Truxillic acid
Appearance

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4-Diphenyl-1,3-cyclobutanedicarboxylic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.478 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 296.322 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Truxillic acids are any of several crystalline stereoisomeric cyclic dicarboxylic acids with the formula (C6H5)2C4H4(COOH)2 that yield cinnamic acid on distillation.[1] They are obtained by a photochemical cycloaddition from cinnamic acid, where the two trans alkenes react head-to-tail. The isolated stereoisomers are called truxillic acids.
These compounds are found in a variety of plants, for example in coca.[2][3]
Isomers
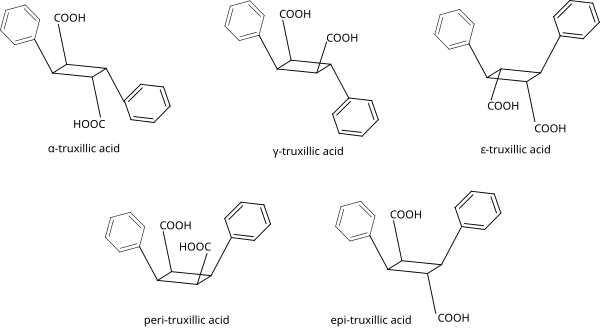
These compounds have four chiral carbon atoms, which looks like there should be 16 (24) stereoisomers. However, the symmetry of the molecule allows for only five possibilities:[4][5]

| Isomer | a | b | c | d | e | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-truxillic acid (cocaic acid[6]) |
COOH | H | H | C6H5 | H | COOH |
| γ-truxillic acid | COOH | H | H | C6H5 | COOH | H |
| ε-truxillic acid | H | COOH | C6H5 | H | H | COOH |
| peri-truxillic acid | COOH | H | C6H5 | H | COOH | H |
| epi-truxillic acid | COOH | H | C6H5 | H | H | COOH |
Derivatives
Incarvillateine, an alkaloid from the plant Incarvillea sinensis, is a derivative of α-truxillic acid.
See also
- Truxinic acids, which are isomers of the truxillic acids
References
- ^ Hein, Sara M. (2006). "An Exploration of a Photochemical Pericyclic Reaction Using NMR Data". Journal of Chemical Education. 83: 940–942. doi:10.1021/ed083p940.
- ^ Liebermann (1888). "Cinnamic acid polymers obtained from the minor alkaloids of cocaine". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 21: 3372–3376. doi:10.1002/cber.188802102223.
- ^ Krauze-Baranowska, Miroslawa (2002). "Truxillic and truxinic acids-occurrence in plant kingdom". Acta poliniae Pharmaceutica-Drug research. 59 (5): 403–410.
- ^ Stoermer (1924). "Five stereoisomers have been obtained: alfa-, gamma-, epsilon-, peri- and epi-isomers. Stereochemical configurations". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen. 57B: 15–23.
- ^ Agarwai, O. P. (2011). Organic Chemistry Reactions and Reagents. Krishna Prakashan Media. ISBN 8187224657.
- ^ "ChemSpider ID 10218892". ChemSpider. Retrieved 15 October 2016.

