User:Daniel Mietchen/Contagious period
Intro
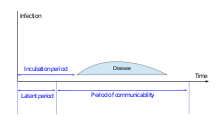
[edit]In epidemiology, the contagious period forms part of the timeline of an infection with a contagious disease and is the interval during which an organism infected with a contagious pathogen facilitates pathogen transmission to other organisms. It is also known under various other names, including period of contagiousness, transmission period, transmissibility period, communicability period or period of communicability. The closely related infectious period (also known as period of infectiousness or interval of infectivity), which describes the interval during which the pathogen maintains infectivity, i.e. the ability to establish an infection in another host, is often used synonymously as well.
The mean duration of a pathogen's contagious period in a given host population is one of the parameters determining the basic reproduction number of a pathogen in that host population. It varies across different pathogen-host combinations and within a population of infected individuals. It can be longer or shorter than the incubation period and may overlap with it. Variability of the contagious period has been suggested to affect the temporal dynamics of an epidemic.[1]
Usage of synonyms
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Wilkinson, Robert R.; Sharkey, Kieran J. (2018). "Impact of the infectious period on epidemics". Physical Review E. 97 (5). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.97.052403. ISSN 2470-0045.
