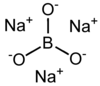
Trisodium orthoborate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Trisodium orthoborate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 117865 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na3BO3 | |
| Molar mass | 127.78 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | 320 °C (608 °F; 593 K) [1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H319, H360, H361d, H412 | |
| P203, P264+P265, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P318, P337+P317, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Trisodium borate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen, with formula Na3BO3, or (Na+)3[BO3]3−.[3] It is a sodium salt of the orthoboric acid B(OH)3.
The compound is also called trisodium orthoborate, sodium orthoborate, or just sodium borate. However, "sodium orthoborate" has been used also for a compound with formula Na4B2O5, which would correspond to an equimolar mixture of sodium metaborate NaBO2 and trisodium borate proper.[4] and "sodium borate" is sometimes used in the generic sense, for a sodium salt with any of several other borate anions.
Preparation[edit]
Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 will react with sodium metaborate NaBO2 or boric oxide B2O3 to form the orthoborate and carbon dioxide when heated between 600 and 850 °C:[3]
- NaBO2 + Na2CO3 → Na3BO3 + CO2
Difficult to obtain in pure form from melts.[5]
Properties[edit]
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (August 2022) |
Reactions[edit]
When dissolved in water, the orthoborate anion partially hydrolyzes into metaborate [BO2]− and hydroxide OH−:[3]
- [BO3]3− + H2O ⇌ [BO2]− + 3 OH−
Electrolysis of a solution of sodium orthoborate generates sodium perborate at the anode.[6] [7]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c "Trisodium borate" Product page in the World Of Chemicals website. Accessed on 2022-06-27.
- ^ "Boric acid, sodium salt". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ a b c Pasupathy Rajan Subbaiyan (2003): "Study of Trisodium Borate Formation and Its Reaction with Green Liquor in Partial Autocausticizing". Masters Thesis, Western Michigan University.
- ^ Daniel L. Calabretta and Boyd R. Davis (2007) "Investigation of the anhydrous molten Na–B–O–H system and the concept: Electrolytic hydriding of sodium boron oxide species". Journal of Power Sources, volume 164, issue 2, pages 782-791. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.11.023
- ^ G. W. Morey and H. E. Merwin (1936): "Phase Equilibrium Relationships in the Binary System, Sodium Oxide-Boric Oxide, with Some Measurements of the Optical Properties of the Glasses". Journal of the American Chemical Society, volume 58, issue 11, pages 2248–2254. doi:10.1021/ja01302a04
- ^ Wilfrid Gustav Polack (1915): "The anodic behaviour of alkaline borate and perborate solutions". Transactions of the Faraday Society, volume 10, pages 177-196. doi:10.1039/TF9151000177
- ^ Tanatar (1898): Zh. Pys. Chem., volume 26, page 132.
