Flat (music)
 |
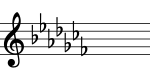 |
In music, flat, or bemolle (Italian: "soft B") means "lower in pitch". In music notation, the flat symbol, ♭, derived from a stylised lowercase "b", lowers a note by a half step (semitone).[1][2] Intonation or tuning is said to be flat when it is below the true pitch.
Flat accidentals are used in the key signatures of F major/D minor, B♭ major/G minor, E♭ major/C minor, A♭ major/F minor, D♭ major/B♭ minor, and the less frequently used keys of G♭ major/E♭ minor, C♭ major/A♭ minor. The order of flats in the key signatures of music notation, following the circle of fifths, is B♭, E♭, A♭, D♭, G♭, C♭, and F♭. A mnemonic for this is: Before Eating A Doughnut Get Coffee First.

The Unicode character ♭ (U+266D) can be found in the block Miscellaneous Symbols; its HTML entity is ♭.
Under twelve tone equal temperament, C♭ for instance is the same as, or enharmonically equivalent to, B♮ (B-natural), and G♭ is the same as F♯ (F-sharp). In any other tuning system, such enharmonic equivalences in general do not exist. To allow extended just intonation, composer Ben Johnston uses a sharp as an accidental to indicate a note is raised 70.6 cents (ratio 25:24), and a flat to indicate a note is lowered 70.6 cents.[3]
Double flats also exist, which look like ![]() (similar to two flats, ♭♭) and lower a note by two semitones, or a whole step. Less often (for instance in microtonal music notation) one will encounter half, or three-quarter, or otherwise altered flats. The Unicode character 𝄫 (U+1D12B) in the Musical Symbols block represents the double-flat sign.
(similar to two flats, ♭♭) and lower a note by two semitones, or a whole step. Less often (for instance in microtonal music notation) one will encounter half, or three-quarter, or otherwise altered flats. The Unicode character 𝄫 (U+1D12B) in the Musical Symbols block represents the double-flat sign.
Although very uncommon, a triple flat (![]() ) can sometimes be found.[4] It lowers a note three semitones.
) can sometimes be found.[4] It lowers a note three semitones.
A quarter-tone flat or half flat, indicating the use of quarter tones, may be marked with various symbols including a flat with a slash (![]() ) or a reversed flat sign (
) or a reversed flat sign (![]() ). A three-quarter-tone flat, flat and a half or sesquiflat, is represented by a half flat and a regular flat (
). A three-quarter-tone flat, flat and a half or sesquiflat, is represented by a half flat and a regular flat (![]() ).
).
See also
References
- ^ Benward & Saker (2003). Music in Theory and Practice, Vol. 1, p. 6. McGraw-Hill, Seventh edition. "Flat (♭)—lowers the pitch a half step."
- ^ Flat, Glossary, Naxos Records
- ^ John Fonville. "Ben Johnston's Extended Just Intonation- A Guide for Interpreters", p. 109, Perspectives of New Music, Vol. 29, No. 2 (Summer, 1991), pp. 106–137. "...the 25/24 ratio is the sharp (♯) ratio...this raises a note approximately 70.6 cents."
- ^ Byrd, Donald (September 2016). "Extremes of Conventional Music Notation". Indiana University Bloomington. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
External links
 Media related to Flats (music) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Flats (music) at Wikimedia Commons



