Debye model: Difference between revisions
Debye model |
ce Tag: Reverted |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:Debye100.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Peter Debye]]]] |
[[File:Debye100.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Peter Debye]]]] |
||
{{Statistical mechanics|cTopic=Models}} |
{{Statistical mechanics|cTopic=Models}} |
||
In [[thermodynamics]] and [[solid-state physics]], the '''Debye model''' is a method developed by [[Peter Debye]] in 1912 for estimating the [[phonon]] contribution to the [[specific heat]] ([[Heat capacity]]) in a [[solid]].<ref>{{cite journal |first=Peter |last=Debye |title=Zur Theorie der spezifischen Waerme |language=de|journal=[[Annalen der Physik]] |volume=39 |issue=4 |pages=789–839 |year=1912 |doi= 10.1002/andp.19123441404 |bibcode = 1912AnP...344..789D |url=https://zenodo.org/record/1424256 }}</ref> It treats the [[oscillation|vibration]]s of the [[Crystal structure#Classification|atomic lattice]] (heat) as [[phonon]]s in a box, in contrast to the [[Einstein solid|Einstein photoelectron model]], which treats the solid as many individual, non-interacting [[quantum harmonic oscillator]]s. The Debye model correctly predicts the low-temperature dependence of the heat capacity of solids, which is proportional to <math>T^3</math> – the '''[[Debye T3 law|Debye ''T''<sup> |
In [[thermodynamics]] and [[solid-state physics]], the '''Debye model''' is a method developed by [[Peter Debye]] in 1912 for estimating the [[phonon]] contribution to the [[specific heat]] ([[Heat capacity]]) in a [[solid]].<ref>{{cite journal |first=Peter |last=Debye |title=Zur Theorie der spezifischen Waerme |language=de|journal=[[Annalen der Physik]] |volume=39 |issue=4 |pages=789–839 |year=1912 |doi= 10.1002/andp.19123441404 |bibcode = 1912AnP...344..789D |url=https://zenodo.org/record/1424256 }}</ref> It treats the [[oscillation|vibration]]s of the [[Crystal structure#Classification|atomic lattice]] (heat) as [[phonon]]s in a box, in contrast to the [[Einstein solid|Einstein photoelectron model]], which treats the solid as many individual, non-interacting [[quantum harmonic oscillator]]s. The Debye model correctly predicts the low-temperature dependence of the heat capacity of solids, which is proportional to <math>T^3</math> – the '''[[Debye T3 law|Debye ''T''<sup>3</sup> law]]'''. Just like the [[Einstein solid|Einstein photoelectron model]], it also recovers the [[Dulong–Petit law]] at high temperatures. But due to simplifying assumptions, its accuracy suffers at intermediate temperatures. |
||
== Derivation == |
== Derivation == |
||
The Debye model is a solid-state equivalent of [[Planck's law of black |
The Debye model is a solid-state equivalent of [[Planck's law of black-body radiation]], where one treats [[electromagnetic radiation]] as a [[photon gas]]. The Debye model treats [[atomic vibration]]s as [[phonon]]s in a box (the box being the solid). Most of the calculation steps are identical as both are examples of a massless [[Bose gas]] with linear [[dispersion relation]]. |
||
Consider a cube of side <math>L</math>. From the [[particle in a box]] article, the resonating modes of the sonic disturbances inside the box (considering for now only those aligned with one axis) have [[Wavelength|wavelengths]] given by |
Consider a cube of side <math>L</math>. From the [[particle in a box]] article, the resonating modes of the sonic disturbances inside the box (considering for now only those aligned with one axis) have [[Wavelength|wavelengths]] given by |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
:<math>E_n\ =h\nu_n\,,</math> |
:<math>E_n\ =h\nu_n\,,</math> |
||
where <math>h</math> is [[Planck |
where <math>h</math> is the [[Planck constant]] and <math>\nu_{n}</math> is the frequency of the phonon. Making the approximation that the frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength, we have |
||
:<math>E_n=h\nu_n={hc_{\rm s}\over\lambda_n}={hc_sn\over 2L}\,,</math> |
:<math>E_n=h\nu_n={hc_{\rm s}\over\lambda_n}={hc_sn\over 2L}\,,</math> |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
in which <math>p_n</math> is the [[magnitude]] of the [[Three-dimensional space|three-dimensional]] [[momentum]] of the [[phonon]]. |
in which <math>p_n</math> is the [[magnitude]] of the [[Three-dimensional space|three-dimensional]] [[momentum]] of the [[phonon]]. |
||
The approximation that the [[frequency]] is [[inversely proportional]] to the [[wavelength]] (giving a constant speed of [[sound]]) is good for low-energy [[ |
The approximation that the [[frequency]] is [[inversely proportional]] to the [[wavelength]] (giving a constant speed of [[sound]]) is good for low-energy [[phonon]]s but not for high-energy phonons. This disagreement is one of the limitations of the Debye model. It produces incorrect results at intermediate temperatures, whereas the results are exact at the low and high temperatures limits. |
||
Let's now compute the total energy in the box, |
Let's now compute the total energy in the box, |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
:<math>U = \sum_{n_x}\sum_{n_y}\sum_{n_z}E_n\,\bar{N}(E_n)\,.</math> |
:<math>U = \sum_{n_x}\sum_{n_y}\sum_{n_z}E_n\,\bar{N}(E_n)\,.</math> |
||
Here, the '''Debye model''' and [[Planck's law of black |
Here, the '''Debye model''' and [[Planck's law of black-body radiation]] differ. Unlike [[electromagnetic radiation]] in a box, there is a finite number of [[phonon]] [[energy state]]s because a [[phonon]] cannot have arbitrarily high [[Frequency|frequencies]]. Its frequency is bounded by the medium of its propagation—the atomic lattice of the [[solid]]. Consider an illustration of a transverse [[phonon]] below. |
||
[[Image:Debye limit.svg|400px]] |
[[Image:Debye limit.svg|400px]] |
||
It is reasonable to assume that the minimum [[wavelength]] of a [[phonon]] is twice the atom separation, as shown in the lower figure. There are <math>N</math> atoms in a solid. Our solid is a cube, which means there are |
It is reasonable to assume that the minimum [[wavelength]] of a [[phonon]] is twice the atom separation, as shown in the lower figure. There are <math>N</math> atoms in a solid. Our solid is a cube, which means there are <math>\sqrt[3]{N}</math> atoms per edge. Atom separation is then given by <math>L/\sqrt[3]{N}</math>, and the minimum [[wavelength]] is |
||
:<math>\lambda_{\rm min} = {2L \over \sqrt[3]{N}}\,,</math> |
:<math>\lambda_{\rm min} = {2L \over \sqrt[3]{N}}\,,</math> |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
:<math>\langle N\rangle_{BE} = {1\over e^{E/kT}-1}\,.</math> |
:<math>\langle N\rangle_{BE} = {1\over e^{E/kT}-1}\,.</math> |
||
Because a phonon has three possible polarization states (one [[longitudinal wave|longitudinal]], and two [[transverse wave|transverse]] which approximately do not affect its |
Because a phonon has three possible polarization states (one [[longitudinal wave|longitudinal]], and two [[transverse wave|transverse]], which approximately do not affect its |
||
energy) the formula above must be multiplied by 3, |
energy) the formula above must be multiplied by 3, |
||
:<math>\bar{N}(E) = {3\over e^{E/kT}-1}\,.</math> |
:<math>\bar{N}(E) = {3\over e^{E/kT}-1}\,.</math> |
||
Actually one uses an ''effective sonic velocity'' <math>c_s:=c_ |
Actually one uses an ''effective sonic velocity'' <math>c_s:=c_{\rm eff}</math>, i.e. the Debye temperature <math>T_{\rm D}</math> (see below) is proportional to <math>c_{\rm eff}</math>, more precisely <math>T_{\rm D}^{-3}\propto c_{\rm eff}^{-3}:=(1/3)c_{\rm long}^{-3}+(2/3)c_{\rm trans}^{-3}</math>, where one distinguishes longitudinal and transversal [[Sound wave|sound-wave]] velocities (contributions 1/3 and 2/3, respectively). The Debye temperature or the effective sonic velocity is a measure of the hardness of the crystal. |
||
Substituting into the energy integral yields |
Substituting into the energy integral yields |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
:<math>U = {3\pi\over2} kT \left({2LkT\over hc_{\rm s}}\right)^3\int_0^{hc_{\rm s}R/2LkT} {x^3\over e^x-1}\, dx.</math> |
:<math>U = {3\pi\over2} kT \left({2LkT\over hc_{\rm s}}\right)^3\int_0^{hc_{\rm s}R/2LkT} {x^3\over e^x-1}\, dx.</math> |
||
To simplify the appearance |
To simplify the appearance of this expression, define the '''Debye temperature''' <math>T_{\rm D}</math> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
of this expression, define the '''Debye temperature''' <math>T_{\rm D}</math> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
where <math>V</math> is the volume of the cubic box of side <math>L</math>. |
where <math>V</math> is the volume of the cubic box of side <math>L</math>. |
||
Many references<ref name=Kittel>{{cite book |last=Kittel |first=Charles |title=[[Introduction to Solid State Physics]] |edition=8 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2004 |isbn=978-0471415268}}</ref><ref>Schroeder, Daniel V. "An Introduction to Thermal Physics" Addison-Wesley, San Francisco (2000). Section 7.5</ref> describe the Debye temperature as merely shorthand for some constants and material-dependent variables. However, as shown below, <math> kT_{\rm D}</math> is roughly equal to the phonon energy of |
