Greater scaup: Difference between revisions
nontoxic=>non toxic |
|||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
==Human interactions == |
==Human interactions == |
||
[[File:Greater scaup.jpg|thumb|Greater Scaup decoys, the one on the left looks like a male and the one on the right looks like a female. Each is attached to a lead weight]] |
[[File:Greater scaup.jpg|thumb|Greater Scaup decoys, the one on the left looks like a male and the one on the right looks like a female. Each is attached to a lead weight]] |
||
Greater Scaup are a popular [[game bird]] in North America and Europe.<ref name=eumanagement>{{cite web |url=http://ec.europa.eu/environment/nature/conservation/wildbirds/hunting/docs/Scaup%20EU_MP.pdf |title=European Union Management Plan|accessdate=2 November 2011 |work=EU |publisher=European Union}}</ref> They are hunted in Denmark, Germany, Greece, France, the United Kingdom, and Ireland,<ref name=eumanagement/> and in Iran for both sport and commercial reasons.<ref name="EuropeBirdguide"/> Greater Scaup are hunted with [[shotguns]], because they must be shot on the fly, a very challenging task, as they can fly at up to {{convert|121|kph|abbr=on}}. Greater Scaup are hunted from shorelines and in open water [[hunting blind]]s or [[layout boat]]s, low-profile [[kayak]]-like boats that hunters lie inside. Hunters frequently use [[decoys]] to attract the birds, often arranged to simulate a raft of Greater Scaup and featuring an open area to attract the birds to land.<ref name=discoveroutdoors>{{cite web |url=http://www.dto.com/hunting/speciesProfile/118 |title=Greater Scaup |accessdate=19 November 2011 |publisher=Discover the Outdoors}}</ref> In most countries where Greater Scaup are hunted, a [[duck stamp]] is required along with the normal hunting lisences that are required to pursue other game. In America and Canada, waterfowl must be hunted with |
Greater Scaup are a popular [[game bird]] in North America and Europe.<ref name=eumanagement>{{cite web |url=http://ec.europa.eu/environment/nature/conservation/wildbirds/hunting/docs/Scaup%20EU_MP.pdf |title=European Union Management Plan|accessdate=2 November 2011 |work=EU |publisher=European Union}}</ref> They are hunted in Denmark, Germany, Greece, France, the United Kingdom, and Ireland,<ref name=eumanagement/> and in Iran for both sport and commercial reasons.<ref name="EuropeBirdguide"/> Greater Scaup are hunted with [[shotguns]], because they must be shot on the fly, a very challenging task, as they can fly at up to {{convert|121|kph|abbr=on}}. Greater Scaup are hunted from shorelines and in open water [[hunting blind]]s or [[layout boat]]s, low-profile [[kayak]]-like boats that hunters lie inside. Hunters frequently use [[decoys]] to attract the birds, often arranged to simulate a raft of Greater Scaup and featuring an open area to attract the birds to land.<ref name=discoveroutdoors>{{cite web |url=http://www.dto.com/hunting/speciesProfile/118 |title=Greater Scaup |accessdate=19 November 2011 |publisher=Discover the Outdoors}}</ref> In most countries where Greater Scaup are hunted, a [[duck stamp]] is required along with the normal hunting lisences that are required to pursue other game. In America and Canada, waterfowl must be hunted with non toxic shot. |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 16:16, 18 December 2011
| Greater Scaup Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult male in California | |

| |
| Adult female in California | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | F. Boie, 1822
|
| Species: | A. marila
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aythya marila (Linnaeus, 1761)
| |
| Subspecies | |
|
A. m. marila (Linnaeus, 1761) | |
| |
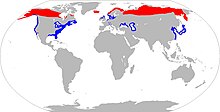
| Greater Scaup range map | |
The Greater Scaup (Aythya marila), just Scaup in Europe, or colloquially "Bluebill" in North America for its bright blue bill,[3] is small compared to other diving ducks; however, it is larger than the closely related Lesser Scaup. The scientific name Aythya marila comes from the Ancient Greek word for an unidentified seabird. It is a circumpolar duck, which means that its range circles one of Earth's poles. It spends the summer months breeding in Alaska, northern Canada, Siberia, and the northernmost reaches of Europe. During the winter, it migrates south down the coasts of North America, Europe, and Japan.
Drake Greater Scaup are larger and have more rounded heads than females; they have a bright blue bill and yellow eyes. They have dark heads with a glossy green tint, white undersides and wings with white on the tips. The females are mostly brown, with white bands located on their wingtips. They have a blue bill that is slightly duller then the drake's.
