Macromolecular assembly: Difference between revisions
Futurefirst (talk | contribs) m Added "citation needed" for how biomembrane structure extends MA definition |
consistent citation formatting; templated cites |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{more footnotes|date=October 2019}} |
{{more footnotes|date=October 2019}} |
||
[[Image:010 large subunit-1FFK.gif|thumb|right|Structure of nucleoprotein MA: The 50S ribosomal subunit from ''[[Haloarcula|H. marismortui]]'' [[X-ray crystallography|X-ray crystallographic]] model of 29 of the 33 native components, from the laboratory of [[Thomas Steitz]]. Of the 31 component proteins, 27 are shown (blue), along with its 2 RNA strands (orange/yellow).<ref name=Ban>{{cite journal |vauthors=Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore |
[[Image:010 large subunit-1FFK.gif|thumb|right|Structure of nucleoprotein MA: The 50S ribosomal subunit from ''[[Haloarcula|H. marismortui]]'' [[X-ray crystallography|X-ray crystallographic]] model of 29 of the 33 native components, from the laboratory of [[Thomas Steitz]]. Of the 31 component proteins, 27 are shown (blue), along with its 2 RNA strands (orange/yellow).<ref name=Ban>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA | title = The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution | journal = Science | volume = 289 | issue = 5481 | pages = 905–920 | date = August 2000 | pmid = 10937989 | doi = 10.1126/science.289.5481.905 | citeseerx = 10.1.1.58.2271 | bibcode = 2000Sci...289..905B }}</ref> Scale: assembly is approx. 24 nm across.<ref>{{cite web| vauthors = McClure W |url=http://www.bio.cmu.edu/courses/03231/LecF03/Lec22/lec22img.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051124223341/http://www.bio.cmu.edu/courses/03231/LecF03/Lec22/lec22img.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=2005-11-24 |title=50S Ribosome Subunit |access-date=2019-10-09}}</ref>]] |
||
The term '''macromolecular assembly''' (MA) refers to massive chemical structures such as [[virus]]es and non-biologic [[nanoparticle]]s, cellular [[organelle]]s and [[cell membrane|membranes]] and [[ribosome]]s, etc. that are complex mixtures of [[polypeptide]], [[polynucleotide]], [[polysaccharide]] or other polymeric [[macromolecule]]s. They are generally of more than one of these types, and the mixtures are defined spatially (i.e., with regard to their chemical shape), and with regard to their underlying chemical composition and [[chemical structure|structure]]. [[Macromolecule]]s are found in living and nonliving things, and are composed of many hundreds or thousands of [[atom]]s held together by [[covalent bond]]s; they are often characterized by repeating units (i.e., they are [[polymers]]). Assemblies of these can likewise be biologic or non-biologic, though the MA term is more commonly applied in biology, and the term [[supramolecular assembly]] is more often applied in non-biologic contexts (e.g., in [[supramolecular chemistry]] and [[nanotechnology]]). MAs of macromolecules are held in their defined forms by [[non-covalent]] [[intermolecular interaction]]s (rather than covalent bonds), and can be in either non-repeating structures (e.g., as in the [[ribosome]] (image) and [[cell membrane]] architectures), or in repeating linear, circular, spiral, or other patterns (e.g., as in [[actin filaments]] and the [[flagellum|flagellar motor]], image). The process by which MAs are formed has been termed [[molecular self-assembly]], a term especially applied in non-biologic contexts. A wide variety of physical/biophysical, chemical/biochemical, and computational methods exist for the study of MA; given the scale (molecular dimensions) of MAs, efforts to elaborate their composition and structure and discern mechanisms underlying their functions are at the forefront of modern structure science. |
The term '''macromolecular assembly''' (MA) refers to massive chemical structures such as [[virus]]es and non-biologic [[nanoparticle]]s, cellular [[organelle]]s and [[cell membrane|membranes]] and [[ribosome]]s, etc. that are complex mixtures of [[polypeptide]], [[polynucleotide]], [[polysaccharide]] or other polymeric [[macromolecule]]s. They are generally of more than one of these types, and the mixtures are defined spatially (i.e., with regard to their chemical shape), and with regard to their underlying chemical composition and [[chemical structure|structure]]. [[Macromolecule]]s are found in living and nonliving things, and are composed of many hundreds or thousands of [[atom]]s held together by [[covalent bond]]s; they are often characterized by repeating units (i.e., they are [[polymers]]). Assemblies of these can likewise be biologic or non-biologic, though the MA term is more commonly applied in biology, and the term [[supramolecular assembly]] is more often applied in non-biologic contexts (e.g., in [[supramolecular chemistry]] and [[nanotechnology]]). MAs of macromolecules are held in their defined forms by [[non-covalent]] [[intermolecular interaction]]s (rather than covalent bonds), and can be in either non-repeating structures (e.g., as in the [[ribosome]] (image) and [[cell membrane]] architectures), or in repeating linear, circular, spiral, or other patterns (e.g., as in [[actin filaments]] and the [[flagellum|flagellar motor]], image). The process by which MAs are formed has been termed [[molecular self-assembly]], a term especially applied in non-biologic contexts. A wide variety of physical/biophysical, chemical/biochemical, and computational methods exist for the study of MA; given the scale (molecular dimensions) of MAs, efforts to elaborate their composition and structure and discern mechanisms underlying their functions are at the forefront of modern structure science. |
||
[[Image:Protein translation.gif|thumb|right|300px| A eukaryotic [[ribosome]], which catalytically [[translation (biology)|translate]] the information content contained in [[mRNA]] molecules into proteins. The animation presents the elongation and membrane targeting stages of [[eukaryotic translation]], showing the mRNA as a black arc, the [[ribosome]] subunits in green and yellow, tRNAs in dark blue, proteins such as [[elongation factors|elongation]] and other factors involved in light blue, the growing polypeptide chain as a black thread growing vertically from the curve of the mRNA. At end of the animation, the polypeptide produced is extruded through a light blue SecY pore<ref name=pmid16212506>{{cite journal | vauthors = Osborne AR, Rapoport TA, van den Berg B | title = Protein translocation by the Sec61/SecY channel | journal = Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology | volume = 21 | pages = |