Many references<ref name=Kittel>{{cite book |last=Kittel |first=Charles |title=[[Introduction to Solid State Physics]] |edition=8 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2004 |isbn=978-0471415268}}</ref><ref>Schroeder, Daniel V. "An Introduction to Thermal Physics" Addison-Wesley, San Francisco (2000). Section 7.5</ref> describe the Debye temperature as merely shorthand for some constants and material-dependent variables. However, as shown below, <math> kT_{\rm D}</math> is roughly equal to the phonon energy of the minimum wavelength mode, and so we can interpret the Debye temperature as the temperature at which the highest-frequency mode (and hence every mode) is excited. |
||
Continuing, we then have the specific internal energy: |
Continuing, we then have the specific internal energy: |
||
:<math>\frac{U}{Nk} = 9T \left({T\over T_{\rm D}}\right)^3\int_0^{T_{\rm D}/T} {x^3\over e^x-1}\, dx = 3T D_3 \left({T_{\rm D}\over T}\right)\,,</math> |
:<math>\frac{U}{Nk} = 9T \left({T\over T_{\rm D}}\right)^3\int_0^{T_{\rm D}/T} {x^3\over e^x-1}\, dx = 3T D_3 \left({T_{\rm D}\over T}\right)\,,</math> |
||
where <math>D_3(x)</math> is the (third) [[Debye function]]. |
where <math>D_3(x)</math> is the (third) [[Debye function]]. |
||
Differentiating with respect to <math>T</math> we get the dimensionless heat capacity: |
Differentiating with respect to <math>T</math> we get the dimensionless heat capacity: |
||
:<math> \frac{C_V}{Nk} = 9 \left({T\over T_{\rm D}}\right)^3\int_0^{T_{\rm D}/T} {x^4 e^x\over\left(e^x-1\right)^2}\, dx\,.</math> |
:<math> \frac{C_V}{Nk} = 9 \left({T\over T_{\rm D}}\right)^3\int_0^{T_{\rm D}/T} {x^4 e^x\over\left(e^x-1\right)^2}\, dx\,.</math> |
||
| Line 117: | Line 114: | ||
Debye derived his equation somewhat differently and more simply. Using [[continuum mechanics]], he found that the number of vibrational states with a [[frequency]] less than a particular value was asymptotic to |
Debye derived his equation somewhat differently and more simply. Using [[continuum mechanics]], he found that the number of vibrational states with a [[frequency]] less than a particular value was asymptotic to |
||
:<math> n \sim {1 \over 3} \nu^3 V F\,, </math> |
:<math> n \sim {1 \over 3} \nu^3 V F\,, </math> |
||
in which <math> V </math> is the volume and <math> F </math> is a factor which he calculated from [[Elasticity (physics)|elasticity coefficient]]s and density. Combining this formula with the expected energy of a harmonic oscillator at temperature T (already used by [[Einstein solid|Einstein]] in his model) would give an energy of |
in which <math> V </math> is the volume and <math> F </math> is a factor which he calculated from [[Elasticity (physics)|elasticity coefficient]]s and density. Combining this formula with the expected energy of a harmonic oscillator at temperature T (already used by [[Einstein solid|Einstein]] in his model) would give an energy of |
||
:<math>U = \int_0^\infty \,{h\nu^3 V F\over e^{h\nu/kT}-1}\, d\nu\,,</math> |
:<math>U = \int_0^\infty \,{h\nu^3 V F\over e^{h\nu/kT}-1}\, d\nu\,,</math> |
||
if the vibrational frequencies continued to infinity. This form gives the <math>T^3</math> behaviour which is correct at low temperatures. But Debye realized that there could not be more than <math>3N</math> vibrational states for N atoms. He made the assumption that in an atomic [[solid]], the [[spectrum]] of [[Frequency|frequencies]] of the vibrational states would continue to follow the above rule, up to a maximum [[frequency]] <math>\nu_m</math>chosen so that the total number of states is |
if the vibrational frequencies continued to infinity. This form gives the <math>T^3</math> behaviour which is correct at low temperatures. But Debye realized that there could not be more than <math>3N</math> vibrational states for N atoms. He made the assumption that in an atomic [[solid]], the [[spectrum]] of [[Frequency|frequencies]] of the vibrational states would continue to follow the above rule, up to a maximum [[frequency]] <math>\nu_m</math>chosen so that the total number of states is |
||
:<math> 3N = {1 \over 3} \nu_m^3 V F \,.</math> |
:<math> 3N = {1 \over 3} \nu_m^3 V F \,.</math> |
||
Debye knew that this assumption was not really correct (the higher [[Frequency|frequencies]] are more closely spaced than assumed), but it guarantees the proper behaviour at high temperature (the [[Dulong–Petit law]]). The energy is then given by |
Debye knew that this assumption was not really correct (the higher [[Frequency|frequencies]] are more closely spaced than assumed), but it guarantees the proper behaviour at high temperature (the [[Dulong–Petit law]]). The energy is then given by |
||
:<math>\begin{align} |
:<math>\begin{align} |
||
U &= \int_0^{\nu_m} \,{h\nu^3 V F\over e^{h\nu/kT}-1}\, d\nu\,,\\ |
U &= \int_0^{\nu_m} \,{h\nu^3 V F\over e^{h\nu/kT}-1}\, d\nu\,,\\ |
||
| Line 139: | Line 130: | ||
&= 3 N k T D_3(T_{\rm D}/T)\,, |
&= 3 N k T D_3(T_{\rm D}/T)\,, |
||
\end{align}</math> |
\end{align}</math> |
||
where <math>D_3</math> is the function later given the name of third-order [[Debye function]]. |
where <math>D_3</math> is the function later given the name of third-order [[Debye function]]. |
||
== Another derivation == |
== Another derivation == |
||
First we derive the [[vibrational frequency]] distribution; the following derivation is based on Appendix VI from.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Hill|first1=Terrell L.|title=An Introduction to Statistical Mechanics|date=1960|publisher=Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.|location=Reading, Massachusetts, U.S.A.|isbn=9780486652429|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/introductiontost0000hill}}</ref> Consider a [[Three-dimensional space|three-dimensional]] [[Isotropy|isotropic]] [[elastic solid]] with N atoms in the shape of a [[rectangular parallelepiped]] with side-lengths <math>L_x, L_y, L_z</math>. The [[Elastic Wave|elastic wave]] will obey the [[wave equation]] and will be [[plane waves]]; consider the [[wave vector]] <math>\mathbf{k} = (k_x, k_y, k_z)</math> and define <math>l_x=\frac{k_x}{|\mathbf{k}|}, l_y=\frac{k_y}{|\mathbf{k}|}, l_z=\frac{k_z}{|\mathbf{k}|}</math>. Note that we have |
First we derive the [[vibrational frequency]] distribution; the following derivation is based on Appendix VI from.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Hill|first1=Terrell L.|title=An Introduction to Statistical Mechanics|date=1960|publisher=Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.|location=Reading, Massachusetts, U.S.A.|isbn=9780486652429|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/introductiontost0000hill}}</ref> Consider a [[Three-dimensional space|three-dimensional]] [[Isotropy|isotropic]] [[elastic solid]] with N atoms in the shape of a [[rectangular parallelepiped]] with side-lengths <math>L_x, L_y, L_z</math>. The [[Elastic Wave|elastic wave]] will obey the [[wave equation]] and will be [[plane waves]]; consider the [[wave vector]] <math>\mathbf{k} = (k_x, k_y, k_z)</math> and define <math>l_x=\frac{k_x}{|\mathbf{k}|}, l_y=\frac{k_y}{|\mathbf{k}|}, l_z=\frac{k_z}{|\mathbf{k}|}</math>. Note that we have |
||
{{NumBlk|:|<math> l_x^2 + l_y^2 + l_z^2 = 1.</math>|{{EquationRef|1}}}} |
{{NumBlk|:|<math> l_x^2 + l_y^2 + l_z^2 = 1.</math>|{{EquationRef|1}}}} |
||
Solutions to the [[wave equation]] are |
Solutions to the [[wave equation]] are |
||
:<math> u(x,y,z,t) = \sin(2\pi\nu t)\sin\left(\frac{2\pi l_x x}{\lambda}\right)\sin\left(\frac{2\pi l_y y}{\lambda}\right)\sin\left(\frac{2\pi l_z z}{\lambda}\right) </math> |
:<math> u(x,y,z,t) = \sin(2\pi\nu t)\sin\left(\frac{2\pi l_x x}{\lambda}\right)\sin\left(\frac{2\pi l_y y}{\lambda}\right)\sin\left(\frac{2\pi l_z z}{\lambda}\right) </math> |
||
and with the [[boundary conditions]] <math>u=0</math> at <math>x,y,z=0, x=L_x, y=L_y, z=L_z</math>, we have |
and with the [[boundary conditions]] <math>u=0</math> at <math>x,y,z=0, x=L_x, y=L_y, z=L_z</math>, we have |
||
{{NumBlk|:|<math> \frac{2l_xL_x}{\lambda}=n_x; \frac{2l_yL_y}{\lambda}=n_y; \frac{2l_zL_z}{\lambda}=n_z </math>|{{EquationRef|2}}}} |
{{NumBlk|:|<math> \frac{2l_xL_x}{\lambda}=n_x; \frac{2l_yL_y}{\lambda}=n_y; \frac{2l_zL_z}{\lambda}=n_z </math>|{{EquationRef|2}}}} |
||
where <math>n_x,n_y,n_z</math> are [[positive integers]]. Substituting ({{EquationNote|2}}) into ({{EquationNote|1}}) and also using the [[dispersion relation]] <math>c_s=\lambda\nu</math>, we have |
where <math>n_x,n_y,n_z</math> are [[positive integers]]. Substituting ({{EquationNote|2}}) into ({{EquationNote|1}}) and also using the [[dispersion relation]] <math>c_s=\lambda\nu</math>, we have |
||
:<math> \frac{n_x^2}{(2\nu L_x/c_s)^2} + \frac{n_y^2}{(2\nu L_y/c_s)^2} + \frac{n_z^2}{(2\nu L_z/c_s)^2} = 1. </math> |
:<math> \frac{n_x^2}{(2\nu L_x/c_s)^2} + \frac{n_y^2}{(2\nu L_y/c_s)^2} + \frac{n_z^2}{(2\nu L_z/c_s)^2} = 1. </math> |
||
| Line 164: | Line 148: | ||
Following the derivation from,<ref>{{cite book|last1=Oberai|first1=M. M.|last2=Srikantiah|first2=G|title=A First Course in Thermodynamics | date=1974|publisher=Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited|location=New Delhi, India|isbn=9780876920183}}</ref> we define an upper limit to the frequency of vibration <math>\nu_D</math>; since there are N atoms in the solid, there are 3N quantum harmonic oscillators (3 for each x-, y-, z- direction) oscillating over the range of frequencies <math>[0,\nu_D]</math>. Hence we can determine <math> \nu_D </math> using |
