Torso: Difference between revisions
Callumgare (talk | contribs) Reformatted to use the standard formatting style for the "For the movie by the same name, see..." |
Callumgare (talk | contribs) m Self correction: "human" should be "animal" |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{About|the |
{{About|the animal anatomy|the movie by the same name|Torso (1973 film)|other uses|Torso (disambiguation)}} |
||
'''Trunk''' or '''torso''' is an anatomical term for the central part of the many animal bodies (including that of the human) from which extend the neck and limbs.<ref>{{DorlandsDict|eight/000111388|trunk}}</ref> The trunk includes the [[thorax]] and [[abdomen]]. |
'''Trunk''' or '''torso''' is an anatomical term for the central part of the many animal bodies (including that of the human) from which extend the neck and limbs.<ref>{{DorlandsDict|eight/000111388|trunk}}</ref> The trunk includes the [[thorax]] and [[abdomen]]. |
||
Revision as of 10:06, 2 February 2011
| Torso | |
|---|---|
 The human male torso. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | truncus |
| MeSH | D060726 |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.013 A14.1.09.244 A14.2.03.003 |
| TA2 | 124 |
| FMA | 7181 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Trunk or torso is an anatomical term for the central part of the many animal bodies (including that of the human) from which extend the neck and limbs.[1] The trunk includes the thorax and abdomen.
Anatomy
Major organs
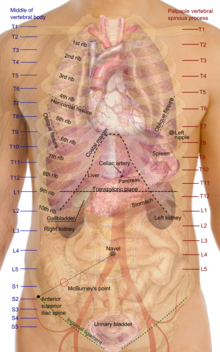
Most critical organs are housed within the trunk. In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains the majority of organs responsible for digestion: the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the large and small intestines, which extract nutrients from food; the anus, from which fecal wastes are excreted; the rectum, which stores feces; the gallbladder, which stores and concentrates bile and produces chyme; the ureters, which passes urine to the bladder; the bladder, which stores urine; and the urethra, which excretes urine and passes sperm through the seminal vesicles. Finally, the pelvic region houses both the male and female reproductive organs.
Major muscle groups
The trunk also harbours many of the main groups of muscles in the body, including the:
Innervation
The organs and muscles etc. are innervated by various nerves, mainly originating from thoracic vertebral segments. For instance, the cutaneous innervation is provided by:
