Self-sovereign identity: Difference between revisions
Addition of academic references that pertain to the main concerns associated with SSI. |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
=== Korea === |
=== Korea === |
||
The Korean government created a public/private consortia specifically for decentralized identity.<ref>{{Cite web |last=협회입니다 |first=한국디지털인증협회는 디지털신원증명의 진본성과 신뢰성을 확고히 하는 디지털 신원 인증 서비스를 위해 설립된 오픈 산업 |title=한국디지털인증협회 |url=http://www.didalliance.org/ |access-date=2022-08-12 |website=한국디지털인증협회 |language=ko}}</ref> |
The Korean government created a public/private consortia specifically for decentralized identity.<ref>{{Cite web |last=협회입니다 |first=한국디지털인증협회는 디지털신원증명의 진본성과 신뢰성을 확고히 하는 디지털 신원 인증 서비스를 위해 설립된 오픈 산업 |title=한국디지털인증협회 |url=http://www.didalliance.org/ |access-date=2022-08-12 |website=한국디지털인증협회 |language=ko}}</ref> |
||
== Concerns == |
|||
=== Implementation and semantic confusion === |
|||
SSI is a value laden technology whose technical operationalizations differ (see Technical aspects).<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Sedlmeir |first=Johannes |last2=Smethurst |first2=Reilly |last3=Rieger |first3=Alexander |last4=Fridgen |first4=Gilbert |date=2021-10-01 |title=Digital Identities and Verifiable Credentials |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-021-00722-y |journal=Business & Information Systems Engineering |language=en |volume=63 |issue=5 |pages=603–613 |doi=10.1007/s12599-021-00722-y |issn=1867-0202 |pmc=PMC8488925}}</ref> Therefore, it's implementations can vary significantly and embed into the very technology different goals, agenda, and intentions.<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |last=Weigl |first=Linda |last2=Barbereau |first2=Tom |last3=Rieger |first3=Alexander |last4=Fridgen |first4=Gilbert |date=2022 |title=The Social Construction of Self-Sovereign Identity: An Extended Model of Interpretive Flexibility |url=http://hdl.handle.net/10125/79649 |journal=Proceedings of the 55th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences |doi=10.24251/HICSS.2022.316}}</ref> |
|||
The term "self-sovereign identity" can create expectations that individuals have absolute control and ownership over their digital identities, akin to physical possessions. However, in practice, SSI involves complex technical infrastructure, interactions with identity issuers and verifiers, and compliance with legal frameworks. The reality may not align with the perception generated by the term, leading to semantic confusion.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Smethurst |first=Reilly |date=2023 |title=Digital Identity Wallets and their Semantic Contradictions |url=https://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2023_rp/288/ |journal=Proceedings of the 31st European Conference on Information Systems |via=AIS Library}}</ref> |
|||
=== Digital literacy === |
|||
Critics argue that SSI may exacerbate social inequalities and exclude those with limited access to technology or digital literacy.<ref name=":1" /><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Giannopoulou |first=Alexandra |date=2023-05-11 |title=Digital Identity Infrastructures: a Critical Approach of Self-Sovereign Identity |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s44206-023-00049-z |journal=Digital Society |language=en |volume=2 |issue=2 |pages=18 |doi=10.1007/s44206-023-00049-z |issn=2731-4669 |pmc=PMC10172062 |pmid=37200582}}</ref> SSI assumes reliable internet connectivity, access to compatible devices, and proficiency in navigating digital systems. Consequently, marginalized populations, including the elderly, individuals in developing regions, or those with limited technological resources, may face exclusion and reduced access to the benefits of SSI. |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 08:02, 26 June 2023
This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. (June 2020) |

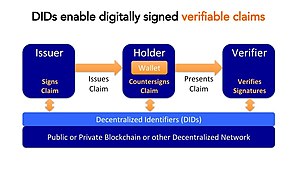
Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is an approach to digital identity that gives individuals control over the information they use to prove who they are to websites, services, and applications across the web. Without SSI, individuals with persistent accounts (identities) across the internet must rely on a number of large identity providers, such as Facebook (Facebook Connect) and Google (Google Sign-In), that have control of the information associated with their identity.[2] If a user chooses not to use a large identity provider, then they have to create new accounts with each service provider, which fragments their web experiences. Self-sovereign identity offers a way to avoid these two undesirable alternatives. In a self-sovereign identity system, the user accesses services in a streamlined and secure manner, while maintaining control over the information associated with their identity.[3][4]
Background
The TCP/IP protocol provides identifiers for machines, but not for the people and organisations operating the machines. This makes the network-level identifiers on the internet hard to trust and rely on for information and communication for a number of reasons: 1) hackers can easily change a computer’s hardware or IP address, 2) services provide identifiers for the user, not the network. The absence of reliable identifiers is one of the primary sources of cybercrime, fraud, and threats to privacy on the internet.[5]
With the advent of blockchain technology, a new model for decentralized identity emerged in 2015.[6] The FIDO Alliance proposed an identity model that was no longer account-based, but identified people through direct, private, peer-to-peer connections secured by public/private key cryptography. Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) summarises all components of the decentralized identity model: digital wallets, digital credentials, and digital connections.[7]
Technical aspects
SSI addresses the difficulty of establishing trust in an interaction. In order to be trusted, one party in an interaction will present credentials to the other parties, and those relying on parties can verify that the credentials came from an issuer that they trust. In this way, the verifier's trust in the issuer is transferred to the credential holder.[8] This basic structure of SSI with three participants is sometimes called "the trust triangle".[7]
It is generally recognized that for an identity system to be self-sovereign, users control the verifiable credentials that they hold and their consent is required to use those credentials.[9] This reduces the unintended sharing of users' personal data. This is contrasted with the centralized identity paradigm where identity is provided by some outside entity.[10]
In an SSI system, holders generate and control unique identifiers called decentralized identifiers. Most SSI systems are decentralized, where the credentials are managed using crypto wallets and verified using public-key cryptography anchored on a distributed ledger.[11] The credentials may contain data from an issuer's database, a social media account, a history of transactions on an e-commerce site, or attestation from friends or colleagues.
