Quark–gluon plasma: Difference between revisions
Filling in 12 references using Reflinks |
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 3 sources. #IABot |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Experiments at [[CERN]]'s [[Super Proton Synchrotron]] (SPS) first tried to create the QGP in the 1980s and 1990s: the results led CERN to announce indirect evidence for a "new state of matter"<ref>{{cite web|url=http://newstate-matter.web.cern.ch/newstate-matter/Experiments.html |title=A New State of Matter - Experiments |publisher=Newstate-matter.web.cern.ch |date=2000-02-04 |accessdate=2016-03-04}}</ref> in 2000. Current experiments (2011) at the [[Brookhaven National Laboratory]]'s [[Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider]] (RHIC) on Long Island (NY, USA) and at CERN's recent [[Large Hadron Collider]] near Geneva (Switzerland) are continuing this effort,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bnl.gov/rhic/ |title=RHIC | Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider |publisher=Bnl.gov |date= |accessdate=2016-03-04}}</ref><ref name="RHIC" /> by colliding relativistically accelerated gold (at RHIC) or lead (at LHC) with each other or with protons. Although the results have yet to be independently verified as of February 2010, scientists at Brookhaven RHIC have tentatively claimed to have created a quark–gluon plasma with an approximate temperature of 4 trillion (4×10<sup>12</sup>) [[kelvin]].<ref name="RHIC">http://www.bnl.gov/rhic/news2/news.asp?a=1074&t=pr 'Perfect' Liquid Hot Enough to be Quark Soup</ref> |
Experiments at [[CERN]]'s [[Super Proton Synchrotron]] (SPS) first tried to create the QGP in the 1980s and 1990s: the results led CERN to announce indirect evidence for a "new state of matter"<ref>{{cite web|url=http://newstate-matter.web.cern.ch/newstate-matter/Experiments.html |title=A New State of Matter - Experiments |publisher=Newstate-matter.web.cern.ch |date=2000-02-04 |accessdate=2016-03-04}}</ref> in 2000. Current experiments (2011) at the [[Brookhaven National Laboratory]]'s [[Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider]] (RHIC) on Long Island (NY, USA) and at CERN's recent [[Large Hadron Collider]] near Geneva (Switzerland) are continuing this effort,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bnl.gov/rhic/ |title=RHIC | Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider |publisher=Bnl.gov |date= |accessdate=2016-03-04}}</ref><ref name="RHIC" /> by colliding relativistically accelerated gold (at RHIC) or lead (at LHC) with each other or with protons. Although the results have yet to be independently verified as of February 2010, scientists at Brookhaven RHIC have tentatively claimed to have created a quark–gluon plasma with an approximate temperature of 4 trillion (4×10<sup>12</sup>) [[kelvin]].<ref name="RHIC">http://www.bnl.gov/rhic/news2/news.asp?a=1074&t=pr 'Perfect' Liquid Hot Enough to be Quark Soup</ref> |
||
As already mentioned, three new experiments running on CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC), on the spectrometers [[A Large Ion Collider Experiment|ALICE]],<ref> |
As already mentioned, three new experiments running on CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC), on the spectrometers [[A Large Ion Collider Experiment|ALICE]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aliceinfo.cern.ch/index.html |accessdate=July 12, 2005 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060213023750/http://aliceinfo.cern.ch:80/index.html |archivedate=February 13, 2006 }}</ref> [[ATLAS experiment|ATLAS]] and [[Compact Muon Solenoid|CMS]], will continue studying properties of QGP. Starting in November 2010, CERN temporarily ceased colliding [[protons]], and began colliding [[lead]] Ions for the ALICE experiment. They were looking to create a QGP and were expected to stop December 6, colliding protons again in January.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://press.web.cern.ch/press/PressReleases/Releases2010/PR20.10E.html |accessdate=November 5, 2010 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20101107090326/http://press.web.cern.ch:80/press/PressReleases/Releases2010/PR20.10E.html |archivedate=November 7, 2010 }}</ref> A new record breaking temperature was set by [[ALICE: A Large Ion Collider Experiment]] at CERN on August, 2012 in the ranges of 5.5 trillion (5.5×10<sup>12</sup>) kelvin as claimed in their Nature PR.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://blogs.nature.com/news/2012/08/hot-stuff-cern-physicists-create-record-breaking-subatomic-soup.html |title=Hot stuff: CERN physicists create record-breaking subatomic soup : News blog |publisher=Blogs.nature.com |date=2012-08-13 |accessdate=2016-03-04}}</ref> |