Following the derivation from,<ref>{{cite book|last1=Oberai|first1=M. M.|last2=Srikantiah|first2=G|title=A First Course in Thermodynamics | date=1974|publisher=Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited|location=New Delhi, India|isbn=9780876920183}}</ref> we define an upper limit to the frequency of vibration <math>\nu_D</math>; since there are N atoms in the solid, there are 3N quantum harmonic oscillators (3 for each x-, y-, z- direction) oscillating over the range of frequencies <math>[0,\nu_D]</math>. Hence we can determine <math> \nu_D </math> using |
||
{{NumBlk|:|<math> 3N = N(\nu_{\rm D}) = \frac{4\pi\nu_{\rm D}^3V}{3c_{\rm s}^3} </math>.|{{EquationRef|4}}}} |
{{NumBlk|:|<math> 3N = N(\nu_{\rm D}) = \frac{4\pi\nu_{\rm D}^3V}{3c_{\rm s}^3} </math>.|{{EquationRef|4}}}} |
||
By defining <math>\nu_{\rm D} = \frac{kT_{\rm D}}{h}</math>, where k is [[Boltzmann |
By defining <math>\nu_{\rm D} = \frac{kT_{\rm D}}{h}</math>, where ''k'' is the [[Boltzmann constant]] and ''h'' is the [[Planck constant]], and substituting ({{EquationNote|4}}) into ({{EquationNote|3}}), we get |
||
| ⚫ | {{NumBlk|:|<math> N(\nu) = \frac{3Nh^3\nu^3}{k^3T_{\rm D}^3},</math>|{{EquationRef|5}}}}this definition is more standard. We can find the energy contribution for all [[Oscillation|oscillators]] oscillating at [[frequency]] <math>\nu</math>. [[Quantum harmonic oscillator|Quantum harmonic oscillators]] can have energies <math>E_i = (i+1/2)h\nu</math> where <math>i = 0,1,2,\dotsc</math> and using [[Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics]], the number of particles with energy <math>E_i</math> is |
||
| ⚫ | {{NumBlk|:|<math> N(\nu) = \frac{3Nh^3\nu^3}{k^3T_{\rm D}^3},</math>|{{EquationRef|5}}}}this definition is more standard. We can find the energy contribution for all [[Oscillation|oscillators]] oscillating at [[frequency]] <math>\nu</math>. [[Quantum harmonic oscillator|Quantum harmonic oscillators]] can have energies <math>E_i = (i+1/2)h\nu</math> where <math>i = 0,1,2,\dotsc</math> and using [[ |
||
:<math>n_i=\frac{1}{A}e^{-E_i/(kT)}=\frac{1}{A}e^{-(i+1/2)h\nu/(kT)}.</math> |
:<math>n_i=\frac{1}{A}e^{-E_i/(kT)}=\frac{1}{A}e^{-(i+1/2)h\nu/(kT)}.</math> |
||
The energy contribution for [[Oscillation|oscillators]] with frequency <math>\nu</math> is then |
The energy contribution for [[Oscillation|oscillators]] with frequency <math>\nu</math> is then |
||
{{NumBlk|:|<math> dU(\nu) = \sum_{i=0}^\infty E_i\frac{1}{A}e^{-E_i/(kT)}</math>.|{{EquationRef|6}}}} |
{{NumBlk|:|<math> dU(\nu) = \sum_{i=0}^\infty E_i\frac{1}{A}e^{-E_i/(kT)}</math>.|{{EquationRef|6}}}} |
||
By noting that <math>\sum_{i=0}^\infty n_i = dN(\nu)</math> (because there are <math>dN(\nu)</math> modes oscillating with [[frequency]] <math>\nu</math>), we have |
By noting that <math>\sum_{i=0}^\infty n_i = dN(\nu)</math> (because there are <math>dN(\nu)</math> modes oscillating with [[frequency]] <math>\nu</math>), we have |
||
:<math>\frac{1}{A}e^{-1/2h\nu/(kT)}\sum_{i=0}^\infty e^{-ih\nu/(kT)} = \frac{1}{A}e^{-1/2h\nu/(kT)}\frac{1}{1-e^{-h\nu/(kT)}} = dN(\nu) .</math> |
:<math>\frac{1}{A}e^{-1/2h\nu/(kT)}\sum_{i=0}^\infty e^{-ih\nu/(kT)} = \frac{1}{A}e^{-1/2h\nu/(kT)}\frac{1}{1-e^{-h\nu/(kT)}} = dN(\nu) .</math> |
||
| Line 224: | Line 203: | ||
The scale of the Debye model is <math>T_{\rm D}</math>, the Debye temperature. Both are usually found by fitting the models to the experimental data. (The Debye temperature can theoretically be calculated from the speed of sound and crystal dimensions.) Because the two methods approach the problem from different directions and different geometries, Einstein and Debye scales are '''not''' the same, that is to say |
The scale of the Debye model is <math>T_{\rm D}</math>, the Debye temperature. Both are usually found by fitting the models to the experimental data. (The Debye temperature can theoretically be calculated from the speed of sound and crystal dimensions.) Because the two methods approach the problem from different directions and different geometries, Einstein and Debye scales are '''not''' the same, that is to say |
||
:<math>{\epsilon\over k} \ne T_{\rm D}\,,</math> |
:<math>{\epsilon\over k} \ne T_{\rm D}\,,</math> |
||
which means that plotting them on the same set of axes makes no sense. They are two models of the same thing, but of different scales. If one defines '''Einstein condensation temperature''' as |
which means that plotting them on the same set of axes makes no sense. They are two models of the same thing, but of different scales. If one defines '''Einstein condensation temperature''' as |
||
:<math>T_{\rm E} \ \stackrel{\mathrm{def}}{=}\ {\epsilon\over k}\,,</math> |
:<math>T_{\rm E} \ \stackrel{\mathrm{def}}{=}\ {\epsilon\over k}\,,</math> |
||
then one can say |
then one can say |
||
:<math>T_{\rm E} \ne T_{\rm D}\,,</math> |
:<math>T_{\rm E} \ne T_{\rm D}\,,</math> |
||
and, to relate the two, we must seek the ratio |
and, to relate the two, we must seek the ratio |
||
:<math>\frac{T_{\rm E}}{ T_{\rm D}} \, .</math> |
:<math>\frac{T_{\rm E}}{ T_{\rm D}} \, .</math> |
||
The [[Einstein solid]] is composed of '''single'''-frequency [[quantum harmonic oscillator]]s, <math>\epsilon = \hbar\omega = h\nu</math>. That frequency, if it indeed existed, would be related to the speed of sound in the solid. If one imagines the propagation of sound as a sequence of atoms ''hitting'' one another, then it becomes obvious that the frequency of oscillation must correspond to the minimum wavelength sustainable by the atomic lattice, <math>\lambda_{min}</math>. Where |
The [[Einstein solid]] is composed of '''single'''-frequency [[quantum harmonic oscillator]]s, <math>\epsilon = \hbar\omega = h\nu</math>. That frequency, if it indeed existed, would be related to the speed of sound in the solid. If one imagines the propagation of sound as a sequence of atoms ''hitting'' one another, then it becomes obvious that the frequency of oscillation must correspond to the minimum wavelength sustainable by the atomic lattice, <math>\lambda_{min}</math>. Where |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
which makes the '''Einstein temperature''' |
which makes the '''Einstein temperature''' |
||
:<math>T_{\rm E} = {\epsilon\over k} = {h\nu\over k} = {h c_{\rm s}\over 2k}\sqrt[3]{N\over V}\,,</math> |
:<math>T_{\rm E} = {\epsilon\over k} = {h\nu\over k} = {h c_{\rm s}\over 2k}\sqrt[3]{N\over V}\,,</math> |
||
and the sought ratio is therefore |
and the sought ratio is therefore |
||
:<math>{T_{\rm E}\over T_{\rm D}} = \sqrt[3]{\pi\over6}\ = 0.805995977...</math> |
:<math>{T_{\rm E}\over T_{\rm D}} = \sqrt[3]{\pi\over6}\ = 0.805995977...</math> |
||
| Line 360: | Line 328: | ||
=== Definition === |
=== Definition === |
||
Assuming the [[dispersion relation]] is |
Assuming the [[dispersion relation]] is |
||
:<math> \omega = v_{\rm s} |\mathbf k| ,</math> |
:<math> \omega = v_{\rm s} |\mathbf k| ,</math> |
||
with <math>v_{\rm s}</math> the [[speed of sound]] in the crystal; and '''k''' the wave vector, the value of the Debye frequency is as follows: |
with <math>v_{\rm s}</math> the [[speed of sound]] in the crystal; and '''k''' the wave vector, the value of the Debye frequency is as follows: |
||
For a one dimensional monatomic chain the Debye frequency is equal to<ref>{{Cite web| url=https://openphysicslums.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/latticevibrations.pdf| title=The one dimensional monatomic solid| access-date=2018-04-27}}</ref> |
For a one dimensional monatomic chain the Debye frequency is equal to<ref>{{Cite web| url=https://openphysicslums.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/latticevibrations.pdf| title=The one dimensional monatomic solid| access-date=2018-04-27}}</ref> |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = v_{\rm s} \pi / a = v_{\rm s} \pi N / L = v_{\rm s} \pi \lambda ,</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = v_{\rm s} \pi / a = v_{\rm s} \pi N / L = v_{\rm s} \pi \lambda ,</math> |
||
with <math>a</math> the distance between two neighbouring atoms in the chain when the system is in its [[ground state]] of energy (in this case that means that none of the atoms are moving with respect to each other); <math>N</math> the total number of atoms in the chain; and <math>L</math> the size (volume) of the system (length of the chain); and <math> \lambda </math> is the [[linear density|linear number density]]. Where the following relation holds: <math>L = N a</math>. |
with <math>a</math> the distance between two neighbouring atoms in the chain when the system is in its [[ground state]] of energy (in this case that means that none of the atoms are moving with respect to each other); <math>N</math> the total number of atoms in the chain; and <math>L</math> the size (volume) of the system (length of the chain); and <math> \lambda </math> is the [[linear density|linear number density]]. Where the following relation holds: <math>L = N a</math>. |
||
For a two dimensional monatomic square lattice the Debye frequency is equal to |