[[Image:Protein translation.gif|thumb|right|300px| A eukaryotic [[ribosome]], which catalytically [[translation (biology)|translate]] the information content contained in [[mRNA]] molecules into proteins. The animation presents the elongation and membrane targeting stages of [[eukaryotic translation]], showing the mRNA as a black arc, the [[ribosome]] subunits in green and yellow, tRNAs in dark blue, proteins such as [[elongation factors|elongation]] and other factors involved in light blue, the growing polypeptide chain as a black thread growing vertically from the curve of the mRNA. At end of the animation, the polypeptide produced is extruded through a light blue SecY pore<ref name=pmid16212506>{{cite journal | vauthors = Osborne AR, Rapoport TA, van den Berg B | title = Protein translocation by the Sec61/SecY channel | journal = Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology | volume = 21 | pages = 529–550 | date = 2005 | pmid = 16212506 | doi = 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.133214 }}</ref> into the gray interior of the [[endoplasmic reticulum|ER]].]] |
||
{{toclimit|3}} |
{{toclimit|3}} |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
A '''biomolecular complex''', also called a '''biomacromolecular complex''', is any biological complex made of more than one [[biopolymer]] ([[protein]], [[RNA]], [[DNA]], |
A '''biomolecular complex''', also called a '''biomacromolecular complex''', is any biological complex made of more than one [[biopolymer]] ([[protein]], [[RNA]], [[DNA]], |
||
<ref name=biomolecular_complex_protein_DNA_RNA__2005>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kleinjung J, Fraternali F | title = POPSCOMP: an automated interaction analysis of biomolecular complexes | journal = Nucleic Acids Research | volume = 33 | issue = Web Server issue | pages = W342-W346 | date = July 2005 | pmid = 15980485 | pmc = 1160130 | doi = 10.1093/nar/gki369 }}</ref> |
|||
<ref name=biomolecular_complex_protein_DNA_RNA__2005>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1093/nar/gki369 |
|||
| issn = 0305-1048 |
|||
| volume = 33 |
|||
| issue = suppl 2 |
|||
| pages = W342–W346 |
|||
| last = Kleinjung |
|||
| first = Jens |
|||
|author2=Franca Fraternali |
|||
| title = POPSCOMP: an automated interaction analysis of biomolecular complexes |
|||
| journal = [[Nucleic Acids Research]] |
|||
| date = 2005-07-01 |
|||
| pmid=15980485 |
|||
| pmc=1160130 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
[[carbohydrate]]) or large non-polymeric biomolecules ([[lipid]]). The interactions between these biomolecules are non-covalent. |
[[carbohydrate]]) or large non-polymeric biomolecules ([[lipid]]). The interactions between these biomolecules are non-covalent. |
||
<ref name=Ribosome_macromolecular_device_2012_REVIEW>{{ |
<ref name=Ribosome_macromolecular_device_2012_REVIEW>{{cite journal | vauthors = Moore PB | title = How should we think about the ribosome? | journal = Annual Review of Biophysics | volume = 41 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–19 | date = 2012 | pmid = 22577819 | doi = 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102314 }}</ref> |
||
| doi = 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102314 |
|||
| volume = 41 |
|||
| issue = 1 |
|||
| pages = 1–19 |
|||
| last = Moore |
|||
| first = Peter B. |
|||
| title = How Should We Think About the Ribosome? |
|||
| journal = [[Annual Review of Biophysics]] |
|||
| date = 2012 |
|||
| pmid = 22577819 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Examples: |
Examples: |
||
* [[Protein complex]]es, some of which are [[multienzyme complex]]es: [[proteasome]], [[DNA polymerase III holoenzyme]], [[RNA polymerase II holoenzyme]], symmetric viral [[capsid]]s, chaperonin complex [[GroEL]]-[[GroES]], [[photosystem I]], [[ATP synthase]], [[ferritin]]. |
* [[Protein complex]]es, some of which are [[multienzyme complex]]es: [[proteasome]], [[DNA polymerase III holoenzyme]], [[RNA polymerase II holoenzyme]], symmetric viral [[capsid]]s, chaperonin complex [[GroEL]]-[[GroES]], [[photosystem I]], [[ATP synthase]], [[ferritin]]. |
||
| Line 44: | Line 19: | ||
* DNA-protein complexes: [[nucleosome]]. |
* DNA-protein complexes: [[nucleosome]]. |
||
* Protein-lipid complexes: [[lipoprotein]].<ref name=Trends_in_biochemical_sciences_2015> |
* Protein-lipid complexes: [[lipoprotein]].<ref name=Trends_in_biochemical_sciences_2015> |
||
{{cite journal | vauthors = Neuman N | title = The Complex Macromolecular Complex | journal = Trends in Biochemical Sciences | volume = 41 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–3 | date = January 2016 | pmid = 26699226 | doi = 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.11.006 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name=Structure_2005> |
|||
{{Cite journal| |
|||
{{cite journal | vauthors = Dutta S, Berman HM | title = Large macromolecular complexes in the Protein Data Bank: a status report | journal = Structure | volume = 13 | issue = 3 | pages = 381–388 | date = March 2005 | pmid = 15766539 | doi = 10.1016/j.str.2005.01.008 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
doi = 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.11.006| |
|||
pmid = 26699226| |
|||
volume = 41| |
|||
issue = 1| |
|||
pages = 1–3| |
|||
last = Neuman| |
|||
first = Nicole| |
|||
title = The Complex Macromolecular Complex: Trends in Biochemical Sciences| |
|||
journal = Trends in Biochemical Sciences| |
|||
date = January 2016| |
|||
doi-access = free}}</ref><ref name=Structure_2005> |
|||
{{Cite journal| |
|||
doi = 10.1016/j.str.2005.01.008| |
|||
pmid = 15766539| |
|||
issn = 0969-2126| |
|||
volume = 13| |
|||
issue = 3| |
|||
pages = 381–388| |
|||
last1 = Dutta| |
|||
first1 = Shuchismita| |
|||
last2 = Berman| |
|||
first2 = Helen M.| |
|||
title = Large Macromolecular Complexes in the Protein Data Bank: A Status Report| |
|||
journal = Structure| |
|||
date = 2005-03-01| |
|||
doi-access = free}}</ref> |
|||
The biomacromolecular complexes are studied structurally by [[X-ray crystallography]], [[Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins|NMR spectroscopy of proteins]], [[cryo-electron microscopy]] and successive [[single particle analysis]], and [[electron tomography]]. |
The biomacromolecular complexes are studied structurally by [[X-ray crystallography]], [[Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins|NMR spectroscopy of proteins]], [[cryo-electron microscopy]] and successive [[single particle analysis]], and [[electron tomography]]. |
||
<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Russell RB, Alber F, Aloy P, Davis FP, Korkin D, Pichaud M, Topf M, Sali A | display-authors = 6 | title = A structural perspective on protein-protein interactions | journal = Current Opinion in Structural Biology | volume = 14 | issue = 3 | pages = 313–324 | date = June 2004 | pmid = 15193311 | doi = 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.04.006 }}</ref> |
|||
<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.04.006 |
|||
| pmid = 15193311 |
|||
| issn = 0959-440X |
|||
| volume = 14 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 313–324 |
|||
| last = Russell |
|||
| first = Robert B |
|||
|author2=Frank Alber |author3=Patrick Aloy |author4=Fred P Davis |author5=Dmitry Korkin |author6=Matthieu Pichaud |author7=Maya Topf |author8=Andrej Sali |
|||
