Submucosal plexus
| Submucous plexus | |
|---|---|
 The plexus of the submucosa from the rabbit. X 50. | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Plexus nervosus submucosus, plexus submucosus, plexus Meissneri |
| MeSH | D013368 |
| TA98 | A14.3.03.042 |
| TA2 | 6728 |
| FMA | 63252 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
 |
| This article is one of a series on the |
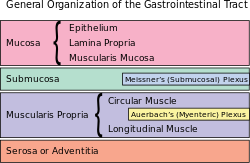
| Gastrointestinal wall |
|---|
The submucous plexus (Meissner's plexus, plexus of the submucosa, plexus submucosus) lies in the submucosa of the intestinal wall. The nerves of this plexus are derived from the myenteric plexus which itself is derived from the plexuses of parasympathetic nerves around the superior mesenteric artery. Branches from the myenteric plexus perforate the circular muscle fibers to form the submucous plexus. Ganglia from the plexus extend into the muscularis mucosae and to the mucous membrane.
They contain Dogiel cells.[1] The nerve bundles of the submucous plexus are finer than those of the myenteric plexus. Its function is to innervate cells in the epithelial layer and the smooth muscle of the muscularis mucosae.
14% of submucosal plexus neurons are sensory neurons - Dogiel type II, also known as enteric primary afferent neurons or intrinsic primary afferent neurons.[2]
History
German Georg Meissner was one of the first to further research the nervous system and found Meissners' plexus.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1177 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1177 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Stach, W (1979). "[Differentiated vascularization of Dogiel's cell types and the preferred vascularization of type I/2 cells within plexus myentericus (Auerbach) ganglia of the pig (author's transl)]". Anatomischer Anzeiger (in German). 145 (5): 464–73. PMID 507375.
- ^ Anatomy and physiology of the enteric nervous system, M Costa,S J H Brookes,G W Hennig, Gut 2000;47:iv15-iv19 doi:10.1136/gut.47.suppl_4.iv15 , http://gut.bmj.com/content/47/suppl_4/iv15.full
