Ulnar artery
| Ulnar artery | |
|---|---|
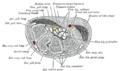
 Palm of (corrected) right hand, showing position of skin creases and bones, and surface markings for the volar arches. | |
 Front of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones, arteries, and nerves. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Brachial artery |
| Branches | Anterior ulnar recurrent artery posterior ulnar recurrent artery common interosseous artery (volar, dorsal) muscular artery volar carpal dorsal carpal deep volar superficial volar arch |
| Vein | Ulnar vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria Ulnaris |
| MeSH | D017535 |
| TA98 | A12.2.09.041 |
| TA2 | 4655 |
| FMA | 22796 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspect of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.
Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins.
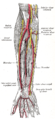
The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between the elbow and the wrist. It then runs along the ulnar border to the wrist, crosses the transverse carpal ligament on the radial side of the pisiform bone, and immediately beyond this bone divides into two branches, which enter into the formation of the superficial and deep volar arches.
Branches
Forearm: Anterior ulnar recurrent artery, Posterior ulnar recurrent artery, Common interosseous is very short around 1 cm and gives rise to both the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries and Close to the wrist it gives off the palmar carpal branch which is the ulnar contribution to the palmar carpal arch and it also gives a dorsal carpal branch which is the ulnar contribution to dorsal carpal arch
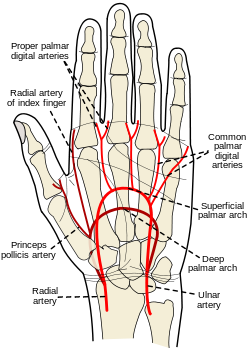
Hand: Deep palmar branch of ulnar artery which passes through the hypothenar muscles to anastomose with the deep palmar arch which is formed predominantly by the radial artery and the terminal branch of the ulnar artery is then to form the superficial palmar arch.
Relations
In its upper half, it is deeply seated, being covered by the Pronator teres, Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus, and Flexor digitorum superficialis; it lies upon the Brachialis and Flexor digitorum profundus.
The median nerve is in relation with the medial side of the artery for about 2.5 cm. and then crosses the vessel, being separated from it by the ulnar head of the Pronator teres.
In the lower half of the forearm it lies upon the Flexor digitorum profundus, being covered by the integument and the superficial and deep fasciæ, and placed between the Flexor carpi ulnaris and Flexor digitorum superficialis.
It is accompanied by two venæ comitantes, and is overlapped in its middle third by the Flexor carpi ulnaris; the ulnar nerve lies on the medial side of the lower two-thirds of the artery, and the palmar cutaneous branch of the nerve descends on the lower part of the vessel to the palm of the hand.
Wrist
At the wrist the ulnar artery is covered by the integument and the volar carpal ligament, and lies upon the Flexor retinaculum of the hand. On its medial side is the pisiform bone, and, somewhat behind the artery, the ulnar nerve.
Peculiarities
The ulnar artery varies in its origin in the proportion of about one in thirteen cases; it may arise about 5 to 7 cm. below the elbow, but more frequently higher, the brachial being more often the source of origin than the axillary.
Variations in the position of this vessel are more common than in the radial. When its origin is normal, the course of the vessel is rarely changed.
When it arises high up, it is almost invariably superficial to the Flexor muscles in the forearm, lying commonly beneath the fascia, more rarely between the fascia and integument.
In a few cases, its position was subcutaneous in the upper part of the forearm, and subaponeurotic in the lower part.
See also
Additional images
-
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
-
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
-
Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
-
The palmar aponeurosis.
-
Diagram of the anastomosis around the elbow-joint.
-
Arteries of the right forearm - anterior view.
-
Ulnar and radial arteries. Deep view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 595 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 595 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=101056520.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Ulnar artery at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- lesson4artofforearm at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)