| title = A structural perspective on protein–protein interactions |
|||
| journal = [[Current Opinion in Structural Biology]] |
|||
| date = June 2004 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
The atomic structure models obtained by X-ray crystallography and biomolecular NMR spectroscopy can be [[Macromolecular docking|docked]] into the much larger structures of biomolecular complexes obtained by lower resolution techniques like electron microscopy, electron tomography, and [[small-angle X-ray scattering]]. |
The atomic structure models obtained by X-ray crystallography and biomolecular NMR spectroscopy can be [[Macromolecular docking|docked]] into the much larger structures of biomolecular complexes obtained by lower resolution techniques like electron microscopy, electron tomography, and [[small-angle X-ray scattering]]. |
||
<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = van Dijk AD, Boelens R, Bonvin AM | title = Data-driven docking for the study of biomolecular complexes | journal = The FEBS Journal | volume = 272 | issue = 2 | pages = 293–312 | date = January 2005 | pmid = 15654870 | doi = 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2004.04473.x | hdl-access = free | s2cid = 20148856 | hdl = 1874/336958 }}</ref> |
|||
<ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| doi = 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2004.04473.x |
|||
| pmid = 15654870 |
|||
| issn = 1742-4658 |
|||
| volume = 272 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = 293–312 |
|||
| last = van Dijk |
|||
| first = Aalt D. J. |author2=Rolf Boelens |author3=Alexandre M. J. J. Bonvin |
|||
| title = Data-driven docking for the study of biomolecular complexes |
|||
| journal = [[FEBS Journal]] |
|||
| year = 2005 |
|||
| hdl = 1874/336958 |
|||
| s2cid = 20148856 |
|||
| hdl-access = free |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Complexes of macromolecules occur ubiquitously in nature, where they are involved in the construction of viruses and all living cells. In addition, they play fundamental roles in all basic life processes ([[translation (biology)|protein translation]], [[cell division]], [[vesicle trafficking]], intra- and inter-cellular exchange of material between compartments, etc.). In each of these roles, complex mixtures of become organized in specific structural and spatial ways. While the individual macromolecules are held together by a combination of covalent bonds and ''intra''molecular non-covalent forces (i.e., associations between parts within each molecule, via [[charge-charge interaction]]s, [[van der Waals forces]], and [[dipole-dipole interaction]]s such as [[hydrogen bond]]s), by definition MAs themselves are held together solely via the [[noncovalent bonding|noncovalent]] forces, except now exerted ''between'' molecules (i.e., [[intermolecular interaction]]s).{{citation needed|date=March 2019}} |
Complexes of macromolecules occur ubiquitously in nature, where they are involved in the construction of viruses and all living cells. In addition, they play fundamental roles in all basic life processes ([[translation (biology)|protein translation]], [[cell division]], [[vesicle trafficking]], intra- and inter-cellular exchange of material between compartments, etc.). In each of these roles, complex mixtures of become organized in specific structural and spatial ways. While the individual macromolecules are held together by a combination of covalent bonds and ''intra''molecular non-covalent forces (i.e., associations between parts within each molecule, via [[charge-charge interaction]]s, [[van der Waals forces]], and [[dipole-dipole interaction]]s such as [[hydrogen bond]]s), by definition MAs themselves are held together solely via the [[noncovalent bonding|noncovalent]] forces, except now exerted ''between'' molecules (i.e., [[intermolecular interaction]]s).{{citation needed|date=March 2019}} |
||
| Line 110: | Line 32: | ||
The images above give an indication of the compositions and scale (dimensions) associated with MAs, though these just begin to touch on the complexity of the structures; in principle, each living cell is composed of MAs, but is itself an MA as well. In the examples and other such complexes and assemblies, MAs are each often millions of [[dalton (unit)|dalton]]s in molecular weight (megadaltons, i.e., millions of times the weight of a single, simple atom), though still having measurable component ratios ([[stoichiometries]]) at some level of precision. As alluded to in the image legends, when properly prepared, MAs or component subcomplexes of MAs can often be crystallized for study by [[protein crystallography]] and related methods, or studied by other physical methods (e.g., [[spectroscopy]], [[microscopy]]).{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} |
The images above give an indication of the compositions and scale (dimensions) associated with MAs, though these just begin to touch on the complexity of the structures; in principle, each living cell is composed of MAs, but is itself an MA as well. In the examples and other such complexes and assemblies, MAs are each often millions of [[dalton (unit)|dalton]]s in molecular weight (megadaltons, i.e., millions of times the weight of a single, simple atom), though still having measurable component ratios ([[stoichiometries]]) at some level of precision. As alluded to in the image legends, when properly prepared, MAs or component subcomplexes of MAs can often be crystallized for study by [[protein crystallography]] and related methods, or studied by other physical methods (e.g., [[spectroscopy]], [[microscopy]]).{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} |
||
[[File:Phospholipids aqueous solution structures.svg|thumb|left|200px|Cross-sections of phospholipid (PLs) relevant to [[biomembrane]] MAs. Yellow-orange indicates [[hydrophobic]] lipid tails; black and white spheres represent PL polar regions (''v.i.''). Bilayer/liposome dimensions (obscured in graphic): hydrophobic and polar regions, each ~30 Å (3.0 nm) "thick"—the polar from ~15 Å (1.5 nm) ''on each side''.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blanco.biomol.uci.edu/Bilayer_Struc.html |title=Structure of Fluid Lipid Bilayers |publisher=Blanco.biomol.uci.edu |date=2009-11-10 |access-date=2019-10-09}}</ref><ref>Experimental system, dioleoyl[[phosphatidylcholine]] bilayers. The hydrophobic hydrocarbon region of the lipid is ~30 Å (3.0 nm) as determined by a combination of neutron and X-ray scattering methods; likewise, the polar/interface region (glyceryl, phosphate, and headgroup moieties, with their combined hydration) is ~15 Å (1.5 nm) ''on each side'', for a total thickness about equal to the hydrocarbon region. See S.H. White references, preceding and following.</ref><ref>{{cite journal| |
