Ares I: Difference between revisions
connect the dots, i.e. "Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars (mythology)" |
|||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
*[http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/constellation/ares/aresI.html NASA Ares I page] |
*[http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/constellation/ares/aresI.html NASA Ares I page] |
||
*[http://www.tallgeorge.com/projectconstellation.php A Visual History of Project Constellation] |
*[http://www.tallgeorge.com/projectconstellation.php A Visual History of Project Constellation] |
||
*[http://www.nasaconstellation.com Transitioning to the Constellation Program] |
|||
{{Project Constellation}} |
{{Project Constellation}} |
||
Revision as of 02:02, 3 November 2007
- This article is about the Ares I launch vehicle. For other uses, see Ares (disambiguation).
 Artist's impression of Ares I launch | |
| Function | man-rated orbital launch vehicle |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Alliant Techsystems (Stage I) Boeing (Stage II) |
| Size | |
| Height | 94 m (309 ft) |
| Diameter | 5.5 m |
| Mass | TBC |
| Stages | 2 |
| Capacity | |
| Payload to LEO | 25,000 kg |
| Launch history | |
| Status | In Development, ready for test on LC-39B |
| Launch sites | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39B |
| Total launches | 0 |
| First flight | Scheduled for 2009 |
| First stage | |
| Engines | 1 Solid |
| Thrust | TBC |
| Burn time | ~150 seconds |
| Propellant | Solid |
| Second stage | |
| Engines | 1 J-2X |
| Thrust | TBC |
| Burn time | TBC |
| Propellant | LH2/LOX |

Ares I is the crew launch vehicle being developed by NASA as a component of Project Constellation. NASA will use Ares I to launch Orion, the spacecraft being designed for NASA human spaceflight missions after the Space Shuttle is retired in 2010. Ares I was previously known as the Crew Launch Vehicle or CLV. The larger, unmanned Ares V is being designed as a complement to the Ares I; it will be the cargo launch vehicle for Project Constellation. Ares I and V are named after the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars.
Ares I’s role in Project Constellation
Ares I is the crew launch component of Project Constellation. Unlike the Space Shuttle, where both crew and cargo are launched simultaneously on the same rocket, the plans for Project Constellation outline having two separate launch vehicles, the Ares I and the Ares V, for crew and cargo, respectively. Having two separate launch vehicles will allow for more specialized designs for the different purposes the rockets will fulfill.

The Ares I rocket is specifically being designed to launch the Orion Crew Vehicle. Orion is intended as a crew capsule, similar in design to the Project Apollo capsule, to transport astronauts to the International Space Station, the Moon, and eventually Mars.
Design
First stage
The first stage is a more powerful and reusable solid fuel rocket derived from the current Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster (SRB). Compared with the current SRB, which has four segments, the most notable difference is the addition of a fifth segment. This fifth segment will enable the Ares I to produce more thrust, burn longer, and attain a higher orbit than a standard four-segment SRB. Other changes made to the SRB are the removal of the Space Shuttle External Tank (ET) attachment points, the parachutes and other recovery equipment, and the replacement of the SRB nosecone with a new forward adapter that will interface with the liquid-fueled second stage. The adapter will be equipped with solid-fueled separation motors to facilitate the disconnection of the stages during ascent.
Upper stage
The upper stage will be propelled by one J-2X rocket engine fueled by liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX).[1] The J-2X is derived from the J-2 engine used on the Saturn IB and Saturn V rockets. On 16 July 2007, NASA awarded Rocketdyne a sole-source contract for the J-2X engines to be used for ground and flight tests.[2] Originally, NASA was to use a Space Shuttle Main Engine, but due to the high costs (~$55-60 million USD per engine), the need to redesign the engine to start up in both the air and in vacuum, and that the Ares I upper stage is expendable, the engine was dropped in favor of the J-2X, which cost only a fraction of the price (~$20 million USD), and was designed, from the beginning, for high-altitude use.