For a two dimensional monatomic square lattice the Debye frequency is equal to |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {4 \pi}{a^2} v_{\rm s}^2 = \frac {4 \pi N}{A} v_{\rm s}^2 \equiv 4 \pi \sigma v_{\rm s}^2 ,</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {4 \pi}{a^2} v_{\rm s}^2 = \frac {4 \pi N}{A} v_{\rm s}^2 \equiv 4 \pi \sigma v_{\rm s}^2 ,</math> |
||
where <math>a</math> and <math> N </math> are the same as before; <math> A \equiv L^{2} = N a^{2} </math> is the size (area) of the surface; and <math>\sigma</math> the [[surface density|surface number density]]. |
where <math>a</math> and <math> N </math> are the same as before; <math> A \equiv L^{2} = N a^{2} </math> is the size (area) of the surface; and <math>\sigma</math> the [[surface density|surface number density]]. |
||
For a three dimensional monatomic [[cubic crystal system|primitive cubic crystal]], the Debye frequency is equal to<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/sm1/lectures/node71.html|title=Specific heats of solids| last=Fitzpatrick|first=Richard|date=2006|website=Richard Fitzpatrick [[University of Texas at Austin]]|access-date=2018-04-27}}</ref> |
For a three dimensional monatomic [[cubic crystal system|primitive cubic crystal]], the Debye frequency is equal to<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/sm1/lectures/node71.html|title=Specific heats of solids| last=Fitzpatrick|first=Richard|date=2006|website=Richard Fitzpatrick [[University of Texas at Austin]]|access-date=2018-04-27}}</ref> |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 = \frac {6 \pi^2}{a^3} v_{\rm s}^3 = \frac {6 \pi^2 N}{V} v_{\rm s}^3 \equiv 6 \pi^2 \rho v_{\rm s}^3 ,</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 = \frac {6 \pi^2}{a^3} v_{\rm s}^3 = \frac {6 \pi^2 N}{V} v_{\rm s}^3 \equiv 6 \pi^2 \rho v_{\rm s}^3 ,</math> |
||
where <math>a</math> and <math> N </math> are the same as before; <math> V \equiv L^3 = N a^3 </math> the size of the system; and <math>\rho</math> the [[density|volume number density]]. |
where <math>a</math> and <math> N </math> are the same as before; <math> V \equiv L^3 = N a^3 </math> the size of the system; and <math>\rho</math> the [[density|volume number density]]. |
||
| Line 393: | Line 353: | ||
====Three dimensional crystal==== |
====Three dimensional crystal==== |
||
In Debye's derivation of the [[heat capacity]] he sums over all possible modes of the system. That is: including different directions and [[polarization (waves)|polarization]]s. He assumed the total number of modes per polarization to be <math>3N</math> (with <math>N</math> the amount of masses in the system), or in mathematical language<ref name=":0" /> |
In Debye's derivation of the [[heat capacity]] he sums over all possible modes of the system. That is: including different directions and [[polarization (waves)|polarization]]s. He assumed the total number of modes per polarization to be <math>3N</math> (with <math>N</math> the amount of masses in the system), or in mathematical language<ref name=":0" /> |
||
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=3 N,</math> |
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=3 N,</math> |
||
where the <math>3</math> on both sides is because of the three polarizations, so the sum runs over all modes for one specific polarization. Debye made this assumption because he knew from [[classical mechanics]] that the number of modes per polarization in a chain of masses should always be equal to the amount of masses in the chain. |
where the <math>3</math> on both sides is because of the three polarizations, so the sum runs over all modes for one specific polarization. Debye made this assumption because he knew from [[classical mechanics]] that the number of modes per polarization in a chain of masses should always be equal to the amount of masses in the chain. |
||
| Line 401: | Line 359: | ||
First of all, by assuming <math>L</math> to be very large (<math>L</math>>>1, with <math>L</math> the size of the system in any of the three directions) the smallest wave vector in any direction could be approximated by: <math> d k_i = 2 \pi / L </math>, with <math>i = x, y, z</math>. Smaller wave vectors cannot exist because of the [[periodic boundary conditions]]. Thus the summation would become [https://podcasts.ox.ac.uk/series/oxford-solid-state-basics 4] |
First of all, by assuming <math>L</math> to be very large (<math>L</math>>>1, with <math>L</math> the size of the system in any of the three directions) the smallest wave vector in any direction could be approximated by: <math> d k_i = 2 \pi / L </math>, with <math>i = x, y, z</math>. Smaller wave vectors cannot exist because of the [[periodic boundary conditions]]. Thus the summation would become [https://podcasts.ox.ac.uk/series/oxford-solid-state-basics 4] |
||
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=\frac {3 V}{(2 \pi)^3} \iiint d \mathbf k,</math> |
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=\frac {3 V}{(2 \pi)^3} \iiint d \mathbf k,</math> |
||
where <math> \mathbf k \equiv (k_x, k_y, k_z) </math>; <math> V \equiv L^3 </math> is the size of the system; and the integral is (as the summation) over all possible modes, which is assumed to be a finite region (bounded by the cut-off frequency). |
where <math> \mathbf k \equiv (k_x, k_y, k_z) </math>; <math> V \equiv L^3 </math> is the size of the system; and the integral is (as the summation) over all possible modes, which is assumed to be a finite region (bounded by the cut-off frequency). |
||
The triple integral could be rewritten as a single integral over all possible values of the absolute value of <math> \mathbf k </math> (see: [[Jacobian matrix and determinant|Jacobian for spherical coordinates]]). The result is |
The triple integral could be rewritten as a single integral over all possible values of the absolute value of <math> \mathbf k </math> (see: [[Jacobian matrix and determinant|Jacobian for spherical coordinates]]). The result is |
||
:<math>\frac {3 V}{(2 \pi)^3} \iiint d \mathbf k = \frac {3 V}{2 \pi^2} \int_0^{k_{\rm D}} |\mathbf k|^2 d \mathbf k ,</math> |
:<math>\frac {3 V}{(2 \pi)^3} \iiint d \mathbf k = \frac {3 V}{2 \pi^2} \int_0^{k_{\rm D}} |\mathbf k|^2 d \mathbf k ,</math> |
||
with <math>k_{\rm D}</math> the absolute value of the wave vector corresponding with the Debye frequency, so <math>k_{\rm D} = \omega_{\rm D}/v_{\rm s}</math>. |
with <math>k_{\rm D}</math> the absolute value of the wave vector corresponding with the Debye frequency, so <math>k_{\rm D} = \omega_{\rm D}/v_{\rm s}</math>. |
||
Since we know the dispersion relation to be <math>\omega =v_{\rm s}|\mathbf k|</math>, this can be written as an integral over all possible <math> \omega </math> |
Since we know the dispersion relation to be <math>\omega =v_{\rm s}|\mathbf k|</math>, this can be written as an integral over all possible <math> \omega </math> |
||
:<math> \frac {3 V}{2 \pi^2} \int_0^{k_{\rm D}} |\mathbf k|^2 d \mathbf k = \frac {3 V}{2 \pi^2 v_{\rm s}^3} \int_0^{\omega_{\rm D}} \omega^2 d \omega ,</math> |
:<math> \frac {3 V}{2 \pi^2} \int_0^{k_{\rm D}} |\mathbf k|^2 d \mathbf k = \frac {3 V}{2 \pi^2 v_{\rm s}^3} \int_0^{\omega_{\rm D}} \omega^2 d \omega ,</math> |
||
After solving the integral it is again equated to <math>3 N</math> to find |
After solving the integral it is again equated to <math>3 N</math> to find |
||
:<math> \frac {V}{2 \pi^2 v_{\rm s}^3} \omega_{\rm D}^3 = 3 N .</math> |
:<math> \frac {V}{2 \pi^2 v_{\rm s}^3} \omega_{\rm D}^3 = 3 N .</math> |
||
Conclusion: |
Conclusion: |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 =\frac {6 \pi^2 N}{V} v_{\rm s}^3 .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 =\frac {6 \pi^2 N}{V} v_{\rm s}^3 .</math> |
||
====One dimensional chain in 3D space==== |
====One dimensional chain in 3D space==== |
||
The same derivation could be done for a one dimensional chain of atoms. The number of modes remains unchanged, because there are still three polarizations. So |
The same derivation could be done for a one dimensional chain of atoms. The number of modes remains unchanged, because there are still three polarizations. So |
||
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=3 N.</math> |
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=3 N.</math> |
||
The rest of the derivation is analogous to the previous, so again the left hand side is rewritten; |
The rest of the derivation is analogous to the previous, so again the left hand side is rewritten; |
||
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=\frac {3 L}{2 \pi} \int_{-k_{\rm D}}^{k_{\rm D}}d k = \frac {3 L}{\pi v_{\rm s}} \int_{0}^{\omega_{\rm D}}d \omega.</math> |
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=\frac {3 L}{2 \pi} \int_{-k_{\rm D}}^{k_{\rm D}}d k = \frac {3 L}{\pi v_{\rm s}} \int_{0}^{\omega_{\rm D}}d \omega.</math> |
||
In the last step the multiplication by two is because the integrand in the first integral is even and the bounds of integration are symmetric about the origin, so the integral can be rewritten as from 0 to <math>k_D</math> after scaling by a factor of 2. Applying a change a substitution of <math>k=\frac{\omega}{v_s}</math> , our bounds are now 0 to <math>\omega_D = k_Dv_s</math>, which gives us our rightmost integral. |