[[File:Phospholipids aqueous solution structures.svg|thumb|left|200px|Cross-sections of phospholipid (PLs) relevant to [[biomembrane]] MAs. Yellow-orange indicates [[hydrophobic]] lipid tails; black and white spheres represent PL polar regions (''v.i.''). Bilayer/liposome dimensions (obscured in graphic): hydrophobic and polar regions, each ~30 Å (3.0 nm) "thick"—the polar from ~15 Å (1.5 nm) ''on each side''.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blanco.biomol.uci.edu/Bilayer_Struc.html |title=Structure of Fluid Lipid Bilayers |publisher=Blanco.biomol.uci.edu |date=2009-11-10 |access-date=2019-10-09}}</ref><ref>Experimental system, dioleoyl[[phosphatidylcholine]] bilayers. The hydrophobic hydrocarbon region of the lipid is ~30 Å (3.0 nm) as determined by a combination of neutron and X-ray scattering methods; likewise, the polar/interface region (glyceryl, phosphate, and headgroup moieties, with their combined hydration) is ~15 Å (1.5 nm) ''on each side'', for a total thickness about equal to the hydrocarbon region. See S.H. White references, preceding and following.</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wiener MC, White SH | title = Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure | journal = Biophysical Journal | volume = 61 | issue = 2 | pages = 434–447 | date = February 1992 | pmid = 1547331 | pmc = 1260259 | doi = 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81849-0 | bibcode = 1992BpJ....61..434W }}</ref>{{primary source inline|date=October 2019}}<ref>Hydrocarbon dimensions vary with temperature, mechanical stress, PL structure and coformulants, etc. by single- to low double-digit percentages of these values.{{citation needed|date=October 2019}}</ref>]] |
||
[[File:CowpeaMosaicVirus3D.png|thumb|right|A graphical representation of the structure of a viral MA, [[cowpea mosaic virus]], with 30 copies of each of its coat proteins, the small coat protein (S, yellow) and the large coat protein (L, green), which, along with 2 molecules of [[Sense (molecular biology)|positive-sense]] [[RNA]] (RNA-1 and RNA-2, not visible) constitute the virion. The assembly is highly [[symmetry|symmetric]], and is ~280 Å (28 nm) across at its widest point.{{verification needed|date=October 2019}}{{citation needed|date=October 2019}}]] |
[[File:CowpeaMosaicVirus3D.png|thumb|right|A graphical representation of the structure of a viral MA, [[cowpea mosaic virus]], with 30 copies of each of its coat proteins, the small coat protein (S, yellow) and the large coat protein (L, green), which, along with 2 molecules of [[Sense (molecular biology)|positive-sense]] [[RNA]] (RNA-1 and RNA-2, not visible) constitute the virion. The assembly is highly [[symmetry|symmetric]], and is ~280 Å (28 nm) across at its widest point.{{verification needed|date=October 2019}}{{citation needed|date=October 2019}}]] |
||
[[Virus structure]]s were among the first studied MAs; other biologic examples include ribosomes (partial image above), proteasomes, and translation complexes (with [[protein]] and [[nucleic acid]] components), procaryotic and eukaryotic transcription complexes, and [[nuclear pore|nuclear]] and other biological [[wiktionary:pore|pore]]s that allow material passage between cells and cellular compartments. [[Biomembrane]]s are also generally considered MAs, though the requirement for structural and spatial definition is modified to accommodate the inherent [[molecular dynamics]] of membrane [[lipid]]s, and of proteins within [[lipid bilayer]]s.<ref>{{ |
[[Virus structure]]s were among the first studied MAs; other biologic examples include ribosomes (partial image above), proteasomes, and translation complexes (with [[protein]] and [[nucleic acid]] components), procaryotic and eukaryotic transcription complexes, and [[nuclear pore|nuclear]] and other biological [[wiktionary:pore|pore]]s that allow material passage between cells and cellular compartments. [[Biomembrane]]s are also generally considered MAs, though the requirement for structural and spatial definition is modified to accommodate the inherent [[molecular dynamics]] of membrane [[lipid]]s, and of proteins within [[lipid bilayer]]s.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gerle C | title = Essay on Biomembrane Structure | journal = The Journal of Membrane Biology | volume = 252 | issue = 2-3 | pages = 115–130 | date = June 2019 | pmid = 30877332 | pmc = 6556169 | doi = 10.1007/s00232-019-00061-w }}</ref> |
||
===Virus assembly=== |
===Virus assembly=== |
||
During assembly of the [[Escherichia virus T4|bacteriophage (phage) T4]] [[virus|virion]], the morphogenetic proteins encoded by the phage [[gene]]s interact with each other in a characteristic sequence. Maintaining an appropriate balance in the amounts of each of these proteins produced during viral infection appears to be critical for normal phage T4 [[morphogenesis]].<ref>Floor E |
During assembly of the [[Escherichia virus T4|bacteriophage (phage) T4]] [[virus|virion]], the morphogenetic proteins encoded by the phage [[gene]]s interact with each other in a characteristic sequence. Maintaining an appropriate balance in the amounts of each of these proteins produced during viral infection appears to be critical for normal phage T4 [[morphogenesis]].<ref name="pmid4907266">{{cite journal | vauthors = Floor E | title = Interaction of morphogenetic genes of bacteriophage T4 | journal = Journal of Molecular Biology | volume = 47 | issue = 3 | pages = 293–306 | date = February 1970 | pmid = 4907266 | doi = 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90303-7 }}</ref> Phage T4 encoded proteins that determine virion structure include major structural components, minor structural components and non-structural proteins that catalyze specific steps in the morphogenesis sequence<ref name="pmid4878023">{{cite journal | vauthors = Snustad DP | title = Dominance interactions in Escherichia coli cells mixedly infected with bacteriophage T4D wild-type and amber mutants and their possible implications as to type of gene-product function: catalytic vs. stoichiometric | journal = Virology | volume = 35 | issue = 4 | pages = 550–63 | date = August 1968 | pmid = 4878023 | doi = 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90285-7 }}</ref> |
||
== Research into MAs == |
== Research into MAs == |
||
| Line 124: | Line 46: | ||
Finally, biology is not the sole domain of MAs. The fields of [[supramolecular chemistry]] and [[nanotechnology]] each have areas that have developed to elaborate and extend the principles first demonstrated in biologic MAs. Of particular interest in these areas has been elaborating the fundamental processes of [[molecular machine]]s, and extending known machine designs to new types and processes.{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} |
Finally, biology is not the sole domain of MAs. The fields of [[supramolecular chemistry]] and [[nanotechnology]] each have areas that have developed to elaborate and extend the principles first demonstrated in biologic MAs. Of particular interest in these areas has been elaborating the fundamental processes of [[molecular machine]]s, and extending known machine designs to new types and processes.{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} |
||
==See also== |
== See also == |
