Template:Cell biology/doc
Appearance
| This is a documentation subpage for Template:Cell biology. It may contain usage information, categories and other content that is not part of the original template page. |
Usage
[edit]- All fields are optional
- Setting a value for any of the cell or organelle attributes will make its diagram visible
- Any number and combination of diagram attributes may be set
- When multiple diagrams are activated, the title is suppressed
{{Cell biology
|celltypes = yes <!-- Display a diagram comparing a eukaryote to a prokaryote. -->
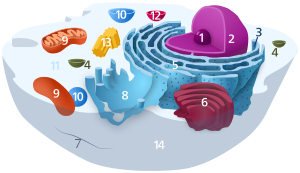
|animalcell = yes <!-- Diagram of an animal cell and its constituent organelles. -->
|plantcell = yes <!-- Diagram of a plant cell and its constituent organelles. -->
|nucleus = yes <!-- Diagram of a nucleus and its constituent parts. -->
|ribosome = <!-- Not yet implemented. -->
|golgi = yes <!-- Diagram of a Golgi complex. -->
|centrosome = yes <!-- Diagram of a centrosome. -->
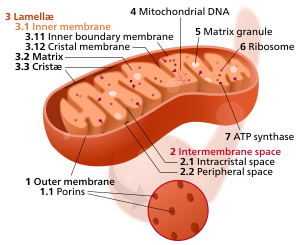
|mitochondrion = yes <!-- Diagram of a mitochondrion. -->
|chloroplast = yes <!-- Diagram of a chloroplast. -->
}}
Example
[edit]An example of the template with all diagrams activated.
- Note: title bars are currently disabled in this view.