In the last step the multiplication by two is because the integrand in the first integral is even and the bounds of integration are symmetric about the origin, so the integral can be rewritten as from 0 to <math>k_D</math> after scaling by a factor of 2. Applying a change a substitution of <math>k=\frac{\omega}{v_s}</math> , our bounds are now 0 to <math>\omega_D = k_Dv_s</math>, which gives us our rightmost integral. |
||
We continue; |
We continue; |
||
:<math> \frac {3 L}{\pi v_{\rm s}} \int_{0}^{\omega_{\rm D}}d \omega = \frac {3 L}{\pi v_{\rm s}} \omega_{\rm D} = 3 N .</math> |
:<math> \frac {3 L}{\pi v_{\rm s}} \int_{0}^{\omega_{\rm D}}d \omega = \frac {3 L}{\pi v_{\rm s}} \omega_{\rm D} = 3 N .</math> |
||
Conclusion: |
Conclusion: |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = \frac {\pi v_{\rm s} N}{L} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = \frac {\pi v_{\rm s} N}{L} .</math> |
||
====Two dimensional crystal==== |
====Two dimensional crystal==== |
||
The same derivation could be done for a two dimensional crystal. Again, the number of modes remains unchanged, because there are still three polarizations. The derivation is analogous to the previous two. We start with the same equation, |
The same derivation could be done for a two dimensional crystal. Again, the number of modes remains unchanged, because there are still three polarizations. The derivation is analogous to the previous two. We start with the same equation, |
||
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=3 N.</math> |
:<math>\sum_{\rm modes}3=3 N.</math> |
||
And then the left hand side is rewritten and equated to <math>3N</math> |
And then the left hand side is rewritten and equated to <math>3N</math> |
||
:<math> \sum_{\rm modes}3=\frac {3 A}{(2 \pi)^2} \iint d \mathbf k = \frac {3 A}{2 \pi v_{\rm s}^2} \int_{0}^{\omega_{\rm D}} \omega d \omega = \frac {3 A \omega_{\rm D}^2}{4 \pi v_{\rm s}^2} = 3 N ,</math> |
:<math> \sum_{\rm modes}3=\frac {3 A}{(2 \pi)^2} \iint d \mathbf k = \frac {3 A}{2 \pi v_{\rm s}^2} \int_{0}^{\omega_{\rm D}} \omega d \omega = \frac {3 A \omega_{\rm D}^2}{4 \pi v_{\rm s}^2} = 3 N ,</math> |
||
where <math> A \equiv L^2</math> is the size of the system. |
where <math> A \equiv L^2</math> is the size of the system. |
||
Conclusion |
Conclusion |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {4 \pi N}{A} v_{\rm s}^2 .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {4 \pi N}{A} v_{\rm s}^2 .</math> |
||
| Line 464: | Line 407: | ||
====One dimension==== |
====One dimension==== |
||
Once again the summation over the modes is rewritten |
Once again the summation over the modes is rewritten |
||
:<math> \sum_{i}\sum_{\rm modes} 1 = \sum_i \frac {L}{\pi v_{s,i}} \int_0^{\omega_{\rm D}} d \omega_i = 3 N .</math> |
:<math> \sum_{i}\sum_{\rm modes} 1 = \sum_i \frac {L}{\pi v_{s,i}} \int_0^{\omega_{\rm D}} d \omega_i = 3 N .</math> |
||
The result is |
The result is |
||
:<math> \frac {L \omega_{\rm D}}{\pi} (\frac {1}{v_{s,1}} + \frac {1}{v_{s,2}} + \frac {1}{v_{s,3}}) = 3 N .</math> |
:<math> \frac {L \omega_{\rm D}}{\pi} (\frac {1}{v_{s,1}} + \frac {1}{v_{s,2}} + \frac {1}{v_{s,3}}) = 3 N .</math> |
||
Thus the Debye frequency is found |
Thus the Debye frequency is found |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = \frac {3 \pi N}{L} \frac {v_{s,1} v_{s,2} v_{s,3}}{v_{s,2} v_{s,3} + v_{s,1} v_{s,3} + v_{s,1} v_{s,2}} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = \frac {3 \pi N}{L} \frac {v_{s,1} v_{s,2} v_{s,3}}{v_{s,2} v_{s,3} + v_{s,1} v_{s,3} + v_{s,1} v_{s,2}} .</math> |
||
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations to be the same (to have the same phase speed and frequency) |
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations to be the same (to have the same phase speed and frequency) |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = \frac {3 \pi N}{L} \frac {v_{s,t}v_{s,l}}{2v_{s,l} + v_{s,t}} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D} = \frac {3 \pi N}{L} \frac {v_{s,t}v_{s,l}}{2v_{s,l} + v_{s,t}} .</math> |
||
| Line 483: | Line 422: | ||
====Two dimensions==== |
====Two dimensions==== |
||
The same derivation can be done for a two dimensional crystal to find (the derivation is analogous to previous derivations) |
The same derivation can be done for a two dimensional crystal to find (the derivation is analogous to previous derivations) |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {12 \pi N}{A} \frac {(v_{s,1} v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^2}{(v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^2 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,3})^2 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,2})^2} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {12 \pi N}{A} \frac {(v_{s,1} v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^2}{(v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^2 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,3})^2 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,2})^2} .</math> |
||
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations are equal (although for two dimensions it would be more logical if all polarizations would be different): |
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations are equal (although for two dimensions it would be more logical if all polarizations would be different): |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {12 \pi N}{A} \frac {(v_{s,t} v_{s,l})^2}{2 v_{s,l}^2 + v_{s,t}^2} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^2 = \frac {12 \pi N}{A} \frac {(v_{s,t} v_{s,l})^2}{2 v_{s,l}^2 + v_{s,t}^2} .</math> |
||
| Line 494: | Line 431: | ||
====Three dimensions==== |
====Three dimensions==== |
||
The same derivation can be done for a three dimensional crystal to find (the derivation is analogous to previous derivations) |
The same derivation can be done for a three dimensional crystal to find (the derivation is analogous to previous derivations) |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 = \frac {18 \pi^2 N}{V} \frac {(v_{s,1} v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^3}{(v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^3 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,3})^3 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,2})^3} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 = \frac {18 \pi^2 N}{V} \frac {(v_{s,1} v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^3}{(v_{s,2} v_{s,3})^3 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,3})^3 + (v_{s,1} v_{s,2})^3} .</math> |
||
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations are equal (although for three dimensions it would be more logical when all polarizations would be the same): |
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations are equal (although for three dimensions it would be more logical when all polarizations would be the same): |
||
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 = \frac {18 \pi^2 N}{V} \frac {(v_{s,t} v_{s,l})^3}{2 v_{s,l}^3 + v_{s,t}^3} .</math> |
:<math> \omega_{\rm D}^3 = \frac {18 \pi^2 N}{V} \frac {(v_{s,t} v_{s,l})^3}{2 v_{s,l}^3 + v_{s,t}^3} .</math> |
||
| Line 506: | Line 441: | ||
[[File:phonon k 3k.gif|right|thumb|250px|Because only the [[Discretization|discretized]] points matter, two different waves could render the same physical manifestation (see [[Phonon]]).]] |
[[File:phonon k 3k.gif|right|thumb|250px|Because only the [[Discretization|discretized]] points matter, two different waves could render the same physical manifestation (see [[Phonon]]).]] |
||
This problem could be made more insightful by making it more complex. Instead of using the dispersion relation <math> \omega = v_{\rm s} k </math>, the correct dispersion relation is now going to be assumed. From classical mechanics it is known that for an equidistant chain of masses which interact harmonically with each other the dispersion relation reads as follows<ref name=":0" /> |
This problem could be made more insightful by making it more complex. Instead of using the dispersion relation <math> \omega = v_{\rm s} k </math>, the correct dispersion relation is now going to be assumed. From classical mechanics it is known that for an equidistant chain of masses which interact harmonically with each other the dispersion relation reads as follows<ref name=":0" /> |
||
<math display="block"> \omega (k) = 2 \sqrt {\frac {\kappa}{m}}\left|\sin\left(\frac {k a}{2}\right)\right| .</math> |
<math display="block"> \omega (k) = 2 \sqrt {\frac {\kappa}{m}}\left|\sin\left(\frac {k a}{2}\right)\right| .</math> |
||
Revision as of 23:17, 1 October 2022
This article's tone or style may not reflect the encyclopedic tone used on Wikipedia. (March 2021) |

| Statistical mechanics |
|---|
 |
In thermodynamics and solid-state physics, the Debye model is a method developed by Peter Debye in 1912 for estimating the phonon contribution to the specific heat (Heat capacity) in a solid.[1] It treats the vibrations of the atomic lattice (heat) as phonons in a box, in contrast to the Einstein photoelectron model, which treats the solid as many individual, non-interacting quantum harmonic oscillators. The Debye model correctly predicts the low-temperature dependence of the heat capacity of solids, which is proportional to – the Debye T3 law. Just like the Einstein photoelectron model, it also recovers the Dulong–Petit law at high temperatures. But due to simplifying assumptions, its accuracy suffers at intermediate temperatures.
