User:Eewilson/SLat
| This is a Wikipedia user page. This is not an encyclopedia article or the talk page for an encyclopedia article. |
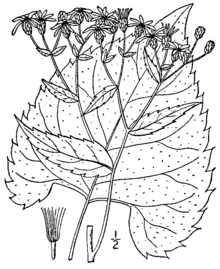
Symphyotrichum lateriflorum[edit]
Description[edit]
- "where applicable its Floral formula. Floral diagrams may also be useful."
Similar species[edit]
S. boreale (northern bog aster) S. cordifolium (common blue wood aster, heartleaf aster) S. drummondii (Drummond's aster) S. dumosum (bushy aster, rice button aster) S. ericoides (white heath aster) S. lanceolatum (panicled aster) S. ontarionis (Ontario aster, bottomland aster) S. pilosum (hairy white oldfield aster, awl aster) S. praealtum (willowleaf aster) S. racemosum (smooth white oldfield aster, small white aster) S. tradescantii (Tradescant's aster, shore aster) S. urophyllum (arrowleaf aster)
Eurybia chlorolepis (mountain wood aster) Eurybia divaricata (white wood aster) Eurybia furcata (forked aster) Eurybia macrophylla (large-leaved aster) Eurybia mirabilis (bouquet aster) Eurybia radula (rough wood aster) Eurybia schreberi (Schreber's wood aster)
 |
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
|||
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
|||
 |
|||
 |
|||
 |
|||
| Eurybia mirabilis | |||
 |
|||
 |
Phytochemistry[edit]
- See Semple and Brammall 1982 for flavinoids
- Wilzer et al. 1989 for coumarins - (Coumarins from Aster praealtus. Phytochemistry 28: 1729-1736)
Taxonomy[edit]
Phylogeny[edit]
"Modern taxonomy is based on phylogenetic analyses and to present such work, if available, is essential. Mention whether there are still doubts about monophyly and the most closely related sister group. An account of the current relationships of the taxon is best illustrated with a cladogram. Include an account of what evidence (e.g. morphology, embryology, chromosomes, karyology, cytogenetics, biogeography, ecology, palynology, phytochemistry, proteins and nucleic acid segments) was used in constructing the phylogeny, and the processes involved."
- ChmielewskiSemple2001 & SempleBrammall1982 will help with this
- Evolutionary processes
"For a discussion of the most appropriate place to discuss evolution, see here"
"Describe how the evolutionary processes, lines and history and biogeography have contributed to the diversity, and discuss speciation where appropriate. For many taxa below the genus level this may not be informative. Where a cladistic analysis is available, consider including a cladogram to illustrate the relationships, using Clade, which may be embedded in the Cladogram template (see, for example Rhododendron:Phylogenetic analyses). The Clade template allows additional bracketing of a group of clades within a cladogram (see, for example Cladogram of the monocots). Include the fossil record where known and explain to what degree it supports the constructed phylogeny. Some evolutionary information may be better presented as a Timeline."
Hybrids[edit]
...more detail?
Distribution and habitat[edit]
Habitat[edit]
- "elevation range, climatic range, soil types it is found in, plants associated with it (associates, vegetation type), and how densely it grows."
Ecology[edit]
- Phenology - Growth cycles (life cycle) - seasonal changes. ChmielewskiSemple2001 p. 842 - phenology
- interaction with the environment
 In progress Symbiotic relationships. -- need nectar info, EOL
In progress Symbiotic relationships. -- need nectar info, EOL- How do various natural phenomena, such as seasonal changes, fires, and drought, affect the species?
- Relationship to the Raunkiær system of life-forms (e.g. phanerophytes, epiphytes).
- How do other animals or plants use it, such as for construction of nests?
- -> my note: Birds, Rabbits, and deer
- -> my note: Separate out pollinators from nectar drinkers where applicable
- -> my note: r|ChmielewskiSemple2001|p=839 p. 839 cultivated in Europe (Hoffman 1996 - Escaped and cultivated North American asters of entral Europe. Feddes Repert. 107: 163-188) and used in breeding programs (Hetterscheid and Van Den Berg 1996 - Cultonomy of Aster L. - Acta Bot. Neerl. 45: 173-181)