||
==General introduction== |
==General introduction== |
||
Quark–gluon plasma is a [[state of matter]] in which the elementary particles that make up the hadrons of [[baryon]]ic matter are freed of their [[Strong interaction|strong]] attraction for one another under extremely high [[Energy density|energy densities]]. These particles are the [[quark]]s and [[gluon]]s that compose baryonic matter.<ref> |
Quark–gluon plasma is a [[state of matter]] in which the elementary particles that make up the hadrons of [[baryon]]ic matter are freed of their [[Strong interaction|strong]] attraction for one another under extremely high [[Energy density|energy densities]]. These particles are the [[quark]]s and [[gluon]]s that compose baryonic matter.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://theory.tifr.res.in/~sgupta/ilgti/infocenter/ |accessdate=May 20, 2005 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20050212185849/http://theory.tifr.res.in:80/~sgupta/ilgti/infocenter/ |archivedate=February 12, 2005 }}</ref> In normal matter quarks are ''[[Color confinement|confined]]''; in the QGP quarks are ''[[Deconfinement|deconfined]]''. In classical QCD quarks are the Fermionic components of mesons and baryons while the gluons are considered the Bosonic components of such particles. The gluons are the force carriers, or bosons, of the QCD color force, while the quarks by themselves are their Fermionic matter counterparts. |
||
Although the experimental high temperatures and densities predicted as producing a quark–gluon plasma have been realized in the laboratory, the resulting matter does ''not'' behave as a quasi-ideal state of free quarks and gluons, but, rather, as an almost perfect dense fluid.<ref name=Zajc>{{Cite journal |title=The fluid nature of quark-gluon plasma |author= WA Zajc |journal=Nuclear Physics A |year=2008 |volume=805 |pages=283c–294c |doi=10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2008.02.285 |arxiv=0802.3552 |postscript=.|bibcode = 2008NuPhA.805..283Z }}</ref> Actually, the fact that the quark–gluon plasma will not yet be "free" at temperatures realized at present accelerators was predicted in 1984 as a consequence of the remnant effects of confinement.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=How free is the quark-gluon plasma |first=M. |last=Plümer |first2=S. |last2=Raha |lastauthoramp=yes |first3=R. M. |last3=Weiner |journal=Nucl. Phys. A |volume=418 |issue= |year=1984 |pages=549–557 |doi=10.1016/0375-9474(84)90575-X |postscript=. |bibcode = 1984NuPhA.418..549P }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |first=M. |last=Plümer |first2=S. |last2=Raha |lastauthoramp=yes |first3=R. M. |last3=Weiner |title=Effect of confinement on the sound velocity in a quark-gluon plasma |journal=Phys. Lett. B |volume=139 |issue=3 |pages=198–202 |year=1984 |doi=10.1016/0370-2693(84)91244-9 |postscript=. |bibcode = 1984PhLB..139..198P }}</ref> |
Although the experimental high temperatures and densities predicted as producing a quark–gluon plasma have been realized in the laboratory, the resulting matter does ''not'' behave as a quasi-ideal state of free quarks and gluons, but, rather, as an almost perfect dense fluid.<ref name=Zajc>{{Cite journal |title=The fluid nature of quark-gluon plasma |author= WA Zajc |journal=Nuclear Physics A |year=2008 |volume=805 |pages=283c–294c |doi=10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2008.02.285 |arxiv=0802.3552 |postscript=.|bibcode = 2008NuPhA.805..283Z }}</ref> Actually, the fact that the quark–gluon plasma will not yet be "free" at temperatures realized at present accelerators was predicted in 1984 as a consequence of the remnant effects of confinement.