Octahedron: Difference between revisions
Octahedron80 (talk | contribs) |
Octahedron80 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Area and volume == |
== Area and volume == |
||
The area ''A'' and the volume ''V'' of a regular octahedron of edge length ''a'' are: |
The area ''A'' and the volume ''V'' of a regular octahedron of edge length ''a'' are: |
||
:<math>A=2\sqrt{3}a^2</math> |
:<math>A=2\sqrt{3}a^2 \approx 3.46410162a^2</math> |
||
:<math>V=\ |
:<math>V=\frac{1}{3} \sqrt{2}a^3 \approx 0.471404521a^3</math> |
||
Thus the volume is four times that of a regular [[tetrahedron]] with the same edge length, while the surface area is twice (because we have 8 vs. 4 triangles). |
Thus the volume is four times that of a regular [[tetrahedron]] with the same edge length, while the surface area is twice (because we have 8 vs. 4 triangles). |
||
Revision as of 07:27, 7 June 2007
| Regular octahedron | |
|---|---|
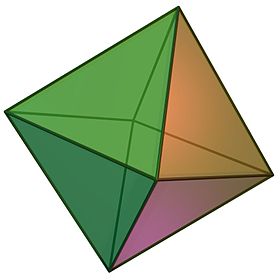 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Platonic solid |
| Elements | F = 8, E = 12 V = 6 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 8{3} |
| Conway notation | O aT |
| Schläfli symbols | {3,4} |
| r{3,3} or {}+{}+{}=3{} | |
| Face configuration | V4.4.4 |
| Wythoff symbol | 4 | 2 3 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry | Oh, BC3, [4,3], (*432) |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432) |
| References | U05, C17, W2 |
| Properties | regular, convexdeltahedron, Hanner polytope |
| Dihedral angle | 109.47122° = arccos(−1⁄3) |
 3.3.3.3 (Vertex figure) |
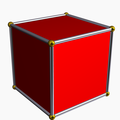 Cube (dual polyhedron) |
 Net | |
An octahedron (plural: octahedra) is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.
The octahedron's symmetry group is Oh, of order 48. This group's subgroups include D3d (order 12), the symmetry group of a triangular antiprism; D4h (order 16), the symmetry group of a square bipyramid; and Td (order 24), the symmetry group of a rectified tetrahedron. These symmetries can be emphasized by different decorations of the faces.
It is a three-dimensional cross polytope.
The octahedron in general
The regular octahedron has 6 vertices and 12 edges, the minimum for an octahedron; nonregular octahedra may have as many as 12 vertices and 18 edges.[1]
There are four important topological types of octahedra with dihedral symmetry:
- Hexagonal prism: 6 squares, 2 hexagons
- Heptagonal pyramid: 7 triangles, 1 heptagon
- Tetragonal bipyramid: 8 triangles, usually isosceles)
- The regular octahedron is a special case with equilateral triangles
- Tetragonal trapezohedron - 8 kites
The term octahedron is rarely used in this general sense, because these have little in common other than the same number of faces.
Cartesian coordinates
An octahedron can be placed with its center at the origin and its vertices on the coordinate axes; the Cartesian coordinates of the vertices are then
- ( ±1, 0, 0 );
- ( 0, ±1, 0 );
- ( 0, 0, ±1 ).
Area and volume
The area A and the volume V of a regular octahedron of edge length a are:
Thus the volume is four times that of a regular tetrahedron with the same edge length, while the surface area is twice (because we have 8 vs. 4 triangles).
Geometric relations
The interior of the compound of two dual tetrahedra is an octahedron, and this compound, called the stella octangula, is its first and only stellation. Correspondingly, a regular octahedron is the result of cutting off from a regular tetrahedron, four regular tetrahedra of half the linear size (i.e. rectifying the tetrahedron). The vertices of the octahedron lie at the midpoints of the edges of the tetrahedron, and in this sense it relates to the tetrahedron in the same way that the cuboctahedron and icosidodecahedron relate to the other Platonic solids. One can also divide the edges of an octahedron in the ratio of the golden mean to define the vertices of an icosahedron. This is done by first placing vectors along the octahedron's edges such that each face is bounded by a cycle, then similarly partitioning each edge into the golden mean along the direction of its vector. There are five octahedra that define any given icosahedron in this fashion, and together they define a regular compound.
Octahedra and tetrahedra can be alternated to form a vertex, edge, and face-uniform tessellation of space, called the octet truss by Buckminster Fuller. This is the only such tiling save the regular tessellation of cubes, and is one of the 28 convex uniform honeycombs. Another is a tessellation of octahedra and cuboctahedra.
The octahedron is unique among the Platonic solids in having an even number of faces meeting at each vertex. Consequently, it is the only member of that group to possess mirror planes that do not pass through any of the faces.
Using the standard nomenclature for Johnson solids, an octahedron would be called a square bipyramid.
Related polyhedra
The octahedron can also be considered a rectified tetrahedron. This can be shown by a 2-color face model. With this coloring, the octahedron has tetrahedral symmetry.
Compare this truncation sequence between a tetrahedron and its dual:
 Tetrahedron |
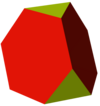 Truncated tetrahedron |
 octahedron |
 Truncated tetrahedron |
 Tetrahedron |
Octahedra in the physical world
- Especially in roleplaying games, this solid is known as a d8, one of the more common Polyhedral dice.
- If each edge of an octahedron is replaced by a one ohm resistor, the resistance between opposite vertices is 1/2 ohms, and that between adjacent vertices 5/12 ohms.[1]
See also
- Spinning octahedron
- Triakis octahedron
- Hexakis octahedron
- Truncated octahedron
- Octahedral molecular geometry
References
- ^ Klein, Douglas J. (2002). "Resistance-Distance Sum Rules" (PDF). Croatica Chemica Acta. 75 (2): 633–649. Retrieved 2006-09-30.
External links
- Octahedron - Mathworld.com
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- Paper Models of Polyhedra Many links



