Rhinal sulcus
| Rhinal sulcus | |
|---|---|
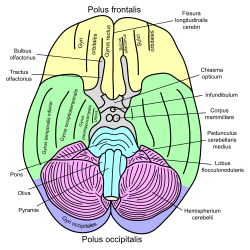 Basal view of a human brain (Rhinal sulcus not labeled, but is visible posterior to parahippocampal gyrus.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sulcus rhinalis; fissura rhinalis; sulcus rhinicus; fissura rhinica |
| NeuroNames | 41 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1368 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.240 |
| TA2 | 5443 |
| FMA | 83746 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In the human brain, the rhinencephalon appears as a longitudinal elevation, with a corresponding internal furrow, on the under surface of the hemisphere close to the lamina terminalis; it is separated from the lateral surface of the hemisphere by a furrow, the external rhinal fissure (or rhinal sulcus), and is continuous behind with that part of the hemisphere, which will ultimately form the anterior end of the temporal lobe.
External links
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 744 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 744 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