National digital identity systems
European Union

The European Union is exploring decentralized digital identity through a number of initiatives including the International Association for Trusted Blockchain Application (INATBA) , the EU Blockchain Observatory & Forum and the European SSI Framework. In 2019 the EU created an eIDAS compatible European Self-Sovereign Identity Framework (ESSIF). The ESSIF makes use of decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and the European Blockchain Services Infrastructure (EBSI).[12][13]
Korea
The Korean government created a public/private consortia specifically for decentralized identity.[14]
Concerns
Implementation and semantic confusion
SSI is a value laden technology whose technical operationalizations differ (see Technical aspects).[15] Therefore, it's implementations can vary significantly and embed into the very technology different goals, agenda, and intentions.[16]
The term "self-sovereign identity" can create expectations that individuals have absolute control and ownership over their digital identities, akin to physical possessions. However, in practice, SSI involves complex technical infrastructure, interactions with identity issuers and verifiers, and compliance with legal frameworks. The reality may not align with the perception generated by the term, leading to semantic confusion.[17]
Digital literacy
Critics argue that SSI may exacerbate social inequalities and exclude those with limited access to technology or digital literacy.[16][18] SSI assumes reliable internet connectivity, access to compatible devices, and proficiency in navigating digital systems. Consequently, marginalized populations, including the elderly, individuals in developing regions, or those with limited technological resources, may face exclusion and reduced access to the benefits of SSI.
References
- ^ "Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^ Windley, Phillip J. (2021). "Sovrin: An Identity Metasystem for Self-Sovereign Identity". Frontiers in Blockchain. 4. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2021.626726.
- ^ "Verifiable Claims Working Group Frequently Asked Questions". World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). 12 August 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Ferdous, Md Sadek; Chowdhury, Farida; Alassafi, Madini O. (2019). "In Search of Self-Sovereign Identity Leveraging Blockchain Technology". IEEE Access. 7: 103059–103079. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931173. ISSN 2169-3536.
- ^ Preukschat, Alexander (2021). Self-sovereign identity : decentralized digital identity and verifiable credentials. Drummond Reed, Christopher Allen, Fabian Vogelsteller, Doc Searls. Shelter Island, NY. ISBN 978-1-63835-102-3. OCLC 1275443730.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "History (2010-2014) Personal Data: Emergence of a New Assets Class". Decentralized Identity Web Directory. 2020-01-02. Retrieved 2022-08-12.
- ^ a b Reed, Drummond; Preukschat, Alex (2021). Self-Sovereign Identity. Manning. p. Chapter 2. ISBN 9781617296598.
- ^ Mühle, Alexander; Grüner, Andreas; Gayvoronskaya, Tatiana; Meinel, Christoph (2018). "A survey on essential components of a self-sovereign identity". Computer Science Review. 30 (1): 80–86. arXiv:1807.06346. doi:10.1016/j.cosrev.2018.10.002. S2CID 49867601.
- ^ Allen, Christopher (April 25, 2016). "The Path to Self-Sovereign Identity". Life With Alacrity. Retrieved February 19, 2021.
Users must control their identities.… Users must agree to the use of their identity.
- ^ "eIDAS supported self-sovereign identity" (PDF). European Commission. May 2019. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- ^ "Blockchain and digital identity" (PDF). eublockchainforum.eu. 2 May 2019. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- ^ "Understanding the European Self-Sovereign Identity Framework (ESSIF)". ssimeetup.org. 7 July 2019. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ^ "European Blockchain Services Infrastructure (EBSI)". European Commission. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ 협회입니다, 한국디지털인증협회는 디지털신원증명의 진본성과 신뢰성을 확고히 하는 디지털 신원 인증 서비스를 위해 설립된 오픈 산업. "한국디지털인증협회". 한국디지털인증협회 (in Korean). Retrieved 2022-08-12.
- ^ Sedlmeir, Johannes; Smethurst, Reilly; Rieger, Alexander; Fridgen, Gilbert (2021-10-01). "Digital Identities and Verifiable Credentials". Business & Information Systems Engineering. 63 (5): 603–613. doi:10.1007/s12599-021-00722-y. ISSN 1867-0202. PMC 8488925.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ^ a b Weigl, Linda; Barbereau, Tom; Rieger, Alexander; Fridgen, Gilbert (2022). "The Social Construction of Self-Sovereign Identity: An Extended Model of Interpretive Flexibility". Proceedings of the 55th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. doi:10.24251/HICSS.2022.316.
- ^ Smethurst, Reilly (2023). "Digital Identity Wallets and their Semantic Contradictions". Proceedings of the 31st European Conference on Information Systems – via AIS Library.
- ^ Giannopoulou, Alexandra (2023-05-11). "Digital Identity Infrastructures: a Critical Approach of Self-Sovereign Identity". Digital Society. 2 (2): 18. doi:10.1007/s44206-023-00049-z. ISSN 2731-4669. PMC 10172062. PMID 37200582.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC format (link)
