Glaucophyte: Difference between revisions
outline, nav |
the conclusions in the rest of that paragraph are not a consequence of "hypothesis that primary chloroplasts" alone, and none of this is particularly well-established |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
The '''glaucophytes''', also known as '''glaucocystophytes''' or '''glaucocystids''', are a small group of freshwater microscopic [[algae]].<ref name="keeling">{{cite journal | journal = American Journal of Botany | year = 2004 | volume = 91 | pages = 1481–1493 | title = Diversity and evolutionary history of plastids and their hosts | author = Patrick J. Keeling | url = http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/content/full/91/10/1481 | doi = 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1481 }}</ref> Together with the [[red algae]] and [[Viridiplantae]] (green algae and land plants) they form the [[Archaeplastida]]. However, the relationships between the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear,<ref name="palmer">{{cite journal | url = http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/content/full/91/10/1437 | title = The plant tree of life: an overview and some points of view | author = Jeffrey D. Palmer, Douglas E. Soltis and Mark W. Chase | journal = American Journal of Botany | year = 2004 | volume = 91 | pages = 1437–1445 | doi = 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1437}}</ref> in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes. |
The '''glaucophytes''', also known as '''glaucocystophytes''' or '''glaucocystids''', are a small group of freshwater microscopic [[algae]].<ref name="keeling">{{cite journal | journal = American Journal of Botany | year = 2004 | volume = 91 | pages = 1481–1493 | title = Diversity and evolutionary history of plastids and their hosts | author = Patrick J. Keeling | url = http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/content/full/91/10/1481 | doi = 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1481 }}</ref> Together with the [[red algae]] and [[Viridiplantae]] (green algae and land plants) they form the [[Archaeplastida]]. However, the relationships between the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear,<ref name="palmer">{{cite journal | url = http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/content/full/91/10/1437 | title = The plant tree of life: an overview and some points of view | author = Jeffrey D. Palmer, Douglas E. Soltis and Mark W. Chase | journal = American Journal of Botany | year = 2004 | volume = 91 | pages = 1437–1445 | doi = 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1437}}</ref> in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes. |
||
The glaucophytes are of |
The glaucophytes are of interest to biologists studying the development of chloroplasts, because they may be similar to the original alga type which led to green plants and red algae (although not all studies find this).<ref name="keeling" /><ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0002621 | year = 2008 | month = Jul | author = Kim, E; Graham, Le | title = EEF2 analysis challenges the monophyly of Archaeplastida and Chromalveolata. | volume = 3 | issue = 7 | pages = e2621 | pmid = 18612431 | pmc = 2440802 | journal = PLoS ONE | url = http://www.plosone.org/article/info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0002621 | format = Free full text }}</ref> |
||
==Characteristics== |
==Characteristics== |
||
Revision as of 16:28, 20 March 2009
| Glaucophyta | |
|---|---|
| |
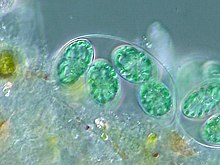
| Glaucocystis sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | Glaucophyta Skuja, 1954
|
| Possible genera | |
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater microscopic algae.[1] Together with the red algae and Viridiplantae (green algae and land plants) they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships between the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear,[2] in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes.
The glaucophytes are of interest to biologists studying the development of chloroplasts, because they may be similar to the original alga type which led to green plants and red algae (although not all studies find this).[1][3]
Characteristics
The chloroplasts of glaucophytes are known as cyanelles. Unlike other eukaryotic plastids they have a peptidoglycan layer which is believed to be a relic of the endosymbiotic origin of plastids from cyanobacteria.[1] Glaucophytes contain the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll a.[1] Along with red algae[1] and cyanobacteria they harvest light via phycobilisomes, structures consisting largely of phycobiliproteins. The green algae and land plants have lost that pigment.
Glaucophytes have mitochondria with flat cristae, and undergo open mitosis without centrioles. Motile forms have two unequal flagella, which may have fine hairs and are anchored by a multilayered system of microtubules, both of which are similar to forms found in some green algae.
Genera
The three main genera included are:
- Glaucocystis is non-motile, though it retains very short vestigial flagella, and has a cellulose wall.
- Cyanophora is motile and lacks a cell wall.
- Gloeochaete has both motile and non-motile stages, and has a cell wall that does not appear to be composed of cellulose.
There are only 13 species of glaucophytes known, none of which are particularly common in nature.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d e f Patrick J. Keeling (2004). "Diversity and evolutionary history of plastids and their hosts". American Journal of Botany. 91: 1481–1493. doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1481.
- ^ Jeffrey D. Palmer, Douglas E. Soltis and Mark W. Chase (2004). "The plant tree of life: an overview and some points of view". American Journal of Botany. 91: 1437–1445. doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1437.
- ^ Kim, E; Graham, Le (2008). "EEF2 analysis challenges the monophyly of Archaeplastida and Chromalveolata" (Free full text). PLoS ONE. 3 (7): e2621. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002621. PMC 2440802. PMID 18612431.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
