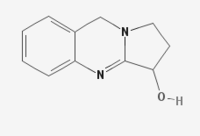
Vasicine
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3,9-Tetrahydropyrrolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-3-ol
| |
| Other names
Peganine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 188.230 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) |
| Solubility in acetone, alcohol, chloroform | Soluble |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Vasicine (peganine) is a quinazoline alkaloid. It is the active compound of Justicia adhatoda, after which the chemical is named.
Vasicine has been compared to theophylline both in vitro and in vivo.[1] It has also been studied in combination with the related alkaloid vasicinone. Both the alkaloids in combination (1:1) showed pronounced bronchodilatory activity in vivo and in vitro.[2] Both alkaloids are also respiratory stimulants.[2] Vasicine has a cardiac–depressant effect, while vasicinone is a weak cardiac stimulant; the effect can be normalized by combining the alkaloids.[2][3] Vasicine is reported to have a uterine stimulant effect.[3]
References
- ^ Nepali, Kunal; Sharma, Sahil; Ojha, Ritu; Dhar, Kanaya Lal (2012). "Vasicine and structurally related quinazolines". Medicinal Chemistry Research. 22 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0002-5. ISSN 1054-2523.
- ^ a b c Avula, B.; et al. (2008). "Quantitative determination of vasicine and vasicinone in Adhatoda vasica by high performance capillary electrophoresis" (PDF). Die Pharmazie – An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 63 (1): 20–22. doi:10.1691/ph.2008.7175.
- ^ a b Rajani, M; Soni, S; Anandjiwala, Sheetal; Patel, G (2008). "Validation of different methods of preparation of Adhatoda vasica leaf juice by quantification of total alkaloids and vasicine". Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 70 (1): 36. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.40329. ISSN 0250-474X.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
