Pamphylia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
addind link for ancient Pamphylian coins - not sure how else to incorporate, but along side Livius |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* [http://www.livius.org/paa-pam/pamphylia/pamphylia.html Livius.org: Pamphylia] |
* [http://www.livius.org/paa-pam/pamphylia/pamphylia.html Livius.org: Pamphylia] |
||
* [http://www.asiaminorcoins.com/gallery/index.php?cat=17 Asia Minor Coins: Pamphylia] ancient Greek and Roman coins from Pamphylia |
|||
{{Historical regions of Anatolia}} |
{{Historical regions of Anatolia}} |
||
Revision as of 01:21, 8 October 2011
| Pamphylia (Παμφυλία) | |
|---|---|
| Ancient Region of Anatolia | |
 Ruins of the main street in Perga, capital of Pamphylia | |
| Location | Southern Anatolia |
| State existed: | - |
| Nation | Pamphylians, Pisidians, Greeks |
| Historical capitals | Perga |
| Roman province | Pamphylia |
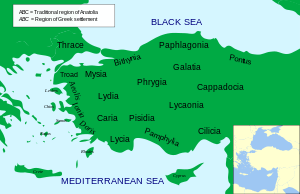 | |
In ancient geography, Pamphylia was the region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (modern day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north by Pisidia and was therefore a country of small extent, having a coast-line of only about 75 miles with a breadth of about 30 miles. Under the Roman administration the term Pamphylia was extended so as to include Pisidia and the whole tract up to the frontiers of Phrygia and Lycaonia, and in this wider sense it is employed by Ptolemy.
Name
The name Pamphylia comes from Greek Παμφυλία,[1] itself from πάμφυλος (pamfulos), literally "of mingled tribes or races",[2] a compound of πᾶν (pan), neuter of πᾶς (pas) "all"[3] + φυλή (phulē), "race, tribe".[4] Herodotus derived its etymology from a Dorian tribe, the Pamphyloi (Πάμφυλοι), who were said to have colonized the region.[5] The tribe, in turn, was said to be named after Pamphulos (Greek: Πάμφῦλος), son of Aigimios.[6][7]
Origins of the Pamphylians
The Pamphylians were a mixture of aboriginal inhabitants, immigrant Cilicians and Greeks[8] who migrated there from Arcadia and Peloponnese in the 12th century BC.[9] The significance of the Greek contribution to the origin of the Pamphylians can be attested alike by tradition and archaeology[10] and Pamphylia can be considered a Greek country from the early Iron Age until the early Middle Ages.[11] There can be little doubt that the Pamphylians and Pisidians were the same people, though the former had received colonies from Greece and other lands, and from this cause, combined with the greater fertility of their territory, had become more civilized than their neighbours in the interior.[citation needed] But the distinction between the two seems to have been established at an early period. Herodotus, who does not mention the Pisidians, enumerates the Pamphylians among the nations of Asia Minor, while Ephorus mentions them both, correctly including the one among the nations on the coast, the other among those of the interior.[citation needed] A number of scholars have distinguished in the Pamphylian dialect important isoglosses with both Arcadian and Cypriot (Arcadocypriot Greek) which allow them to be studied together with the group of dialects sometimes referred to as Achaean since it was settled not only by Achaean tribes but also colonists from other Greek-speaking regions, Dorians and Aeolians.[12] The legend related by Herodotus and Strabo, which ascribed the origin of the Pamphylians to a colony led into their country by Amphilochus and Calchas after the Trojan War, is merely a characteristic myth.[citation needed]
History


The region of Pamphylia first enters history in Hittite documents.[citation needed] In a treaty between the Hittite Great King Tudhaliya IV and his vassal, the king of Tarhuntassa, we read of the city "Parha" (Perge), and the "Kastaraya River" (Classical Kestros River, Turkish Aksu Çayı).[citation needed]