Derivation
The Debye model is a solid-state equivalent of Planck's law of black-body radiation, where one treats electromagnetic radiation as a photon gas. The Debye model treats atomic vibrations as phonons in a box (the box being the solid). Most of the calculation steps are identical as both are examples of a massless Bose gas with linear dispersion relation.
Consider a cube of side . From the particle in a box article, the resonating modes of the sonic disturbances inside the box (considering for now only those aligned with one axis) have wavelengths given by
where is an integer. The energy of a phonon is
where is the Planck constant and is the frequency of the phonon. Making the approximation that the frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength, we have
in which is the speed of sound inside the solid. In three dimensions we will use
in which is the magnitude of the three-dimensional momentum of the phonon.
The approximation that the frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength (giving a constant speed of sound) is good for low-energy phonons but not for high-energy phonons. This disagreement is one of the limitations of the Debye model. It produces incorrect results at intermediate temperatures, whereas the results are exact at the low and high temperatures limits.
Let's now compute the total energy in the box,
where is the number of phonons in the box with energy . In other words, the total energy is equal to the sum of energy multiplied by the number of phonons with that energy (in one dimension). In 3 dimensions we have:
Here, the Debye model and Planck's law of black-body radiation differ. Unlike electromagnetic radiation in a box, there is a finite number of phonon energy states because a phonon cannot have arbitrarily high frequencies. Its frequency is bounded by the medium of its propagation—the atomic lattice of the solid. Consider an illustration of a transverse phonon below.
It is reasonable to assume that the minimum wavelength of a phonon is twice the atom separation, as shown in the lower figure. There are atoms in a solid. Our solid is a cube, which means there are atoms per edge. Atom separation is then given by , and the minimum wavelength is
making the maximum mode number (infinite for photons)
This number bounds the upper limit of the triple energy sum
For slowly varying, well-behaved functions, a sum can be replaced with an integral (also known as Thomas–Fermi approximation)
So far, there has been no mention of , the number of phonons with energy Phonons obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Their distribution is given by the famous Bose–Einstein statistics formula
Because a phonon has three possible polarization states (one longitudinal, and two transverse, which approximately do not affect its energy) the formula above must be multiplied by 3,
Actually one uses an effective sonic velocity , i.e. the Debye temperature (see below) is proportional to , more precisely , where one distinguishes longitudinal and transversal sound-wave velocities (contributions 1/3 and 2/3, respectively). The Debye temperature or the effective sonic velocity is a measure of the hardness of the crystal.
Substituting into the energy integral yields
The ease with which these integrals are evaluated for photons is due to the fact that light's frequency, at least semi-classically, is unbound. As the figure above illustrates, this is not true for phonons. In order to approximate this triple integral, Debye used spherical coordinates.
and approximated the cube by an eighth of a sphere
where is the radius of this sphere, which is found by conserving the number of particles in the cube and in the eighth of a sphere. The volume of the cube is unit-cell volumes,
so we get
The substitution of integration over a sphere for the correct integral introduces another source of inaccuracy into the model.
The energy integral becomes
- .
Changing the integration variable to ,
To simplify the appearance of this expression, define the Debye temperature
where is the volume of the cubic box of side .
Many references[2][3] describe the Debye temperature as merely shorthand for some constants and material-dependent variables. However, as shown below, is roughly equal to the phonon energy of the minimum wavelength mode, and so we can interpret the Debye temperature as the temperature at which the highest-frequency mode (and hence every mode) is excited.
Continuing, we then have the specific internal energy:
where is the (third) Debye function.
Differentiating with respect to we get the dimensionless heat capacity:
These formulae treat the Debye model at all temperatures. The more elementary formulae given further down give the asymptotic behavior in the limit of low and high temperatures. As already mentioned, this behavior is exact, in contrast to the intermediate behavior. The essential reason for the exactness at low and high energies, respectively, is that the Debye model gives (i) the exact dispersion relation at low frequencies, and (ii) corresponds to the exact density of states , concerning the number of vibrations per frequency interval.
Debye's derivation
Debye derived his equation somewhat differently and more simply. Using continuum mechanics, he found that the number of vibrational states with a frequency less than a particular value was asymptotic to
in which is the volume and is a factor which he calculated from elasticity coefficients and density. Combining this formula with the expected energy of a harmonic oscillator at temperature T (already used by Einstein in his model) would give an energy of
if the vibrational frequencies continued to infinity. This form gives the behaviour which is correct at low temperatures. But Debye realized that there could not be more than vibrational states for N atoms. He made the assumption that in an atomic solid, the spectrum of frequencies of the vibrational states would continue to follow the above rule, up to a maximum frequency chosen so that the total number of states is
Debye knew that this assumption was not really correct (the higher frequencies are more closely spaced than assumed), but it guarantees the proper behaviour at high temperature (the Dulong–Petit law). The energy is then given by
Substituting for ,
where is the function later given the name of third-order Debye function.
Another derivation
First we derive the vibrational frequency distribution; the following derivation is based on Appendix VI from.[4] Consider a three-dimensional isotropic elastic solid with N atoms in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped with side-lengths . The elastic wave will obey the wave equation and will be plane waves; consider the wave vector and define . Note that we have
| (1) |
Solutions to the wave equation are
and with the boundary conditions at , we have
| (2) |
where are positive integers. Substituting (2) into (1) and also using the dispersion relation , we have
The above equation, for fixed frequency , describes an eighth of an ellipse in "mode space" (an eighth because are positive). The number of modes with frequency less than is thus the number of integral points inside the ellipse, which, in the limit of (i.e. for a very large parallelepiped) can be approximated to the volume of the ellipse. Hence, the number of modes with frequency in the range is
| (3) |
where is the volume of the parallelepiped. Note that the wave speed in the longitudinal direction is different from the transverse direction and that the waves can be polarised one way in the longitudinal direction and two ways in the transverse direction; thus we define .
Following the derivation from,[5] we define an upper limit to the frequency of vibration ; since there are N atoms in the solid, there are 3N quantum harmonic oscillators (3 for each x-, y-, z- direction) oscillating over the range of frequencies . Hence we can determine using
| . | (4) |
By defining , where k is the Boltzmann constant and h is the Planck constant, and substituting (4) into (3), we get
| (5) |
this definition is more standard. We can find the energy contribution for all oscillators oscillating at frequency . Quantum harmonic oscillators can have energies where and using Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics, the number of particles with energy is
The energy contribution for oscillators with frequency is then
| . | (6) |
By noting that (because there are modes oscillating with frequency ), we have
From above, we can get an expression for 1/A; substituting it into (6), we have
Integrating with respect to ν yields
Low-temperature limit
The temperature of a Debye solid is said to be low if , leading to
This definite integral can be evaluated exactly:
In the low-temperature limit, the limitations of the Debye model mentioned above do not apply, and it gives a correct relationship between (phononic) heat capacity, temperature, the elastic coefficients, and the volume per atom (the latter quantities being contained in the Debye temperature).
