User:PresN/malagasy

Eupleridae is a family of mammals in the order Carnivora. A member of this family is called a euplerid, Malagasy mongoose, or Malagasy carnivoran. All members of this species are found on the island of Madagascar.
The 10 species of Eupleridae are split into 7 genera within 2 subfamilies: the civet-like Euplerinae and the mongoose-like Galidiinae. Historically, the Euplerinae species were included in the civet family Viverridae, and several of the Galidiinae species in the mongoose family Herpestidae, but more recent genetic evidence showed them to be part of the same clade, having evolved from a single ancestor species 18–24 million years ago.
Conventions[edit]
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (2 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (5 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (3 species) |
| LC | Least concern (1 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (0 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (1 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the viverrid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN red list for that species unless otherwise noted.
Classification[edit]
The family Eupleridae consists of 10 extant species belonging to 14 genera in 4 subfamilies and divided into dozens of extant subspecies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species.
- Subfamily Euplerinae
- Genus Cryptoprocta: one species
- Genus Eupleres: two species
- Genus Fossa: one species
- Subfamily Galidiinae
- Genus Galidia: one species
- Genus Galidictis: two species
- Genus Mungotictis: one species
- Genus Salanoia: two species
Euplerids[edit]
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis. This includes the discovery of the Durrell's vontsira, and the splitting the falanouc species into the eastern falanouc and western falanouc.
Subfamily Euplerinae[edit]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fossa | C. ferox Bennett, 1833 |

|
Size: 61–80 cm (24–31 in) long, plus 61–80 cm (24–31 in) tail[1] Habitat: Forest[2] Diet: [2] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern falanouc | E. goudotii Doyère, 1835 |
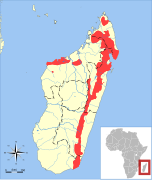
|
Size: Habitat: Forest[3] Diet: [3] |
VU
|
| Western falanouc
|
E. major Lavauden, 1929 |
Size: Habitat: Forest, inland wetlands[4] Diet: [4] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malagasy civet | F. fossana Müller, 1776 |

|
Size: Habitat: Forest[5] Diet: [5] |
VU
|
Subfamily Galidiinae[edit]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ring-tailed vontsira | G. elegans Geoffroy, 1837 Three subspecies
|

|
Size: Habitat: Forest[6] Diet: [6] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad-striped Malagasy mongoose | G. fasciata Gmelin, 1788 Two subspecies
|

|
Size: [convert: needs a number] long, plus 28–30 cm (11–12 in) tail[7] Habitat: Forest[8] Diet: [8] |
VU
|
| Grandidier's mongoose | G. grandidieri Wozencraft, 1986 |

|
Size: Habitat: Forest and shrubland[9] Diet: [9] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow-striped mongoose | M. decemlineata Grandidier, 1867 Two subspecies
|

|
Size: Habitat: Forest and shrubland[10] Diet: [10] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown-tailed mongoose | S. concolor Geoffroy, 1837 |

|
Size: Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands[11] Diet: [11] |
VU
|
| Durrell's vontsira | S. durrelli Durbin et al., 2010 |

|
Size: Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands Diet: |
NE
|
Prehistoric euplerids[edit]
In addition to extant euplerids, a number of prehistoric species have been discovered and classified as a part of Eupleridae.
- Genus Cryptoprocta
- C. spelea (giant fossa)
- Genus Cryptoprocta
References[edit]
- ^ Lundrigan, Barbara; Zachariah, Trevor (2000). "Cryptoprocta ferox". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2016). "Cryptoprocta ferox". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T5760A45197189. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T5760A45197189.en.
- ^ a b c d Hawkins, F. (2016). "Eupleres goudotii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T68336601A45204582. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T68336601A45204582.en.
- ^ a b Hawkins, F. (2016). "Eupleres major". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T39547A45204313. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T39547A45204313.en.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2015). "Fossa fossana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T8668A45197868. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T8668A45197868.en.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2015). "Galidia elegans". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T39426A45204213. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T39426A45204213.en.
- ^ Burrell, Michele (2005). "Galidictis fasciata". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2016). "Galidictis fasciata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T8833A45197977. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T8833A45197977.en.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2015). "Galidictis grandidieri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T8834A45198057. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T8834A45198057.en.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2015). "Mungotictis decemlineata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T13923A45199764. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T13923A45199764.en.
- ^ a b c Hawkins, F. (2016). "Salanoia concolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T19852A45202205. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T19852A45202205.en.









