Tsushima incident
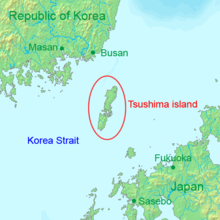
The Tsushima Incident occurred in 1861 when the Russians attempted to establish a year-round anchorage on the coast of the island of Tsushima, a Japanese territory located between Kyushu and Korea.[1]
British version of events
Arrival of the Posadnik
On 13 March 1861, the Russian corvette Posadnik (Посадник, 1856), captained by Nicolai Birilev, arrived in Tsushima island in the inlet of Ozaki, the captain demanding landing rights. This event triggered fear in the Japanese Shogunate, as the Russians had already attempted to breach Japan's isolation policy in the northern island of Hokkaido with the events involving Adam Laxman in 1792, the burning of villages there in 1806, and the events leading to the arrest of Vasilii Golovnin in 1811.[2] At that time, only a few Japanese ports were open to foreign ships (Hakodate, Nagasaki, Yokohama), and Tsushima was clearly not one of them, thus suggesting unfriendly intentions on the part of the Russians. If taken over by the Russians, Tsushima could have become an effective base for further aggression. Japan received British help to support its policy.[3] As tension rose, a second Russian ship arrived, and requests were made by the Russians to build a landing base and to receive supplies.[4]
Clash

On 13 May 1861, the Russians sent a launch to explore the eastern coast of the island, despite the presence of two Saga Domain warships, the Kankō Maru and the Denryū Maru, as well as one British warship.[4] On May 21, 1861, a clash took place between the Russian sailors of a launch and a group of samurai and farmers, in which one farmer was killed and one samurai, who soon committed suicide, was captured by the Russians.[4] In mid-July, Foreign Magistrate Muragaki Narimasa went directly to the Russian Consulate in Hakodate, demanding the departure of the ship to the Russian Consul Goshkevitch.[5]
Russian retreat
As this strategy did not work, the Japanese asked the British to intervene, as they also had an interest in preventing the Russians from extending their influence in Asia.[5] Admiral Hope arrived in Tsushima with two warships on 28 August, and on 19 September 1861 the Posadnik finally had to leave Tsushima.[6]
Russian version of events
Background
The late 1850s saw a period of Russian expansion into the Sea of Japan, with the setting up a post in the estuary of the Amur in 1850, the acquisition of the present Primorsky Krai by the Treaty of Aigun (1858) and the Convention of Peking (1860), and the establishment of Vladivostok in 1860.
In 1858 the Imperial Russian Navy leased a strip of Nagasaki Bay coastline across the village of Inasa as a winter anchorage for the Chinese Flotilla's emerging Pacific Fleet (all domestic anchorages froze up in winter).[7] Flotilla commander Admiral Ivan Likhachev realized the dangers of basing the fleet in a foreign port,[8] and settled on establishing a permanent base in Tsushima.[7] He was aware that the British had attempted to set their flag there in 1859 and had conducted hydrographic surveys around the island in 1855.[9] In 1860 he requested a go-ahead from the government in Saint Petersburg; the cautious foreign minister, Alexander Gorchakov, ruled out any incursions against British interests,[9] while General Admiral Konstantin Nikolayevich suggested making a private deal with the head of Tsushima-Fuchū Domain, as long as it did not disturb "the West".[9] In case of failure the Russian authorities would deny all knowledge of the expedition.[10]
Landing