Greater Scaup nest near water, typically on islands in northern lakes or on floating mats of vegetation. They begin breeding at age two, but start building nests in the first year. The drakes have a complex courtship procedure, which takes place on the return migration to the summer breeding grounds and concludes with the formation of monogamous pairs. Females lay a clutch of six to nine olive-buff colored eggs. The eggs hatch in 24 to 28 days. The down-covered ducklings are able to follow their mother in her search for food immediately after hatching.
Greater Scaup eat aquatic mollusks, plants, and insects, which they obtain by diving underwater. They form large groups, called "rafts", that can number in the thousands. Their main threat is human development, although they are preyed upon by owls, skunks, raccoons, foxes, coyotes, and humans. Greater Scaup populations have been declining since the 1980s; however, they are still listed as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List.
Taxonomy
The genus name is derived from the Greek aithuia which refers to a seabird mentioned by Aristotle, Hesychius and others and thought to refer to a duck, auklet or other seabird but not reliably identified. The species name marila is from the Greek word for charcoal embers or coal dust.[4] The Greater Scaup was first studied by Linnaeus in 1761.[5] Male Greater Scaup from America are distinguishable from those in Europe and Asia by the stronger vermiculation, worm-like carvings or marks[6] on the mantle and scapulars, and are considered a separate subspecies, A. m. nearctica.[7] Females of the subspecies are indistinguishable.[8] Based on size differences, a Pleistocene paleosubspecies, Aythya marila asphaltica, has also been described by Serebrovskij in 1941 from fossils recovered at Binagady, Azerbaijan. The Greater Scaup's name may come from "scalp", a Scottish and Northern English word for a shellfish bed,[9] or from the duck's mating call: "scaup scaup".
A phylogenetic analysis of the diving ducks, examining the skeletal anatomy and skin, found that the Greater and Lesser Scaups are each others' closest relatives, with the Tufted Duck as the next closest relative of the pair.[10]
Description
The adult Greater Scaup is 39–56 cm (15–22 in) long with a 71–84 cm (28–33 in) wingspan and a body mass of 726–1,360 g (1.601–2.998 lb). It has a blue bill and yellow eyes and is 20% heavier and 10% longer than the closely related Lesser Scaup.[11] The male has a dark head with a green sheen, a black breast, a light back, a black tail, and a white underside. The drake or male Greater Scaup is larger and has a more rounded head than the female. The drake's belly and flanks are a bright white. Its neck, upper chest, and tail feathers are a glossy black, while its lower flanks are gray. The drake also has a white speculum on its wings. The adult female has a white band and brown oval shaped patches at the base of the bill, which is a slightly duller shade of blue than the drake's bill. Females have grey on both their legs and feet. They have a brown body and head, with white bands on their wingtips.[12] Juvenile Greater Scaup look similar to adult females. The Greater Scaup drake's eclipse plumage looks similar to its breeding plumage, except the pale parts of the plumage are a buffy gray.[13]
Distribution and habitat
The Greater Scaup has a circumpolar distribution, breeding within the Arctic circle both in the Old World (the Palearctic) and North America (the Nearctic). It spends the summer months in Alaska, Siberia. and the northern parts of Europe. It is also found in Asia, and is present in the Aleutian Islands year round.[14] The summer habitat is marshy lowland tundra and islands in fresh water lakes. In the fall, the Greater Scaup populations start their migration south for the winter. They winter along the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of North America, the coasts of northwest Europe, the Caspian Sea, the Black Sea, the coast of Japan, Yellow Sea and East China Sea.[15] During the winter months, they are found in coastal bays, estuaries, and sometimes inland lakes,[16] such as the lakes of Central Europe and the Great Lakes.[15]
In Europe, the Greater Scaup breeds in Iceland, the northern coasts of the Scandinavian peninsula, including much of the northern parts of the Baltic Sea, the higher mountains of Scandinavia and the areas close to the Arctic Sea in Russia. These birds spend the winters in the British Isles, western Norway, the southern tip of Sweden, the coast from Brittany to Poland, including all of Denmark, the Alps, the eastern Adriatic Sea, the northern and western Black sea and the southwestern Caspian Sea.[17][18]
In North America, the Greater Scaup summers in Newfoundland and Labrador, along with Ungava Bay, the Hudson Bay, Lake Winnipeg, Northern Yukon, Northern Manitoba, and Northern Saskatchewan. It winters in Nova Scotia New Brunswick, and the entire west coast of British Columbia. It will also winter along the entire west coast of North America, including the Baja Peninsula. The Greater Scaup also winters along the shores of the Great Lakes, the Gulf of Mexico and the entire east coast from Maine to Florida.[15]
Behaviour
Breeding
Greater Scaup breed all the way from Iceland to northern Scandinavia, northern Russia, northern Siberia and the western North American Arctic. They breed in the tundra and the boreal forest; it is estimated that 75% of the North American population breed in Alaska. Greater Scaup typically nest on islands in large northern lakes. Greater Scaup begin breeding when they are two years old, although they may start nesting at age one. Drake Greater Scaup have a soft quick whistle to get the attention of hens during their courtship which takes place from late winter to early spring, on the way back to their northern breeding grounds. Female Greater Scaup have a single pitch, a raspy “arrr-arrr-arrr-arrr-arrr” sounding vocalization.[19] The courtship procedure is complex and results in the formation of monogamous pairs.[20] Pairs nest in close proximity to each other in large colonies, usually near water, on an island or shoreline, or on a raft of floating vegetation. The nest consists of a shallow depression made by the female and lined with her down.[11] After the female lays the eggs, the drake abandons the female.[20] The female lays six to nine olive-buff colored eggs,[21] which she incubates for 24–28 days.[22] A large clutch could indicates brood parasitism by other Greater Scaups or even ducks of other species.[23] Newly hatched chicks are covered with down and are soon able to walk, swim, and feed themselves; however, they are not able to fly until 40–45 days after hatching.[15][20] The vulnerable small chicks follow their mother, who protects them from predators.[20]
Feeding

The Greater Scaup dive to obtain food, which they eat on the surface.[11] They mainly eat mollusks, aquatic plants, and aquatic insects,.[19] During the summer months, the Greater Scaup will eat small aquatic crustaceans.[11] There is a report of four Greater Scaups swallowing leopard frogs (with body length about 5 cm (2 inches)), which they dredged out of a roadside freshwater pond.[24] In freshwater ecosystems, the Greater Scaup will eat seeds, leaves, stems and roots, along with sedges, pondweeds, muskgrass, and wild celery.[12] Owing to the Greater Scaup's webbed feet and weight, it can dive up to 6 metres (20 ft) and stay submerged for up to a minute, allowing it to reach food sources that are unobtainable to other diving ducks.[25] The Greater Scaup forms large flocks, some of which can contain thousands of birds. When flocks are in water, they will face the current, and as the ducks float backwards, some fly to the front of the flock to maintain position.
Threats
Common predators of the Greater Scaup are owls, skunks, raccoons, foxes, coyotes, and humans.[5] Greater Scaup often find themselves entangled in fishing nets, thus large numbers of them drown in nets each year. Greater Scaup can catch avian influenza, so future outbreaks have the potential to threaten Greater Scaup populations.[14]
Although the Greater Scaup faces numerous threats, the most significant challenge to their survival is habitat degradation caused by a mix of human development and runoff.[26] Greater Scaup, when moulting and during the winter, are threatened by escalated levels of organochloride contaminants. Oil and sewage pollution also threaten the Greater Scaup. Since 80% of the Greater Scaup population winters in the urbanized part of the Atlantic Flyway, these ducks are subject to high levels of organic contaminates, along with increased levels of heavy metals in foods and habitat.[16]
A joint group of American and Canadian scientists researching Scaup migration across the Great Lakes found that 100% of female Greater Scaup, and 77% of female Lesser Scaup, had escalated levels of selenium in their bodies. Selenium is a occurring semimetallic trace element that occurs naturally in some soils and minute amounts are necessary for animal life. However excessive selenium can cause reproductive harm and is highly toxic. On their migration across the Great Lakes, Greater Scaups are at risk of ingesting selenium by eating the invasive zebra mussels, which can render a hen infertile.[3] This sterilization of hens is causing the population to decrease.
In a study of 107 Scaup, they all had traces of iron, zinc, manganese, copper, lead, cadmium, cobalt and nickel in their tissue samples with varying concentrations of metals in different types of tissues. Further analysis revealed that the kidneys had the highest levels of cadmium, the liver had the highest levels of cooper and manganese, the liver and the stomach had the highest levels of zinc, and the lungs and liver had the highest levels of iron.[27] There was no difference in concentration when comparing genders.