The first historical mention of "Pamphylians" is among the group of nations subdued by the Mermnad kings of Lydia;[citation needed] they afterwards passed in succession under the dominion of the Persian and Hellenistic monarchs. After the defeat of Antiochus III in 190 BC they were included among the provinces annexed by the Romans to the dominions of Eumenes of Pergamum; but somewhat later they joined with the Pisidians and Cilicians in piratical ravages, and Side became the chief centre and slave mart of these freebooters. Pamphylia was for a short time included in the dominions of Amyntas, king of Galatia, but after his death lapsed into a district of a Roman province. The Pamphilians became largely hellenized in Roman times, and have left magnificent memorials of their civilization at Perga, Aspendos and Side.[citation needed]
As of 1911 the district was largely peopled with recent settlers from Greece, Crete and the Balkans, a situation which changed considerably as a result of the disruptions attendant on the fall of the Ottoman Empire and the war between Greece and Turkey in the 1920s.[citation needed]
List of Pamphylians
- Diodorus of Aspendos Pythagorean philosopher (4th c.BC)[13]
- Apollonius of Perga astronomer, mathematician (ca. 262 BC–ca. 190 BC)
- Artemidorus of Perga proxenos in Oropos (ca. 240-180 BC)[14]
- Aetos (son of Apollonius) from Aspendos ,Ptolemaic commander,founder of Arsinoe (Cilicia)(~238 BC)[15]
- Mnaseas (son of Artemon) from Side (sculptor) end 3rd BC[16]
- Orestas (son of Erymneus) from Aspendos proxenos in Dreros (Crete) (end 3rd-beg. 2nd BC)[17]
- Thymilus of Aspendos, stadion race Olympics 176 BC
- Apollonios (son of Koiranos) proxenos in Lappa (Crete)(1st half 2nd BC)[18]
- Asclepiades (son of Myron) from Perga physician honoured by the demos of Seleucia (Pamphylia)[19]
- Menodora (daughter of Megacles) from Sillyon magistrate and benefactor (ca.2nd c. AD)[20]
- Apollonius of Aspendos poet (2nd/early 3rd c. AD)[21]
- Saint Matrona of Perge (late 5th, early 6th c.AD)
Archaeological sites
- Antalya
- Perga
- Side
- Sillyon
- Eurymedon Bridge at Aspendos, a Roman bridge which was reconstructed by the Seljuks and follows a zigzag course over the river
- Eurymedon Bridge at Selge, a Roman bridge
See also
Notes
- ^ Παμφυλία, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ πάμφυλος, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ πᾶς, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ φυλή, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ Herodotus, The Histories, 5.68
- ^ Πάμφῦλος, William J. Slater, Lexicon to Pindar, on Perseus
- ^ George Grote : A History of Greece. p. 286; Irad Malkin : Myth and Territory in the Spartan Mediterranean. Cambridge U Pr, 2003. p. 41.
- ^ Pamphylia, Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ Ahmad Hasan Dani, Jean-Pierre Mohen, J. L. Lorenzo, and V. M. Masson , History of Humanity-Scientific and Cultural Development: From the Third Millennium to the Seventh Century B.C (Vol II), UNESCO, 1996, p.425
- ^ Arnold Hugh Martin Jones, The cities of the eastern Roman provinces, Clarendon Press, 1971, p.123
- ^ John D. Grainger, The cities of Pamphylia, Oxbow Books, 2009, p.27
- ^ A.-F. Christidis, A History of Ancient Greek: From the Beginnings to Late Antiquity, Cambridge University Press, 2007, p.427
- ^ [1][2]
- ^ Epigr. tou Oropou 148
- ^ SEG 39:1426 - The Hellenistic Monarchies: Selected Papers Page 264 By Christian Habicht ISBN 0472111094
- ^ IK Side I 1
- ^ BCH 1936:280,1
- ^ SEG 23:573
- ^ Epigr.Anat. 11:104,5
- ^ Images of Women in Antiquity Page 223 By Averil Cameron, Amélie Kuhrt ISBN 0415090954
- ^ IG VII 1773 - The Context of Ancient Drama Page 192 By Eric Csapo, William J. Slater ISBN 0472082752
External links
- Livius.org: Pamphylia
- Asia Minor Coins: Pamphylia ancient Greek and Roman coins from Pamphylia
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)