High-temperature limit
The temperature of a Debye solid is said to be high if . Using if leads to
where
This is the Dulong–Petit law, and is fairly accurate although it does not take into account anharmonicity, which causes the heat capacity to rise further. The total heat capacity of the solid, if it is a conductor or semiconductor, may also contain a non-negligible contribution from the electrons.
Debye versus Einstein

So how closely do the Debye and Einstein models correspond to the experiment? Surprisingly close, but Debye is correct at low temperatures whereas Einstein is not.
How different are the models? To answer that question, one would naturally plot the two on the same set of axes... except one can't. Both the Einstein model and the Debye model provide a functional form for the heat capacity. They are models, and no model is without a scale. A scale relates the model to its real-world counterpart. One can see that the scale of the Einstein model, which is given by
The scale of the Debye model is , the Debye temperature. Both are usually found by fitting the models to the experimental data. (The Debye temperature can theoretically be calculated from the speed of sound and crystal dimensions.) Because the two methods approach the problem from different directions and different geometries, Einstein and Debye scales are not the same, that is to say
which means that plotting them on the same set of axes makes no sense. They are two models of the same thing, but of different scales. If one defines Einstein condensation temperature as
then one can say
and, to relate the two, we must seek the ratio
The Einstein solid is composed of single-frequency quantum harmonic oscillators, . That frequency, if it indeed existed, would be related to the speed of sound in the solid. If one imagines the propagation of sound as a sequence of atoms hitting one another, then it becomes obvious that the frequency of oscillation must correspond to the minimum wavelength sustainable by the atomic lattice, . Where
which makes the Einstein temperature
and the sought ratio is therefore
Now both models can be plotted on the same graph. Note that this ratio is the cube root of the ratio of the volume of one octant of a 3-dimensional sphere to the volume of the cube that contains it, which is just the correction factor used by Debye when approximating the energy integral above.
Alternately the ratio of the two temperatures can be seen to be the ratio of Einstein's single frequency at which all oscillators oscillate and Debye's maximum frequency. Einstein's single frequency can then be seen to be a mean of the frequencies available to the Debye model.
Debye temperature table
Even though the Debye model is not completely correct, it gives a good approximation for the low temperature heat capacity of insulating, crystalline solids where other contributions (such as highly mobile conduction electrons) are negligible. For metals, the electron contribution to the heat is proportional to , which at low temperatures dominates the Debye result for lattice vibrations. In this case, the Debye model can only be said to approximate the lattice contribution to the specific heat. The following table lists Debye temperatures for several pure elements[2] and sapphire:
|
|
|
|
The Debye model's fit to experimental data is often phenomenologically improved by allowing the Debye temperature to become temperature dependent;[6] for example, the value for water ice increases from about 222 K[7] to 300 K[8] as the temperature goes from absolute zero to about 100 K.
Extension to other quasi-particles
For other bosonic quasi-particles, e.g., for magnons (quantized spin waves) in ferromagnets instead of the phonons (quantized sound waves) one can derive analogous results. In this case at low frequencies one has different dispersion relations of momentum and energy, e.g., in the case of magnons, instead of for phonons (with ). One also has different density of states (e.g., ). As a consequence, in ferromagnets one gets a magnon contribution to the heat capacity, , which dominates at sufficiently low temperatures the phonon contribution, . In metals, in contrast, the main low-temperature contribution to the heat capacity, , comes from the electrons. It is fermionic, and is calculated by different methods going back to Sommerfeld's free electron model.
Extension to liquids
It was long thought that phonon theory is not able to explain the heat capacity of liquids, since liquids only sustain longitudinal, but not transverse phonons, which in solids are responsible for 2/3 of the heat capacity. However, Brillouin scattering experiments with neutrons and with X-rays, confirming an intuition of Yakov Frenkel,[9] have shown that transverse phonons do exist in liquids, albeit restricted to frequencies above a threshold called the Frenkel frequency. Since most energy is contained in these high-frequency modes, a simple modification of the Debye model is sufficient to yield a good approximation to experimental heat capacities of simple liquids.[10]
Debye frequency
This section may require copy editing. (May 2022) |
The Debye frequency (Symbol: or ) is a parameter in the Debye model. It refers to a cut-off angular frequency for waves of a harmonic chain of masses, used to describe the movement of ions in a crystal lattice and more specifically, to correctly predict the heat capacity in such crystals to be constant for high temperatures (Dulong–Petit law). The term was first introduced by Peter Debye in 1912.[11]
Throughout this whole article periodic boundary conditions are assumed.
Definition
Assuming the dispersion relation is
with the speed of sound in the crystal; and k the wave vector, the value of the Debye frequency is as follows:
For a one dimensional monatomic chain the Debye frequency is equal to[12]
with the distance between two neighbouring atoms in the chain when the system is in its ground state of energy (in this case that means that none of the atoms are moving with respect to each other); the total number of atoms in the chain; and the size (volume) of the system (length of the chain); and is the linear number density. Where the following relation holds: .
For a two dimensional monatomic square lattice the Debye frequency is equal to
where and are the same as before; is the size (area) of the surface; and the surface number density.
For a three dimensional monatomic primitive cubic crystal, the Debye frequency is equal to[13]
where and are the same as before; the size of the system; and the volume number density.
The speed of sound in the crystal could depend on (among others) the mass of the atoms, the strength of their interaction, the pressure on the system, and/or the polarization of the spin wave (longitudinal or transverse), but in the following we will first assume the speed of sound to be the same for any polarization (this assumption however does not render far-reaching implications).[14]
The assumed dispersion relation is easily proven wrong for a one-dimensional chain of masses, but in Debye's model this did not prove to be problematic.
Relation to Debye's temperature
The Debye temperature , another parameter in Debye model, is related to the Debye frequency by the relation where is the reduced Planck constant and is the Boltzmann constant.
Debye's derivation
Three dimensional crystal
In Debye's derivation of the heat capacity he sums over all possible modes of the system. That is: including different directions and polarizations. He assumed the total number of modes per polarization to be (with the amount of masses in the system), or in mathematical language[14]
where the on both sides is because of the three polarizations, so the sum runs over all modes for one specific polarization. Debye made this assumption because he knew from classical mechanics that the number of modes per polarization in a chain of masses should always be equal to the amount of masses in the chain.
The left hand side is now to be made explicit to show how it depends on the Debye frequency (here simply introduced as a cut-off frequency, that is: higher frequencies than the Debye frequency cannot exist), so that an expression for it could be found.
First of all, by assuming to be very large (>>1, with the size of the system in any of the three directions) the smallest wave vector in any direction could be approximated by: , with . Smaller wave vectors cannot exist because of the periodic boundary conditions. Thus the summation would become 4
where ; is the size of the system; and the integral is (as the summation) over all possible modes, which is assumed to be a finite region (bounded by the cut-off frequency).
The triple integral could be rewritten as a single integral over all possible values of the absolute value of (see: Jacobian for spherical coordinates). The result is
with the absolute value of the wave vector corresponding with the Debye frequency, so .
Since we know the dispersion relation to be , this can be written as an integral over all possible
After solving the integral it is again equated to to find
Conclusion:
One dimensional chain in 3D space
The same derivation could be done for a one dimensional chain of atoms. The number of modes remains unchanged, because there are still three polarizations. So
The rest of the derivation is analogous to the previous, so again the left hand side is rewritten;
In the last step the multiplication by two is because the integrand in the first integral is even and the bounds of integration are symmetric about the origin, so the integral can be rewritten as from 0 to after scaling by a factor of 2. Applying a change a substitution of , our bounds are now 0 to , which gives us our rightmost integral. We continue;
Conclusion:
Two dimensional crystal
The same derivation could be done for a two dimensional crystal. Again, the number of modes remains unchanged, because there are still three polarizations. The derivation is analogous to the previous two. We start with the same equation,
And then the left hand side is rewritten and equated to
where is the size of the system.
Conclusion
Allowing polarization to make a difference
As mentioned in the introduction: in general, longitudinal waves have a different wave velocity than transverse waves. For clarity they were first assumed to be equal, but now we drop that assumption.
The dispersion relation becomes , where , which correspond to the three polarizations. The cut-off frequency (Debye frequency) however does not depend on . And we can write the total number of modes as , which is again equal to . Here the summation over the modes is (although not explicitly stated) dependent on .
One dimension
Once again the summation over the modes is rewritten
The result is
Thus the Debye frequency is found
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations to be the same (to have the same phase speed and frequency)
One can check this relation is equivalent to the one found earlier (when polarization did not make a difference) by setting .
Two dimensions
The same derivation can be done for a two dimensional crystal to find (the derivation is analogous to previous derivations)
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations are equal (although for two dimensions it would be more logical if all polarizations would be different):
Again, one can check this relation is equivalent to the one found earlier by setting .