Conservation

Greater Scaup are rated as a species of least concern by the IUCN Redlist.[15] During aerial population surveys Greater and Lesser Scaup are counted together, because they look almost identical from the air. It was estimated that the Greater Scaup made up about 11% of the continental Scaup population. Since the 1980s, Scaup populations have been steadily decreasing. Some of the primary factors contributing to this decline are habitat loss, contaminants, changes in breeding habitat, and a lower female survival rate. The 2010 American Scaup population survey was 4.2 million Scaup,[28] however, the worldwide Greater Scaup population survey estimated 1,200,000 to 1,400,000 mature Greater Scaup.[14] Along with the aerial population surveys, there is a banding program for the Greater Scaup. Metal leg bands are placed on them, so that if the Scaup is killed by a hunter or if it is captured by another banding group, the number on the band can be reported to biologists and wildlife organizations. These banding programs yield valuable data about migration patterns, harvest rates, and survival rates.[29]
Human interactions
Greater Scaup are a popular game bird in North America and Europe.[30] They are hunted in Denmark, Germany, Greece, France, the United Kingdom, and Ireland,[30] and in Iran for both sport and commercial reasons.[15] Greater Scaup are hunted with shotguns, because they must be shot on the fly, a very challenging task, as they can fly at up to 121 km/h (75 mph). Greater Scaup are hunted from shorelines and in open water hunting blinds or layout boats, low-profile kayak-like boats that hunters lie inside. Hunters frequently use decoys to attract the birds, often arranged to simulate a raft of Greater Scaup and featuring an open area to attract the birds to land.[31] In most countries where Greater Scaup are hunted, a duck stamp is required along with the normal hunting lisences that are required to pursue other game. In America and Canada, waterfowl must be hunted with non toxic shot.
References
- Notes
- ^ Alvarez (1977). "A pleistocene avifauna from Jalisco, Mexico" (PDF). University of Michigan. p. 214. Retrieved 6 December2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|frst1=ignored (help) - ^ "Aythya marila". IUCN 2011. Retrieved 7 December 2011.
- ^ a b "Bluebills". Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved 3 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 64, 242. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ a b "Greater Scaup". United States Fauna. Retrieved 2 November2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Vermiculation". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 11 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Taxonomic recommendations for British birds: third report". John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Retrieved 13 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Banks, RC (1986). "Subspecies of the Greater Scaup and their names" (PDF). Wilson Bulletin. 98 (3): 433–444.
- ^ (1993)
- ^ Livezey, Bradley C. (1996). "A phylogenetic analysis of modern pochards (Anatidae: Aythyini)" (PDF). The Auk. 113 (1): 74–93.
- ^ a b c d "Greater Scaup". Bird Web. Seattle Audubon Society. Retrieved 26 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Greater Scaup". Ducks Unlimited. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Greater Scaup". e nature. Retrieved 11 December2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b c "Greater Scaup Aythya marila". Bird Life International. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b c d e f "Redlist". IUCN Redlist of Threatened Species. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) Cite error: The named reference "EuropeBirdguide" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ a b "Greater Scaup". The Birds of North America. Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Ullman & (1992), p. 102
- ^ Delin & (2001), p. 50
- ^ a b Mayntz, Melissa. "Greater Scaup". About.com. Retrieved 20 August 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b c d "Greater Scaup". Utah Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Greater Scaup". National Audubon Society, Inc. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Greater Scaup". Ohio Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved 1 December2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Fournier MA & J E Hines (2001). "Breeding Ecology of Sympatric Greater and Lesser Scaup (Aythya marila and Aythya affinis) in the Subarctic Northwest Territories". Arctic. 54 (4): 444–456.
- ^ Longley, William H. (1948). "Greater scaup eating frogs" (PDF).
- ^ "Greater Scaup". Audubon. National Audubon Society. Retrieved 26 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Greater Scaup". National Biological Information Infrastructure. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Trace metals in the soft tissues of scaup ducks (Aythya marila L.) wintering in Gdańsk bay, Baltic sea". Elsevier B.V. Retrieved 13 December2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Waterfowl Hunting Management in North America". Scaup Population Estimates. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service in collaboration with flyway and state waterfowl managers. 29 June 2010. Retrieved 4 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help). - ^ "Banding and Marking Programs". U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 28 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "European Union Management Plan" (PDF). EU. European Union. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Greater Scaup". Discover the Outdoors. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
- Bibliography
- Delin, Håkan (2001). Färgfotoguiden över alla Europas fåglar. Bonniers. ISBN 91-34-51940-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Ullman (maps), Magnus (1992). Fåglar i Europa. Wahlström & Widstrand. ISBN 91-46-17633-0.
- New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 1993. ISBN 0198612710.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
Further reading
- Splitting headaches? Recent taxonomic changes affecting the British and Western Palaearctic lists - Martin Collinson, British Birds vol 99 (June 2006), 306-323
- Madge, Steve (1988). Wildfowl: An Identification Guide to the Ducks, Geese and Swans of the World. London: Christopher Helm. ISBN 0-7470-2201-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)