||
* [[Multi-state modeling of biomolecules]] |
* [[Multi-state modeling of biomolecules]] |
||
* [[Quaternary structure]] |
* [[Quaternary structure]] |
||
| Line 135: | Line 57: | ||
== Further reading == |
== Further reading == |
||
===General reviews=== |
===General reviews=== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
*{{cite journal | last1 = Williamson | first1 = J.R. | year = 2008 | title = Cooperativity in macromolecular assembly | journal = Nature Chemical Biology | volume = 4 | issue = 8| pages = 458–465 | doi=10.1038/nchembio.102| pmid = 18641626 }} |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Williamson JR | title = Cooperativity in macromolecular assembly | journal = Nature Chemical Biology | volume = 4 | issue = 8 | pages = 458–465 | date = August 2008 | pmid = 18641626 | doi = 10.1038/nchembio.102 }} |
|||
* Perrakis A, Musacchio A, Cusack S, Petosa C. Investigating a macromolecular complex: the toolkit of methods. J Struct Biol. 2011 Aug;175(2):106-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2011.05.014. Epub 2011 May 18. Review. PubMed PMID 21620973. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Perrakis A, Musacchio A, Cusack S, Petosa C | title = Investigating a macromolecular complex: the toolkit of methods | journal = Journal of Structural Biology | volume = 175 | issue = 2 | pages = 106–12 | date = August 2011 | pmid = 21620973 | doi = 10.1016/j.jsb.2011.05.014 | url = }} |
|||
* Dafforn TR. So how do you know you have a macromolecular complex? Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2007 Jan;63(Pt 1):17-25. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Review. PubMed PMID 17164522; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2483502. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Dafforn TR | title = So how do you know you have a macromolecular complex? | journal = Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography | volume = 63 | issue = Pt 1 | pages = 17–25 | date = January 2007 | pmid = 17164522 | pmc = 2483502 | doi = 10.1107/S0907444906047044 }} |
|||
* Wohlgemuth I, Lenz C, Urlaub H. Studying macromolecular complex stoichiometries by peptide-based mass spectrometry. Proteomics. 2015 Mar;15(5-6):862-79. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400466. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Review. PubMed PMID 25546807; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5024058. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Wohlgemuth I, Lenz C, Urlaub H | title = Studying macromolecular complex stoichiometries by peptide-based mass spectrometry | journal = Proteomics | volume = 15 | issue = 5-6 | pages = 862–79 | date = March 2015 | pmid = 25546807 | pmc = 5024058 | doi = 10.1002/pmic.201400466 }} |
|||
* Sinha C, Arora K, Moon CS, Yarlagadda S, Woodrooffe K, Naren AP. Förster resonance energy transfer—An approach to visualize the spatiotemporal regulation of macromolecular complex formation and compartmentalized cell signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1840(10):3067-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.07.015. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Review. PubMed PMID 25086255; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4151567. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Sinha C, Arora K, Moon CS, Yarlagadda S, Woodrooffe K, Naren AP | title = Förster resonance energy transfer - an approach to visualize the spatiotemporal regulation of macromolecular complex formation and compartmentalized cell signaling | journal = Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta | volume = 1840 | issue = 10 | pages = 3067–72 | date = October 2014 | pmid = 25086255 | pmc = 4151567 | doi = 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.07.015 }} |
|||
* {{aut|Berg, J.}} {{aut|Tymoczko, J.}} and {{aut|Stryer, L.}}, ''Biochemistry.'' (W. H. Freeman and Company, 2002), {{ISBN|0-7167-4955-6}} |
|||
* {{ |
* {{cite book | vauthors = Berg JM, Tymoczko J, Stryer L |title=Biochemistry |date=2002 |publisher=W.H. Freeman |location=New York |isbn=978-0-7167-4955-4 |edition=5th}} |
||
* {{cite book | vauthors = Lehninger AL, Cox M, Nelson DL |title=Lehninger principles of biochemistry |date=2005 |publisher=W.H. Freeman |location=New York |isbn=978-0-7167-4339-2 |edition=Fourth}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
===Reviews on particular MAs=== |
===Reviews on particular MAs=== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
* Valle M. Almost lost in translation. Cryo-EM of a dynamic macromolecular complex: the ribosome. Eur Biophys J. 2011 May;40(5):589-97. doi: 10.1007/s00249-011-0683-6. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Review. PubMed PMID 21336521. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Valle M | title = Almost lost in translation. Cryo-EM of a dynamic macromolecular complex: the ribosome | journal = European Biophysics Journal : EBJ | volume = 40 | issue = 5 | pages = 589–97 | date = May 2011 | pmid = 21336521 | doi = 10.1007/s00249-011-0683-6 }} |
|||
* Monie TP. The Canonical Inflammasome: A Macromolecular Complex Driving Inflammation. Subcell Biochem. 2017;83:43-73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_2. Review. PubMed PMID 28271472. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Monie TP | title = The Canonical Inflammasome: A Macromolecular Complex Driving Inflammation | journal = Sub-cellular Biochemistry | volume = 83 | issue = | pages = 43–73 | date = 2017 | pmid = 28271472 | doi = 10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_2 }} |
|||
* Perino A, Ghigo A, Damilano F, Hirsch E. Identification of the macromolecular complex responsible for PI3Kgamma-dependent regulation of cAMP levels. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Aug;34(Pt 4):502-3. Review. PubMed PMID 16856844. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Perino A, Ghigo A, Damilano F, Hirsch E | title = Identification of the macromolecular complex responsible for PI3Kgamma-dependent regulation of cAMP levels | journal = Biochemical Society Transactions | volume = 34 | issue = Pt 4 | pages = 502–3 | date = August 2006 | pmid = 16856844 | doi = 10.1042/BST0340502 }} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
===Primary sources=== |
===Primary sources=== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
*{{cite journal | last1 = Lasker | first1 = K. | last2 = Förster | first2 = F. | last3 = Walzthoeni | first3 = T. | last4 = Villa | first4 = E. | last5 = Unverdorben | first5 = P. | last6 = Beck | first6 = F. | last7 = Aebersold | first7 = R. | last8 = Sali | first8 = A. | last9 = Baumeister | first9 = W. | year = 2012 | title = Molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome holocomplex determined by an integrative approach | journal = Proc Natl Acad Sci USA | volume = 109 | issue = 5| pages = 1380–7 | doi=10.1073/pnas.1120559109 | pmid=22307589 | pmc=3277140| bibcode = 2012PNAS..109.1380L | doi-access = free }} |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Lasker K, Förster F, Bohn S, Walzthoeni T, Villa E, Unverdorben P, Beck F, Aebersold R, Sali A, Baumeister W | display-authors = 6 | title = Molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome holocomplex determined by an integrative approach | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 109 | issue = 5 | pages = 1380–1387 | date = January 2012 | pmid = 22307589 | pmc = 3277140 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.1120559109 | doi-access = free | bibcode = 2012PNAS..109.1380L }} |