Although its J-2X engine is derived from an established design, the upper stage itself is wholly new. Originally based on the internal structure of the Shuttle's External Tank, the original design called for separate fuel and oxidizer tanks, separated by an "intertank" structure, was to be employed. Using a concept going back to the Apollo era, the "intertank" structure was dropped to decrease mass, and instead, a common bulkhead would be used between the tanks. A recent design, currently under review, uses the savings to increase propellant capacity: with the common bulkhead, total propellant capacity would be 297,900 pounds.[3] The increase in fuel mass is expected to decrease the initial acceleration of the second stage to around 0.6 G.
The upper portion of the upper stage includes an adapter assembly to mate with the Orion Crew Vehicle, and the lower section includes a thruster system, similar to that used on the Saturn IB and Saturn V rockets, to provide roll control for both the first and second stages of the vehicle during flight. The only part of the Shuttle's External Tank that would be used on the Ares I upper stage, the spray-foam insulation (the same insulation that caused the demise of the Space Shuttle Columbia), would be used to insulate the cryogenic propellants from the warm, moist conditions found at Kennedy Space Center.
NASA announced the winner of the Ares I Upper Stage contract to The Boeing Company on August 28, 2007. The upper stage of Ares I will be built at the NASA Michoud Assembly Facility, the current location of the fabrication and construction of the Shuttle's External Tank, and the former construction site of the Saturn V's S-IC stage, which Boeing built back in the 1960's.
Design history

After President Bush announced the Vision for Space Exploration in January 2004, NASA chartered the Exploration Systems Architecture Study on 29 April 2005 to determine: the "top-level requirements and configurations for crew and cargo launch systems to support the lunar and Mars exploration programs"; to assess the "CEV requirements and plans to enable the CEV to provide crew transport to the ISS"; to "develop a reference lunar exploration architecture concept to support sustained human and robotic lunar exploration operations"; and to "identify key technologies required to enable and significantly enhance these reference exploration systems." [4]
A Shuttle-derived launch architecture was selected by NASA for the Ares I. Originally, the vehicle would have used a 4-segment Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) for the first stage, with a simplified Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) being used for the second stage. An unmanned version, identical with the current design, would have used the 5-segment booster, but with the second stage using the single SSME.
But shortly after the initial design was approved, additional tests revealed that the Orion spacecraft would be too heavy to be lifted with the 4-segment booster. In January, 2006, NASA announced that the Orion spacecraft would be slightly reduced in size, a fifth segment would be added to the solid-rocket first stage, and that the single SSME would be replaced with the Apollo-derived J-2X motor. While the switch from a 4-segment first stage to a 5-segment version would allow NASA to construct virtually identical motors (albeit with some segments being interchangeable), the main reason for the change to the 5-segment booster was the need to adopt the J-2X.
At approximately US$20-25 million per engine, the Rocketdyne-designed and produced J-2X will cost less than half as much as the complex SSME (≈$55 million). And, unlike the current SSME, which was designed to start on the ground, the J-2X was designed from the start to be started in both mid-air and in near-vacuum. This air-start capability was critical, especially in the original J-2 engine used on the Saturn V's S-IVB stage, to propel the Apollo spacecraft to the Moon. The SSME, on the other hand, would have to undergo extensive modifications to be air-startable and to be able to restart in a vacuum (as the Ares I would fly a "direct-insertion" profile, and since the Orion spacecraft has limited fuel reserves), and would have to be "pre-fired" in a manner similar to the "Main Engine tests" conducted on the SSMEs prior to the maiden flights of each NASA orbiter and before the STS-26 flight in 1988.
NASA has announced that ATK Thiokol, the current builders of the Shuttle SRBs, will be the prime contractor for the Ares I first stage[5]; ATK is also bidding to become part of the consortium that will build the Ares I upper stage. Rocketdyne, a division of Pratt & Whitney (formerly under the ownership of Rockwell International and Boeing's North America division), will be the main subcontractor for the J-2X rocket engine. Testing of the engine is currently underway at a facility south of Huntsville, AL.