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=How free is the quark-gluon plasma |first=M. |last=Plümer |first2=S. |last2=Raha |lastauthoramp=yes |first3=R. M. |last3=Weiner |journal=Nucl. Phys. A |volume=418 |issue= |year=1984 |pages=549–557 |doi=10.1016/0375-9474(84)90575-X |postscript=. |bibcode = 1984NuPhA.418..549P }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |first=M. |last=Plümer |first2=S. |last2=Raha |lastauthoramp=yes |first3=R. M. |last3=Weiner |title=Effect of confinement on the sound velocity in a quark-gluon plasma |journal=Phys. Lett. B |volume=139 |issue=3 |pages=198–202 |year=1984 |doi=10.1016/0370-2693(84)91244-9 |postscript=. |bibcode = 1984PhLB..139..198P }}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 03:36, 5 March 2016
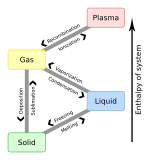
A quark–gluon plasma (QGP) or quark soup[1] is a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics (QCD) which is hypothesized to exist at extremely high temperature, density, or both temperature and density. This state is thought to consist of asymptotically free quarks and gluons, which are several of the basic building blocks of matter. It is believed that up to a few milliseconds after the Big Bang, known as the Quark epoch, the Universe was in a quark–gluon plasma state. In June 2015, an international team of physicists produced quark-gluon plasma at the Large Hadron Collider by colliding protons with lead nuclei at high energy inside the supercollider’s Compact Muon Solenoid detector. They also discovered that this new state of matter behaves like a fluid.[2]
The strength of the color force means that unlike the gas-like plasma, quark–gluon plasma behaves as a near-ideal Fermi liquid, although research on flow characteristics is ongoing.[3] In the quark matter phase diagram, QGP is placed in the high-temperature, high-density regime; whereas, ordinary matter is a cold and rarefied mixture of nuclei and vacuum, and the hypothetical quark stars would consist of relatively cold, but dense quark matter.
Experiments at CERN's Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) first tried to create the QGP in the 1980s and 1990s: the results led CERN to announce indirect evidence for a "new state of matter"[4] in 2000. Current experiments (2011) at the Brookhaven National Laboratory's Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) on Long Island (NY, USA) and at CERN's recent Large Hadron Collider near Geneva (Switzerland) are continuing this effort,[5][6] by colliding relativistically accelerated gold (at RHIC) or lead (at LHC) with each other or with protons. Although the results have yet to be independently verified as of February 2010, scientists at Brookhaven RHIC have tentatively claimed to have created a quark–gluon plasma with an approximate temperature of 4 trillion (4×1012) kelvin.[6]
As already mentioned, three new experiments running on CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC), on the spectrometers ALICE,[7] ATLAS and CMS, will continue studying properties of QGP. Starting in November 2010, CERN temporarily ceased colliding protons, and began colliding lead Ions for the ALICE experiment. They were looking to create a QGP and were expected to stop December 6, colliding protons again in January.[8] A new record breaking temperature was set by ALICE: A Large Ion Collider Experiment at CERN on August, 2012 in the ranges of 5.5 trillion (5.5×1012) kelvin as claimed in their Nature PR.[9]
General introduction
Quark–gluon plasma is a state of matter in which the elementary particles that make up the hadrons of baryonic matter are freed of their strong attraction for one another under extremely high energy densities. These particles are the quarks and gluons that compose baryonic matter.[10] In normal matter quarks are confined; in the QGP quarks are deconfined. In classical QCD quarks are the Fermionic components of mesons and baryons while the gluons are considered the Bosonic components of such particles. The gluons are the force carriers, or bosons, of the QCD color force, while the quarks by themselves are their Fermionic matter counterparts.