|||
*{{cite journal | last1 = Russel | first1 = D. | last2 = Lasker | first2 = K. | last3 = Webb | first3 = B. | last4 = Velázquez-Muriel | first4 = J. | last5 = Tjioe | first5 = E. | last6 = Schneidman-Duhovny | first6 = D. | last7 = Peterson | first7 = B. | last8 = Sali | first8 = A. | year = 2012 | title = Putting the pieces together: integrative modeling platform software for structure determination of macromolecular assemblies | journal = PLOS Biol. | volume = 10 | issue = 1 | doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.1001244 | pages=e1001244 | pmid=22272186 | pmc=3260315}} |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Russel D, Lasker K, Webb B, Velázquez-Muriel J, Tjioe E, Schneidman-Duhovny D, Peterson B, Sali A | display-authors = 6 | title = Putting the pieces together: integrative modeling platform software for structure determination of macromolecular assemblies | journal = PLoS Biology | volume = 10 | issue = 1 | pages = e1001244 | date = January 2012 | pmid = 22272186 | pmc = 3260315 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001244 }} |
|||
* Barhoum S, Palit S, Yethiraj A. Diffusion NMR studies of macromolecular complex formation, crowding and confinement in soft materials. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016 May;94-95:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Review. PubMed PMID 27247282. |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Barhoum S, Palit S, Yethiraj A | title = Diffusion NMR studies of macromolecular complex formation, crowding and confinement in soft materials | journal = Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy | volume = 94-95 | issue = | pages = 1–10 | date = May 2016 | pmid = 27247282 | doi = 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.01.004 }} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
===Other sources=== |
===Other sources=== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
* Nobel Prizes in Chemistry (2012), The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009, Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas A. Steitz, Ada E. Yonath, [http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2009/illpres.html The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009], accessed 13 June 2011. |
* Nobel Prizes in Chemistry (2012), The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009, Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas A. Steitz, Ada E. Yonath, [http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2009/illpres.html The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009], accessed 13 June 2011. |
||
* Nobel Prizes in Chemistry (2012), The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982, Aaron Klug, [http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1982/press.html The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982], accessed 13 June 2011. |
* Nobel Prizes in Chemistry (2012), The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982, Aaron Klug, [http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1982/press.html The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982], accessed 13 June 2011. |
||
{{refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
== External links == |
||
*Beck Group (2019), Structure and function of large macromolecular assemblies (Beck group home page), [http://www.embl.de/research/units/scb/beck/ Beck Group - Structure and function of large molecular assemblies - EMBL], accessed 13 June 2011. |
*Beck Group (2019), Structure and function of large macromolecular assemblies (Beck group home page), [http://www.embl.de/research/units/scb/beck/ Beck Group - Structure and function of large molecular assemblies - EMBL], accessed 13 June 2011. |
||
*DMA Group (2019), Dynamics of macromolecular assembly (DMA Group home page), [https://www.nibib.nih.gov/labs-at-nibib/laboratory-cellular-imaging-and-macromolecular-biophysics-lcimb/dynamics-macromolecular-assembly-section Dynamics of Macromolecular Assembly Section | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering], accessed 13 June 2011. |
*DMA Group (2019), Dynamics of macromolecular assembly (DMA Group home page), [https://www.nibib.nih.gov/labs-at-nibib/laboratory-cellular-imaging-and-macromolecular-biophysics-lcimb/dynamics-macromolecular-assembly-section Dynamics of Macromolecular Assembly Section | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering], accessed 13 June 2011. |
||
Revision as of 07:35, 16 March 2022
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (October 2019) |
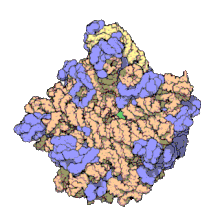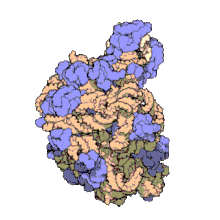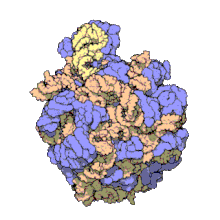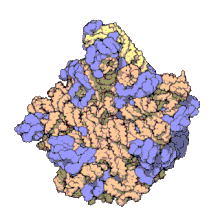
The term macromolecular assembly (MA) refers to massive chemical structures such as viruses and non-biologic nanoparticles, cellular organelles and membranes and ribosomes, etc. that are complex mixtures of polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide or other polymeric macromolecules. They are generally of more than one of these types, and the mixtures are defined spatially (i.e., with regard to their chemical shape), and with regard to their underlying chemical composition and structure. Macromolecules are found in living and nonliving things, and are composed of many hundreds or thousands of atoms held together by covalent bonds; they are often characterized by repeating units (i.e., they are polymers). Assemblies of these can likewise be biologic or non-biologic, though the MA term is more commonly applied in biology, and the term supramolecular assembly is more often applied in non-biologic contexts (e.g., in supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology). MAs of macromolecules are held in their defined forms by non-covalent intermolecular interactions (rather than covalent bonds), and can be in either non-repeating structures (e.g., as in the ribosome (image) and cell membrane architectures), or in repeating linear, circular, spiral, or other patterns (e.g., as in actin filaments and the flagellar motor, image). The process by which MAs are formed has been termed molecular self-assembly, a term especially applied in non-biologic contexts. A wide variety of physical/biophysical, chemical/biochemical, and computational methods exist for the study of MA; given the scale (molecular dimensions) of MAs, efforts to elaborate their composition and structure and discern mechanisms underlying their functions are at the forefront of modern structure science.