Three dimensions
The same derivation can be done for a three dimensional crystal to find (the derivation is analogous to previous derivations)
Or by assuming the two transverse polarizations are equal (although for three dimensions it would be more logical when all polarizations would be the same):
Again, one can check this relation is equivalent to the one found earlier by setting .
Derivation with the actual dispersion relation
This problem could be made more insightful by making it more complex. Instead of using the dispersion relation , the correct dispersion relation is now going to be assumed. From classical mechanics it is known that for an equidistant chain of masses which interact harmonically with each other the dispersion relation reads as follows[14]
After plotting this relation, it is clear that Debye's estimation of the cut-off wavelength was right after all. Because for every wavenumber bigger than (that is: is smaller than ) a wavenumber that is smaller than could be found with the same angular frequency. This means the resulting physical manifestation for the mode with the larger wavenumber is indistinguishable from the one with the smaller wavenumber. Thereby, the study of the dispersion relation can be limited to the first brillouin zone[15] i.e. for .This is possible because the system consists of discretized points, as is demonstrated in the animated picture. Dividing the dispersion relation by and inserting for , we find the speed of a wave with to be
By simply inserting in the original dispersion relation we find
Combining these results the same result is once again found
However, for diatomic chains (and more complex chains) the associated cut-off frequency (and wavelength) is not very accurate, since the cut-off wavelength is twice as big and the dispersion relation consists of two branches (for a diatomic chain). It is also not certain from this whether for more dimensional systems the cut-off frequency was accurately predicted by Debye.
Alternative derivation
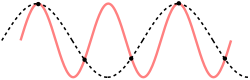
For a one dimensional chain this result could also be reproduced using theory on aliasing. The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is used in the following derivation; the main difference being that in the following derivation the discretization is not in time, but in space. If we use the correct dispersion relation from last paragraph, it will be clear in another insightful way why the cut-off frequency has the value previously (twice) derived. So again, is assumed.
This derivation is completely equivalent to the previous one, that is: the same assumptions are made to retrieve the result. It is not more or less accurate, it is just a different approach.
To determine where the cut-off frequency should be, it is useful to first determine where the cut-off of the wavelength should be. From the dispersion relation we know that for every mode is repeated, so the cut-off wavelength would be at . From this and the periodic boundary conditions you can immediately see that the total number of modes per polarization would be . As seen in the gif of the previous paragraph this is because every wave with a wavelength shorter than could be replaced by a wave with a wavelength longer than to regain the same physical result.
However, the dispersion relation from previous paragraph (the correct one) is not even necessary in reasoning as to why the cut-off should be at . Because, as is depicted, only waves with a longer wavelength than could render the same physical result as another one. So this is another way to correctly predict the cut-off wavelength of phonons without using the correct dispersion relation (or even knowledge from classical mechanics as Debye did). However, using the wrong dispersion relation which Debye assumed, waves with a smaller wavelength would have a higher frequency, but the relative movement of the masses would be the same, so this does not render new modes.
This results again in , rendering
Also here it does not matter which dispersion relation is used (the correct one or the one Debye used), the same cut-off frequency would be found.
Unfortunately, the same method could not be used (as easily) for a two- or three-dimensional crystal, because diagonal waves would have a larger cut-off wavelength, which are also difficult to predict.
See also
References
- ^ Debye, Peter (1912). "Zur Theorie der spezifischen Waerme". Annalen der Physik (in German). 39 (4): 789–839. Bibcode:1912AnP...344..789D. doi:10.1002/andp.19123441404.
- ^ a b Kittel, Charles (2004). Introduction to Solid State Physics (8 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0471415268.
- ^ Schroeder, Daniel V. "An Introduction to Thermal Physics" Addison-Wesley, San Francisco (2000). Section 7.5
- ^ Hill, Terrell L. (1960). An Introduction to Statistical Mechanics. Reading, Massachusetts, U.S.A.: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 9780486652429.
- ^ Oberai, M. M.; Srikantiah, G (1974). A First Course in Thermodynamics. New Delhi, India: Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited. ISBN 9780876920183.
- ^ Patterson, James D; Bailey, Bernard C. (2007). Solid-State Physics: Introduction to the Theory. Springer. pp. 96–97. ISBN 978-3-540-34933-4.
- ^ Shulman, L. M. (2004). "The heat capacity of water ice in interstellar or interplanetary conditions". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 416: 187–190. Bibcode:2004A&A...416..187S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031746.
- ^ Flubacher, P.; Leadbetter, A. J.; Morrison, J. A. (1960). "Heat Capacity of Ice at Low Temperatures". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 33 (6): 1751. Bibcode:1960JChPh..33.1751F. doi:10.1063/1.1731497.
- ^ In his textbook Kinetic Theory of Liquids (engl. 1947)
- ^ Bolmatov, D.; Brazhkin, V. V.; Trachenko, K. (2012). "The phonon theory of liquid thermodynamics". Scientific Reports. 2: 421. arXiv:1202.0459. Bibcode:2012NatSR...2E.421B. doi:10.1038/srep00421. PMC 3359528. PMID 22639729.
- ^ Debye, P. (1912). "Zur Theorie der spezifischen Wärmen". Annalen der Physik. 344 (14): 789–839. Bibcode:1912AnP...344..789D. doi:10.1002/andp.19123441404. ISSN 1521-3889.
- ^ "The one dimensional monatomic solid" (PDF). Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Richard (2006). "Specific heats of solids". Richard Fitzpatrick University of Texas at Austin. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- ^ a b c Simon, Steven H. (2013-06-20). The Oxford Solid State Basics (First ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199680764. OCLC 859577633.
- ^ Srivastava, G. P. (2019-07-16). The Physics of Phonons. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-40955-1.
Further reading
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 56th Edition (1975–1976)
- Schroeder, Daniel V. An Introduction to Thermal Physics. Addison-Wesley, San Francisco (2000). Section 7.5.

















![{\displaystyle {\sqrt[{3}]{N}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2632439311fdaac0db5c94be22a66bc4759c3b3e)
![{\displaystyle L/{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/68ce3128288fa487eb59b377703ca3c31b6ac01d)
![{\displaystyle \lambda _{\rm {min}}={2L \over {\sqrt[{3}]{N}}}\,,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/67ce39568ba1619356396b79fafe20ab2a5b958f)
![{\displaystyle n_{\rm {max}}={\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\,.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/52e26b34255058c420ca488f519532157f051097)
![{\displaystyle U=\sum _{n_{x}}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\sum _{n_{y}}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\sum _{n_{z}}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}E_{n}\,{\bar {N}}(E_{n})\,.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fec6d96639ee52ea7d4e59bc75e719fe094fd5ce)
![{\displaystyle U\approx \int _{0}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\int _{0}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\int _{0}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}E(n)\,{\bar {N}}\left(E(n)\right)\,dn_{x}\,dn_{y}\,dn_{z}\,.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4f378b750c04cde69b47b010798779902e74825b)








![{\displaystyle U=\int _{0}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\int _{0}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}\int _{0}^{\sqrt[{3}]{N}}E(n)\,{3 \over e^{E(n)/kT}-1}\,dn_{x}\,dn_{y}\,dn_{z}\,.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2b05660b876347cc0556fce9c94b050d78867006)




![{\displaystyle R={\sqrt[{3}]{6N \over \pi }}\,.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3f9d4e2bc889e4df97cb5eb25a732323e6d7dbd1)



![{\displaystyle T_{\rm {D}}\ {\stackrel {\mathrm {def} }{=}}\ {hc_{\rm {s}}R \over 2Lk}={hc_{\rm {s}} \over 2Lk}{\sqrt[{3}]{6N \over \pi }}={hc_{\rm {s}} \over 2k}{\sqrt[{3}]{{6 \over \pi }{N \over V}}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1c33435797dd4eb7e671cab70fe5b0248b2b25b9)
































![{\displaystyle [0,\nu ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f3da4e6ef6d591bf2a9654be4fb845ce59a91551)




![{\displaystyle [0,\nu _{D}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f9a2adfa6354fb9930ff419a40f847263676830c)





























![{\displaystyle \nu ={c_{\rm {s}} \over \lambda }={c_{\rm {s}}{\sqrt[{3}]{N}} \over 2L}={c_{\rm {s}} \over 2}{\sqrt[{3}]{N \over V}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9407be4ecc89870f5aa05915f57ff4dd1bb9d428)
![{\displaystyle T_{\rm {E}}={\epsilon \over k}={h\nu \over k}={hc_{\rm {s}} \over 2k}{\sqrt[{3}]{N \over V}}\,,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4e04158867129c173bc190d9c60e4d6422c382ed)
![{\displaystyle {T_{\rm {E}} \over T_{\rm {D}}}={\sqrt[{3}]{\pi \over 6}}\ =0.805995977...}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fb2c9648e406d584fff25220a7a9593260228d6d)




































































![{\textstyle k\in \left[-{\frac {\pi }{a}},{\frac {\pi }{a}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/eb2af5d36cadc62bdb9cae6ad2bc70e6a7460e20)









