swept by Wind and Rain". The New York Times. August 25, 1893. p. 1. Retrieved November 10, 2024 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ "New Haven's Elms Wrecked". The Boston Globe. August 24, 1893. p. 5. Retrieved November 10, 2024 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ "Wind Wrecked Butcher's Cart". The Boston Globe. August 24, 1893. p. 5. Retrieved November 10, 2024 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ a b c d Chenoweth, Michael (December 2014). "A New Compilation of North Atlantic Tropical Cyclones, 1851–98". Journal of Climate. 27 (12). American Meteorological Society. Bibcode:2014JCli...27.8674C. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00771.1. Retrieved April 29, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Partagás, José Fernández; Diaz, Henry F. (1996). Year 1893 (PDF). Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (Report). Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. pp. 49–65. Retrieved September 5, 2023.
- ^ "Report of Damage at Marsh Harbour by the Hurricane of August 26th, 1893". The Nassau Guardian. September 2, 1893. p. 2. Retrieved June 4, 2024.
- ^ "The Late Cyclone". The Nassau Guardian. September 2, 1893. p. 2. Retrieved June 4, 2024.
- ^ "Devastated by Storm". Idaho Daily Statesman. Boise, Idaho. August 29, 1893. p. 1. Retrieved June 4, 2024 – via Newspapers.com.

- ^ "Mad Ruin of the Winds". The Morning News. Savannah, Georgia. August 28, 1893. Retrieved June 4, 2024.

- ^ "Sea Islands Overwhelmed". The New York Times. September 3, 1893. p. 5. Retrieved June 4, 2024.
- ^ a b Rappaport, Edward N.; Partagás, José Fernández; Beven, Jack (April 22, 1997). "Appendix 1. Cyclones with 25+ Deaths". The Deadliest Atlantic Tropical Cyclones, 1492-1996 (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved September 5, 2023.
- ^ Grego, Caroline (November 2019). "Black Autonomy, Red Cross Recovery, and White Backlash after the Great Sea Island Storm of 1893". Journal of Southern History. 85 (4): 803. doi:10.1353/soh.2019.0244. Retrieved June 4, 2024.
- ^ a b "Havoc in the Azores". Los Angeles Herald. September 3, 1893. p. 1. Retrieved June 6, 2024 – via California Digital Newspaper Collection.
- ^ a b c d Roth, David (2010). Louisiana Hurricane History (PDF) (Report). Camp Springs, Maryland: National Weather Service. Retrieved September 5, 2023.
- ^ "Winds". Monthly Weather Review. 21 (9): 254. September 1893. Bibcode:1893MWRv...21..253.. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1893)21[253:W]2.0.CO;2. Retrieved June 9, 2024.
- ^ Barnes, Jay (2007). Florida's Hurricane History. University of North Carolina Press. p. 75. ISBN 978-0807858097. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ a b c "Wind". Monthly Weather Review. 21 (10): 288–289. October 1893. Bibcode:1893MWRv...21..288.. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1893)21[288:W]2.0.CO;2. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ Roth, David; Cobb, Hugh (July 16, 2001). "Late Nineteenth Century Virginia Hurricanes". Virginia Hurricane History (Report). Weather Prediction Center. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ "The Great Storm of 1893 and the Schooner Riverside" (PDF). Advisory Council on Underwater Archaeology. 2010. pp. 219–220. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ Hall, Christie (September 22, 2016). "Cheniere Caminada's "Great October Storm"". Country Roads Magazine. Retrieved September 5, 2023.
- ^ "The Damage in Biloxi". The Biloxi Herald. October 7, 1893. p. 4. Retrieved September 5, 2023 – via Newspapers.com.