Biomolecular complex

A biomolecular complex, also called a biomacromolecular complex, is any biological complex made of more than one biopolymer (protein, RNA, DNA, [5] carbohydrate) or large non-polymeric biomolecules (lipid). The interactions between these biomolecules are non-covalent. [6] Examples:
- Protein complexes, some of which are multienzyme complexes: proteasome, DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, RNA polymerase II holoenzyme, symmetric viral capsids, chaperonin complex GroEL-GroES, photosystem I, ATP synthase, ferritin.
- RNA-protein complexes: ribosome, spliceosome, vault, SnRNP. Such complexes in cell nucleus are called ribonucleoproteins (RNPs).
- DNA-protein complexes: nucleosome.
- Protein-lipid complexes: lipoprotein.[7][8]
The biomacromolecular complexes are studied structurally by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy of proteins, cryo-electron microscopy and successive single particle analysis, and electron tomography. [9] The atomic structure models obtained by X-ray crystallography and biomolecular NMR spectroscopy can be docked into the much larger structures of biomolecular complexes obtained by lower resolution techniques like electron microscopy, electron tomography, and small-angle X-ray scattering. [10]
Complexes of macromolecules occur ubiquitously in nature, where they are involved in the construction of viruses and all living cells. In addition, they play fundamental roles in all basic life processes (protein translation, cell division, vesicle trafficking, intra- and inter-cellular exchange of material between compartments, etc.). In each of these roles, complex mixtures of become organized in specific structural and spatial ways. While the individual macromolecules are held together by a combination of covalent bonds and intramolecular non-covalent forces (i.e., associations between parts within each molecule, via charge-charge interactions, van der Waals forces, and dipole-dipole interactions such as hydrogen bonds), by definition MAs themselves are held together solely via the noncovalent forces, except now exerted between molecules (i.e., intermolecular interactions).[citation needed]
MA scales and examples
The images above give an indication of the compositions and scale (dimensions) associated with MAs, though these just begin to touch on the complexity of the structures; in principle, each living cell is composed of MAs, but is itself an MA as well. In the examples and other such complexes and assemblies, MAs are each often millions of daltons in molecular weight (megadaltons, i.e., millions of times the weight of a single, simple atom), though still having measurable component ratios (stoichiometries) at some level of precision. As alluded to in the image legends, when properly prepared, MAs or component subcomplexes of MAs can often be crystallized for study by protein crystallography and related methods, or studied by other physical methods (e.g., spectroscopy, microscopy).[citation needed]
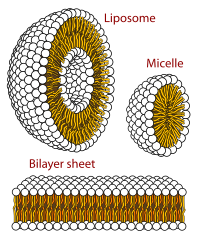

Virus structures were among the first studied MAs; other biologic examples include ribosomes (partial image above), proteasomes, and translation complexes (with protein and nucleic acid components), procaryotic and eukaryotic transcription complexes, and nuclear and other biological pores that allow material passage between cells and cellular compartments. Biomembranes are also generally considered MAs, though the requirement for structural and spatial definition is modified to accommodate the inherent molecular dynamics of membrane lipids, and of proteins within lipid bilayers.[15]
Virus assembly
During assembly of the bacteriophage (phage) T4 virion, the morphogenetic proteins encoded by the phage genes interact with each other in a characteristic sequence. Maintaining an appropriate balance in the amounts of each of these proteins produced during viral infection appears to be critical for normal phage T4 morphogenesis.[16] Phage T4 encoded proteins that determine virion structure include major structural components, minor structural components and non-structural proteins that catalyze specific steps in the morphogenesis sequence[17]
Research into MAs
The study of MA structure and function is challenging, in particular because of their megadalton size, but also because of their complex compositions and varying dynamic natures. Most have had standard chemical and biochemical methods applied (methods of protein purification and centrifugation, chemical and electrochemical characterization, etc.). In addition, their methods of study include modern proteomic approaches, computational and atomic-resolution structural methods (e.g., X-ray crystallography), small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), force spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy and cryo-electron microscopy. Aaron Klug was recognized with the 1982 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on structural elucidation using electron microscopy, in particular for protein-nucleic acid MAs including the tobacco mosaic virus (a structure containing a 6400 base ssRNA molecule and >2000 coat protein molecules). The crystallization and structure solution for the ribosome, MW ~ 2.5 MDa, an example of part of the protein synthetic 'machinery' of living cells, was object of the 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas A. Steitz, and Ada E. Yonath.[18]
Non-biologic counterparts
Finally, biology is not the sole domain of MAs. The fields of supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology each have areas that have developed to elaborate and extend the principles first demonstrated in biologic MAs. Of particular interest in these areas has been elaborating the fundamental processes of molecular machines, and extending known machine designs to new types and processes.[citation needed]
See also
- Multi-state modeling of biomolecules
- Quaternary structure
- Multiprotein complex
- Organelle: the broadest definition of "organelle" includes not only membrane bound cellular structures, but also very large biomolecular complexes.
- Multi-state modeling of biomolecules
References
- ^ Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA (August 2000). "The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution". Science. 289 (5481): 905–920. Bibcode:2000Sci...289..905B. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.58.2271. doi:10.1126/science.289.5481.905. PMID 10937989.
- ^ McClure W. "50S Ribosome Subunit". Archived from the original on 2005-11-24. Retrieved 2019-10-09.
- ^ Osborne AR, Rapoport TA, van den Berg B (2005). "Protein translocation by the Sec61/SecY channel". Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 21: 529–550. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.133214. PMID 16212506.
- ^ Legend, cover art, J. Bacteriol., October 2006.[full citation needed]
- ^ Kleinjung J, Fraternali F (July 2005). "POPSCOMP: an automated interaction analysis of biomolecular complexes". Nucleic Acids Research. 33 (Web Server issue): W342–W346. doi:10.1093/nar/gki369. PMC 1160130. PMID 15980485.
