Two- and four-stroke engines: Difference between revisions
m minor tidy up |
added working cycles description |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<!-- End of AfD message, feel free to edit beyond this point --> |
<!-- End of AfD message, feel free to edit beyond this point --> |
||
{{expert}} |
{{expert}} |
||
''' The M4+2 engine ''', also known as the double piston |
''' The M4+2 engine ''', also known as the double piston internal [[combustion]] engine, is a new type of [[combustion engine]] invented by a Polish patent holder [[Piotr Mężyk]] in the year 1999. |
||
The M4+2 engine took its name from a combination of the two working modes of the known engines, that is from the [[Two-stroke engine]] and [[Four-stroke engine]]. In the M4+2 the advantages of both engines being connected are obvious; the [[piston|pistons]] of the engine working in one [[combustion]] [[cylinder]] are set oppositely to each other, but in different modes. Although the projects of connecting two stroke modes in one cylinder were tried already a long time ago - [[Opposed piston engine]], the combination of the two different cycles had never been tried before. It turned out that the engine is not only able to work, but that the effects are very promising. The engine has a far greater efficiency over the break-even value known to combustion engines (ca 35%) and closer to the one associated with [[steam turbines]] or [[electric engines]] (ca 70%). The other advantages are as follows: |
The M4+2 engine took its name from a combination of the two working modes of the known engines, that is from the [[Two-stroke engine]] and [[Four-stroke engine]]. In the M4+2 the advantages of both engines being connected are obvious; the [[piston|pistons]] of the engine working in one [[combustion]] [[cylinder]] are set oppositely to each other, but in different modes. Although the projects of connecting two stroke modes in one cylinder were tried already a long time ago - [[Opposed piston engine]], the combination of the two different cycles had never been tried before. It turned out that the engine is not only able to work, but that the effects are very promising. The engine has a far greater efficiency over the break-even value known to combustion engines (ca 35%) and closer to the one associated with [[steam turbines]] or [[electric engines]] (ca 70%). The other advantages are as follows: |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<ol> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
</ol> |
|||
<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
The idea was developed at the [[Silesian University of Technology]], Poland, under the leadership of dr [[Adam Ciesiołkiewicz]]. It was granted a [[patent]] nr 195052 by the Polisch [[Patent Office]]. |
The idea was developed at the [[Silesian University of Technology]], Poland, under the leadership of dr [[Adam Ciesiołkiewicz]]. It was granted a [[patent]] nr 195052 by the Polisch [[Patent Office]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Image:m4+2anim.gif|thumb|500px|right|The M4+2 engine working cycle animation]] |
|||
The stages of the working cycle: |
|||
<br> |
|||
*[[Gas]] exhaust |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*Fresh air inlet (two stages) |
|||
[[Image:m4+2anim.gif]] |
|||
*Medium compression |
|||
*Two stage burning |
|||
*Gas expansion |
|||
The filling process takes place at the overpressure phase, using an mechanical [[gas comressor]] and a [[throttle]] for the purpose of regulation.<br> |
|||
The load change is assisted by a four stroke piston, working as a dynamic boosting system and allowing the good scavenging of working space. <br> |
|||
There is a possibility of changing relative piston’s position during the engine work what gives the possibility of changing the compression ratio depending on the temporary sort of the load, what forecast the possibility of different [[fuel]]s combustion(low octane petrol, bio-fuels with high stage of vegetable components) |
|||
The working cycle is characterised by an almost constant characeristic of the workings space volume increasing during the expansion stage. |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 10:55, 19 April 2008
An editor has nominated this article for deletion. You are welcome to participate in the deletion discussion, which will decide whether or not to retain it. |
This article needs attention from an expert on the subject. Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. |
The M4+2 engine , also known as the double piston internal combustion engine, is a new type of combustion engine invented by a Polish patent holder Piotr Mężyk in the year 1999.
The M4+2 engine took its name from a combination of the two working modes of the known engines, that is from the Two-stroke engine and Four-stroke engine. In the M4+2 the advantages of both engines being connected are obvious; the pistons of the engine working in one combustion cylinder are set oppositely to each other, but in different modes. Although the projects of connecting two stroke modes in one cylinder were tried already a long time ago - Opposed piston engine, the combination of the two different cycles had never been tried before. It turned out that the engine is not only able to work, but that the effects are very promising. The engine has a far greater efficiency over the break-even value known to combustion engines (ca 35%) and closer to the one associated with steam turbines or electric engines (ca 70%). The other advantages are as follows:
- more efficient power production (150 Hp from 1000cm in the basic version)
- ability to differentiate fuel types (natural plant oils as well as the traditional ones)
- much better ecological effects – a huge reduction of carbon dioxide and other gas emission
- smaller fuel consumption
- prolonged strokes expansion
- possibility to change the compression parameters without having to stop the engine
- simplicity of construction
The idea was developed at the Silesian University of Technology, Poland, under the leadership of dr Adam Ciesiołkiewicz. It was granted a patent nr 195052 by the Polisch Patent Office.
The M4+2 engine working cycle
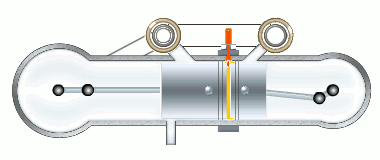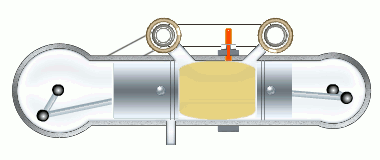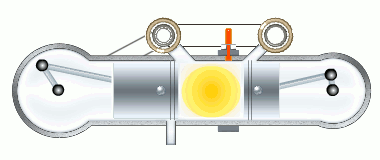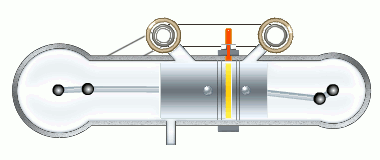
The stages of the working cycle:
- Gas exhaust
- Fresh air inlet (two stages)
- Medium compression
- Two stage burning
- Gas expansion
The filling process takes place at the overpressure phase, using an mechanical gas comressor and a throttle for the purpose of regulation.
The load change is assisted by a four stroke piston, working as a dynamic boosting system and allowing the good scavenging of working space.
There is a possibility of changing relative piston’s position during the engine work what gives the possibility of changing the compression ratio depending on the temporary sort of the load, what forecast the possibility of different fuels combustion(low octane petrol, bio-fuels with high stage of vegetable components)
The working cycle is characterised by an almost constant characeristic of the workings space volume increasing during the expansion stage.
References
- Official site of the city of Myszków, Poland (Polish)
- Journal abstract - Journal of KONES Internal Combustion Engines 2002 No. 1-2 ISSN 1231-4005, the official Polish education site (Pdf)
- The Academical forum monthy(Polish)
- An article on ndw.v.pl(Polish)
- The Polish Patent Office newsletter (Polish, Pdf)
External links
- http://www.izoling.pl/badania/czytaj/engine - a full description at the consturctors site