In line with Likhachev's will and Konstantin's advice Posadnik left Hakodate February 20, 1861 and on March 1 reached the village of Osaki on the western coast of Aso Bay (Tatamura Bay in historical reports).[11] Mune Yoshiori, head of Tsushima clan, immediately informed the Bakufu government, however, the cautious cabinet of Andō Nobumasa delayed their response and Yoshiori had to act on his own.[11] Birilev, captain of the Posadnik, made personal contact with Mune, exchanged courtesy gifts, and secured Yoshiori's consent to survey the Imosaki Bay; Posadnik arrived there on April 2.[11] The crew disembarked, raised the Russian flag, and began building temporary housing, a landing jetty and prepared to refit the ship which needed repairs to propeller and stern tube.[11] Japanese officials tacitly agreed with de facto establishing a naval base and even assigned a team of fifteen local carpenters to help the Russians;[11] the latter rewarded Mune with a gift of small naval cannons.[12] Likhachev inspected the bay twice, March 27 on board the Oprichnik and April 16 on board the Svetlana and recorded friendly behaviour of the Japanese,[11] however, in April the situation irreversibly changed.[12]
Clash
On April 12, 1861 when the Russians disembarked from their launches, a group of local peasants led by one Yasugoro attempted to bar entrance and drive the Russians back.[12] In the ensuing clash Yasugoro was killed, two Japanese peasants taken hostage, the rest fled; no Russian fatalities were recorded.[12] Mune appeased the population, ordering them to wait for a Bakumatsu pronouncement, and did not take any action.[12] Russian sources say nothing about presence of Japanese or British warship in the area.[13]
Aftermath


Oguri Tadamasa, the messenger of Bakumatsu arrived in Tsushima in May and politely told Birilev to leave; Birilev explained that he would not move unless the Admiral orders retreat.[12] After 13 days of waiting in vain Oguri left; he left a letter allowing contacts between Birilev and local administration without prejudices against further radical action by the Japanese.[12] Birilev used the permit to the full, and persuaded the council of Japanese officials to issue a charter agreeing with Russian naval presence in Tsushima. Tsushima elders granted the coastline between Hiroura and Imosaki exclusively to the Russians and agreed to bar entrance to any other foreign nation.[12] The charter, however, clearly said that all these concessions depended on good will of the central government.[12] The latter vehemently opposed the deal and called the British envoy Rutherford Alcock for help.[12] Alcock immediately dispatched two ships under command of Vice Admiral James Hope.[13]
Retreat
Likhachev, as instructed by Konstantin, ordered a general retreat and sent the message to Tsushima with the Oprichnik.[13] Birilev and Posadnik left Tsushima on September 7, 1861, while Oprichnik and Abrek stayed in the harbor; both finally left at the end of September 1861.[13] Likhachev later said that the failure had its upside: "We did not allow the British conquest of the islands",[13] an opinion indirectly supported by contemporary personal meetings between Gorchakov and ambassador Francis Napier; the latter, however, never gave a definite answer about British plans in Tsushima.[13] Likhachev was demoted from his command and tendered a voluntary resignation, which was rejected; the admiral was given command of a Baltic Fleet squadron.[13] The Russian Navy stayed at Nagasaki until the completion of the Port Arthur base in China.[14]
See also
Notes
- ^ Negotiating with Imperialism, Michael R. Auslin, p. 77
- ^ Negotiating with Imperialism, Michael R. Auslin, p. 78
- ^ Negotiating with Imperialism, Michael R. Auslin, pp. 78–9
- ^ a b c Negotiating with Imperialism, Michael R. Auslin, p. 79
- ^ a b Negotiating with Imperialism, Michael R. Auslin, p. 80
- ^ Negotiating with Imperialism, Michael R. Auslin, p. 81
- ^ a b Shirokorad, p. 175
- ^ His fears were not improved by the well-publicized murder of unarmed midshipman Roman Mofet in Nagasaki on August 13, 1859 - Shirokorad, p. 180
- ^ a b c Shirokorad, p. 176
- ^ Memorandum of Likhachev to General Admiral Great Prince Konstantin of 21 May 1860, in The Central State Navy Archive (St Petersburg), fund 410, folder 2, No. 2386, and No. 2386; further O. Belomor in Morskoi Sbornik', 1914, No.6.'
- ^ a b c d e f Shirokorad, p. 177
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Shirokorad, p. 178
- ^ a b c d e f g Shirokorad, p. 179
- ^ Shirokorad, p. 180
Sources
- Alexandr Shirokorad (2005). Rossiya vyhodit v mirovoy okean (Россия выходит в мировой океан). Veche. ISBN 593307519
