Meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve
Appearance
| Meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve | |
|---|---|
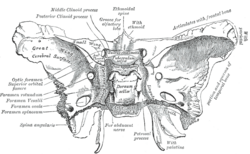 Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. (Foramen spinosum labeled left, second from bottom.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Mandibular nerve |
| Innervates | Dura mater |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ramus meningeus nervi mandibularis |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.065 |
| TA2 | 6247 |
| FMA | 53047 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (also known as the nervus spinosus)[1] is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that enters the middle cranial fossa through either the foramen spinosum or foramen ovale to innervate the meninges of this fossa as well as the mastoid air cells.[2]
Anatomy
[edit]Branches
[edit]It divides into two branches - anterior and posterior - which accompany the main divisions of the middle meningeal artery and supply the dura mater:[1]
- The anterior branch communicates with the meningeal branch of the maxillary nerve.[1]
- The posterior branch also supplies the mucous lining of the mastoid cells.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Gray, Henry (1918). Gray's Anatomy (20th ed.). p. 894.
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 364. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
External links
[edit]- Overview at tufts.edu
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