- ^ Moore PB (2012). "How should we think about the ribosome?". Annual Review of Biophysics. 41 (1): 1–19. doi:10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102314. PMID 22577819.
- ^ Neuman N (January 2016). "The Complex Macromolecular Complex". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 41 (1): 1–3. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2015.11.006. PMID 26699226.
- ^ Dutta S, Berman HM (March 2005). "Large macromolecular complexes in the Protein Data Bank: a status report". Structure. 13 (3): 381–388. doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.01.008. PMID 15766539.
- ^ Russell RB, Alber F, Aloy P, Davis FP, Korkin D, Pichaud M, et al. (June 2004). "A structural perspective on protein-protein interactions". Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 14 (3): 313–324. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2004.04.006. PMID 15193311.
- ^ van Dijk AD, Boelens R, Bonvin AM (January 2005). "Data-driven docking for the study of biomolecular complexes". The FEBS Journal. 272 (2): 293–312. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2004.04473.x. hdl:1874/336958. PMID 15654870. S2CID 20148856.
- ^ "Structure of Fluid Lipid Bilayers". Blanco.biomol.uci.edu. 2009-11-10. Retrieved 2019-10-09.
- ^ Experimental system, dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. The hydrophobic hydrocarbon region of the lipid is ~30 Å (3.0 nm) as determined by a combination of neutron and X-ray scattering methods; likewise, the polar/interface region (glyceryl, phosphate, and headgroup moieties, with their combined hydration) is ~15 Å (1.5 nm) on each side, for a total thickness about equal to the hydrocarbon region. See S.H. White references, preceding and following.
- ^ Wiener MC, White SH (February 1992). "Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure". Biophysical Journal. 61 (2): 434–447. Bibcode:1992BpJ....61..434W. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81849-0. PMC 1260259. PMID 1547331.
- ^ Hydrocarbon dimensions vary with temperature, mechanical stress, PL structure and coformulants, etc. by single- to low double-digit percentages of these values.[citation needed]
- ^ Gerle C (June 2019). "Essay on Biomembrane Structure". The Journal of Membrane Biology. 252 (2–3): 115–130. doi:10.1007/s00232-019-00061-w. PMC 6556169. PMID 30877332.
- ^ Floor E (February 1970). "Interaction of morphogenetic genes of bacteriophage T4". Journal of Molecular Biology. 47 (3): 293–306. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(70)90303-7. PMID 4907266.
- ^ Snustad DP (August 1968). "Dominance interactions in Escherichia coli cells mixedly infected with bacteriophage T4D wild-type and amber mutants and their possible implications as to type of gene-product function: catalytic vs. stoichiometric". Virology. 35 (4): 550–63. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(68)90285-7. PMID 4878023.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009". The Nobel Prize. Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2021. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
Further reading
General reviews
- Williamson JR (August 2008). "Cooperativity in macromolecular assembly". Nature Chemical Biology. 4 (8): 458–465. doi:10.1038/nchembio.102. PMID 18641626.
- Perrakis A, Musacchio A, Cusack S, Petosa C (August 2011). "Investigating a macromolecular complex: the toolkit of methods". Journal of Structural Biology. 175 (2): 106–12. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2011.05.014. PMID 21620973.
- Dafforn TR (January 2007). "So how do you know you have a macromolecular complex?". Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography. 63 (Pt 1): 17–25. doi:10.1107/S0907444906047044. PMC 2483502. PMID 17164522.
- Wohlgemuth I, Lenz C, Urlaub H (March 2015). "Studying macromolecular complex stoichiometries by peptide-based mass spectrometry". Proteomics. 15 (5–6): 862–79. doi:10.1002/pmic.201400466. PMC 5024058. PMID 25546807.
- Sinha C, Arora K, Moon CS, Yarlagadda S, Woodrooffe K, Naren AP (October 2014). "Förster resonance energy transfer - an approach to visualize the spatiotemporal regulation of macromolecular complex formation and compartmentalized cell signaling". Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. 1840 (10): 3067–72. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.07.015. PMC 4151567. PMID 25086255.
- Berg JM, Tymoczko J, Stryer L (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-4955-4.
- Lehninger AL, Cox M, Nelson DL (2005). Lehninger principles of biochemistry (Fourth ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-4339-2.
Reviews on particular MAs
- Valle M (May 2011). "Almost lost in translation. Cryo-EM of a dynamic macromolecular complex: the ribosome". European Biophysics Journal : EBJ. 40 (5): 589–97. doi:10.1007/s00249-011-0683-6. PMID 21336521.
- Monie TP (2017). "The Canonical Inflammasome: A Macromolecular Complex Driving Inflammation". Sub-cellular Biochemistry. 83: 43–73. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_2. PMID 28271472.
- Perino A, Ghigo A, Damilano F, Hirsch E (August 2006). "Identification of the macromolecular complex responsible for PI3Kgamma-dependent regulation of cAMP levels". Biochemical Society Transactions. 34 (Pt 4): 502–3. doi:10.1042/BST0340502. PMID 16856844.
Primary sources
- Lasker K, Förster F, Bohn S, Walzthoeni T, Villa E, Unverdorben P, et al. (January 2012). "Molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome holocomplex determined by an integrative approach". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (5): 1380–1387. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.1380L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1120559109. PMC 3277140. PMID 22307589.
- Russel D, Lasker K, Webb B, Velázquez-Muriel J, Tjioe E, Schneidman-Duhovny D, et al. (January 2012). "Putting the pieces together: integrative modeling platform software for structure determination of macromolecular assemblies". PLoS Biology. 10 (1): e1001244. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001244. PMC 3260315. PMID 22272186.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Barhoum S, Palit S, Yethiraj A (May 2016). "Diffusion NMR studies of macromolecular complex formation, crowding and confinement in soft materials". Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 94–95: 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.01.004. PMID 27247282.
Other sources
- Nobel Prizes in Chemistry (2012), The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009, Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas A. Steitz, Ada E. Yonath, The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009, accessed 13 June 2011.
- Nobel Prizes in Chemistry (2012), The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982, Aaron Klug, The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982, accessed 13 June 2011.
External links
- Beck Group (2019), Structure and function of large macromolecular assemblies (Beck group home page), Beck Group - Structure and function of large molecular assemblies - EMBL, accessed 13 June 2011.
- DMA Group (2019), Dynamics of macromolecular assembly (DMA Group home page), Dynamics of Macromolecular Assembly Section | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, accessed 13 June 2011.
