Gingival and periodontal pocket
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2016) |
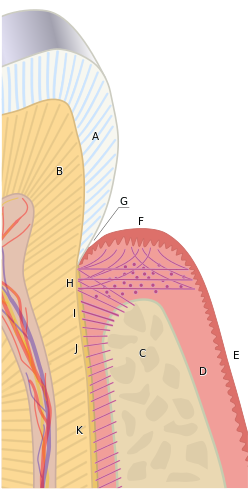
B) Root of the tooth, covered by cementum
C) Alveolar bone
D) Subepithelial connective tissue
E) Oral epithelium
F) Free gingival margin
G) Gingival sulcus (extensions of which are the gingival and periodontal pockets)
H) Principal gingival fibers
I) Alveolar crest fibers of the periodontal ligament (PDL)
J) Horizontal fibers of the PDL
K) Oblique fibers of the PDL
In dental anatomy, the gingival and periodontal pockets (also informally referred to as gum pockets[1]) are dental terms indicating the presence of an abnormal depth of the gingival sulcus near the point at which the gingival (gum) tissue contacts the tooth.
Tooth gingival interface
[edit]The interface between a tooth and the surrounding gingival tissue is a dynamic structure.[2] The gingival tissue forms a crevice surrounding the tooth, similar to a miniature, fluid-filled moat, wherein food debris, endogenous and exogenous cells, and chemicals float. The depth of this crevice, known as a sulcus, is in a constant state of flux due to microbial invasion and subsequent immune response. Located at the depth of the sulcus is the epithelial attachment, consisting of approximately 1 mm of junctional epithelium and another 1 mm of gingival fiber attachment, comprising the 2 mm of biologic width naturally found in the oral cavity. The sulcus is literally the area of separation between the surrounding epithelium and the surface of the encompassed tooth.
Gingival pocket
[edit]A gingival pocket presents when the marginal gingiva experiences an edematous reaction, whether due to localized irritation and subsequent inflammation, systemic issues, or drug induced gingival hyperplasia. Regardless of the etiology, when gingival hyperplasia occurs, greater than normal (the measurement in a pre-pathological state) periodontal probing measurements can be read, creating the illusion that periodontal pockets have developed. This phenomenon is also referred to as a false pocket or pseudopocket. The epithelial attachment does not migrate, it simply remains at the same attachment level found in pre-pathological health. The only anatomical landmark experiencing migration is the gingival margin in a coronal direction.
In a gingival pocket, no destruction of the connective tissue fibers (gingival fibers) or alveolar bone occurs. This early sign of disease in the mouth is completely reversible when the etiology of the edematous reaction is eliminated and frequently occurs without dental surgical therapy. However, in certain situations, a gingivectomy is necessary to reduce the gingival pocket depths to a healthy 1–3 mm.
Periodontal pocket
[edit]
As the original sulcular depth increases and the apical migration of the junctional epithelium has simultaneously occurred, the pocket is now lined by pocket epithelium (PE) instead of junctional epithelium (JE).[3] To have a true periodontal pocket, a probing measurement of 4 mm or more must be clinically evidenced. In this state, much of the gingival fibers that initially attached the gingival tissue to the tooth have been irreversibly destroyed. The depth of the periodontal pockets must be recorded in the patient record for proper monitoring of periodontal disease. Unlike in clinically healthy situations, parts of the sulcular epithelium can sometimes be seen in periodontally involved gingival tissue if air is blown into the periodontal pocket, exposing the newly denuded roots of the tooth. A periodontal pocket can become an infected space and may result in an abscess formation with a papule on the gingival surface. Incision and drainage of the abscess may be necessary, as well as systemic antibiotics; placement of local antimicrobial delivery systems within the periodontal pocket to reduce localized infections may also be considered. It is classified as supra bony and infra bony based on its depth in relation to alveolar bone.[4]
Mucogingival defect
[edit]If the destruction continues unabated apically and reaches the junction of the attached gingiva and alveolar mucosa, the pocket would thus be in violation of the mucogingival junction and would be termed a mucogingival defect.[5]
Pocket formation
[edit]For the periodontal pocket to form, several elements need to be present. It all starts with the dental plaque [tone]. The invasion of the bacteria from the plaque eventually triggers inflammatory response. This in turn results in the gradual destruction of the tissues surrounding the teeth, known as the periodontium. [6] Plaque that has been present long enough to harden and calcify will welcome additional bacteria to the pocket and make it virtually impossible to clean by means of a traditional toothbrush.[7] Continuous destruction of surrounding tissues due to inflammation will lead to degradation of attachment and bone, eventually causing tooth loss. Certain circumstances can worsen the condition and are known as risk factors. These can either be systemic (like diabetes or smoking) or local (like overhanging dental restorative materials causing food trap).[8] It is, therefore, important to manage plaque levels by appropriate oral hygiene measures. The importance of using interdental brushes along with standard or electric toothbrushing should be stressed early on. Early detection of high plaque levels at routine dental visits are found to be beneficial to avoid progression of the pocket formation.[9]
External links
[edit]- Scapoli, L; Girardi, A; Palmieri, A; Testori, T; Zuffetti, F; Monguzzi, R; Lauritano, D; Carinci, F (2012). "Microflora and periodontal disease". Dental Research Journal. 9 (Suppl 2): S202–6. doi:10.4103/1735-3327.109755 (inactive 1 November 2024). PMC 3692174. PMID 23814584.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link)
References
[edit]- ^ "What do your Gum Pocket Measurements really mean?" (Staff Blog). Lorne Park Dental Associates. 3 May 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- ^ Fermin A. Carranza. CARRANZA'S CLINICAL PERIODONTOLOGY, 9th edition, 2002. page 101
- ^ Antonio Nanci, Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Elsevier, 2007, page 383
- ^ Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 129
- ^ Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, Newman, et al, Elsevier, 2011
- ^ Lamont, Thomas; Worthington, Helen V; Clarkson, Janet E; Beirne, Paul V (2018-12-27). Cochrane Oral Health Group (ed.). "Routine scale and polish for periodontal health in adults". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (4): CD004625. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004625.pub5. PMC 6516960. PMID 30590875.
- ^ Worthington, Helen V; MacDonald, Laura; Poklepovic Pericic, Tina; Sambunjak, Dario; Johnson, Trevor M; Imai, Pauline; Clarkson, Janet E (2019-04-10). Cochrane Oral Health Group (ed.). "Home use of interdental cleaning devices, in addition to toothbrushing, for preventing and controlling periodontal diseases and dental caries". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (4): CD012018. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012018.pub2. PMC 6953268. PMID 30968949.
- ^ Manresa, Carolina; Sanz-Miralles, Elena C.; Twigg, Joshua; Bravo, Manuel (1 January 2018). "Supportive periodontal therapy (SPT) for maintaining the dentition in adults treated for periodontitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD009376. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009376.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6491071. PMID 29291254.
- ^ "CKS is only available in the UK". NICE. Retrieved 2020-02-19.