On 4 January 2007, NASA announced that the Ares I had completed its system requirements review, the first such review completed for any manned spacecraft design since the Space Shuttle.[6] This review is the first major milestone in the design process, and is intended to ensure that the Ares I launch system meets all the requirements necessary for Project Constellation. In addition to the release of the review, NASA also announced that a redesign in the tank hardware was made. Instead of separate LH2 and LOX tanks, separated by an "intertank" like that on the Shuttle ET, the new LH2 and LOX tanks will be separated by a common bulkhead like that employed on the Saturn V S-II and S-IVB stages. This will allow NASA to construct a shorter and lighter second stage, along with eliminating the need to design a second stage interstage unit that would have to carry the weight of the Orion spacecraft with it.
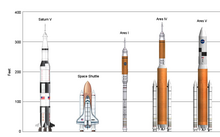
Ares I is a two-stage rocket designed to launch an Orion crew capsule into Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Development schedule
On 4 January 2007 NASA completed the Ares I system requirements review.[6] This review was the first major milestone in the design process of the Ares I rocket. Going forward, NASA intends to refine the project requirements through 2007, beginning project design later that year. Project design will continue through the end of 2009, with development and qualification testing running concurrently starting in 2008 and running through 2012. At the same time, flight articles will begin production towards the end of 2009 for a first launch in June 2011. [7][8]
Criticisms
The proposed Ares I configuration has been criticized on several grounds. First, the production of a launch vehicle in the 25 tonnes (55,000 lb) payload class can be seen as direct competition with existing vehicles, e.g. the Boeing Delta IV-Heavy. It can be argued that lower costs and improved safety are likely to result from the use of an existing vehicle, since it would have lower development costs, a proven track record, and would benefit from a higher flight rate. The NASA study group that selected what would become the Ares I concluded the opposite, however, and rated the vehicle as almost twice as safe as an Atlas or Delta-derived design.[9] Reports of growing political pressure from Congress to cancel the Shuttle-derived system and instead use existing Atlas/Delta vehicles began circulating in mid-2007.
Second, the configuration chosen by NASA requires a new five-segment SRB with its associated $3 billion development cost; this negates many of the supposed advantages of using 'shuttle-derived' hardware. In fact, critics say, the deletion of the SSME and four-segment SRB from the configuration removes the new vehicle from the class "Shuttle-Derived Launch Vehicles" entirely.
Third, technical objections may be raised over the aerodynamic stability of the proposed configuration. The tall, slender 'stick' configuration leads to a forward center of pressure and an aft center of gravity. Thus, the Ares I will continually tend to turn around, being most stable if flying backwards. The thrust vector control system on the SRB will have to constantly cope with this instability, which may lead to increased mechanical loads on the airframe. NASA has ongoing wind tunnel studies to address this problem.
However, supporters of the Ares I claim that the vehicle is essential in ensuring the continued employment of the current STS workforce, as well as those involved in developing several critical components (like the five segment SRB and J-2X engine) of the larger Ares V vehicle.
See also
References
- ^ "Ares I Fact Sheet" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ "NASA Awards Upper Stage Engine Contract for Ares Rockets". NASA. 2007-07-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Ares I Upper Stage change - receives additional capacity". NASASpaceflight.com.
- ^ "Exploration Systems Architecture Study -- Final Report". NASA. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (2006-02-27). "NASA closing in on naming new fleet". NASA SpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 2006-11-22.
- ^ a b "NASA Completes Review Milestone for Ares I Vehicle" (Press release). NASA. 2007-01-04. Retrieved 2007-01-07.
{{cite press release}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Stein, Keith (2007-01-04). "Draft Launch Schedule For Ares Launch Vehicle". Launchspace.com. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ Connolly, John (2006-10). "Constellation Program Overview" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Part 6 of the Exploration Systems Architecture Study Final Report" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 2007-01-10.