Although the experimental high temperatures and densities predicted as producing a quark–gluon plasma have been realized in the laboratory, the resulting matter does not behave as a quasi-ideal state of free quarks and gluons, but, rather, as an almost perfect dense fluid.[11] Actually, the fact that the quark–gluon plasma will not yet be "free" at temperatures realized at present accelerators was predicted in 1984 as a consequence of the remnant effects of confinement.[12][13]
Relation to normal plasma
A plasma is matter in which charges are screened due to the presence of other mobile charges; for example: Coulomb's Law is suppressed by the screening to yield a distance-dependent charge (Q -> Q × exp(-r/α), i.e., the charge Q is reduced exponentially with the distance divided by a screening length α). In a QGP, the color charge of the quarks and gluons is screened. The QGP has other analogies with a normal plasma. There are also dissimilarities because the color charge is non-abelian, whereas the electric charge is abelian. Outside a finite volume of QGP the color-electric field is not screened, so that a volume of QGP must still be color-neutral. It will therefore, like a nucleus, have integer electric charge.
Theory
One consequence of this difference is that the color charge is too large for perturbative computations which are the mainstay of QED. As a result, the main theoretical tools to explore the theory of the QGP is lattice gauge theory.[14][15] The transition temperature (approximately 175 MeV) was first predicted by lattice gauge theory. Since then lattice gauge theory has been used to predict many other properties of this kind of matter. The AdS/CFT correspondence conjecture may provide insights in QGP, moreover the ultimate goal of the fluid/gravity correspondence is to understand QGP. The QGP is believed to be a phase of QCD which is completely locally thermalized and thus suitable for an effective fluid dynamic description.
Production
The QGP can be created by heating matter up to a temperature of 2×1012 K, which amounts to 175 MeV per particle. This can be accomplished by colliding two large nuclei at high energy (note that 175 MeV is not the energy of the colliding beam). Lead and gold nuclei have been used for such collisions at CERN SPS and BNL RHIC, respectively. The nuclei are accelerated to ultrarelativistic speeds (contracting their length) and directed towards each other, creating a "fireball", in the rare event of a collision. Hydrodynamic simulation predicts this fireball will expand under its own pressure, and cool while expanding. By carefully studying the spherical and elliptic flow, experimentalists put the theory to test.
How the QGP fits into the general scheme of physics
QCD is one part of the modern theory of particle physics called the Standard Model. Other parts of this theory deal with electroweak interactions and neutrinos. The theory of electrodynamics has been tested and found correct to a few parts in a billion. The theory of weak interactions has been tested and found correct to a few parts in a thousand. Perturbative forms of QCD have been tested to a few percent. In contrast, non-perturbative forms of QCD have barely been tested. The study of the QGP is part of this effort to consolidate the grand theory of particle physics.
The study of the QGP is also a testing ground for finite temperature field theory, a branch of theoretical physics which seeks to understand particle physics under conditions of high temperature. Such studies are important to understand the early evolution of our universe: the first hundred microseconds or so. It is crucial to the physics goals of a new generation of observations of the universe (WMAP and its successors). It is also of relevance to Grand Unification Theories which seek to unify the three fundamental forces of nature (excluding gravity).
Expected properties
Thermodynamics
The cross-over temperature from the normal hadronic to the QGP phase is about 175 MeV. This "crossover" may actually not be only a qualitative feature, but instead one may have to do with a true (second order) phase transition, e.g. of the universality class of the three-dimensional Ising model, as some theorists say, e.g. Frithjof Karsch and coworkers from the university of Bielefeld. The phenomena involved correspond to an energy density of a little less than 1 GeV/fm3. For relativistic matter, pressure and temperature are not independent variables, so the equation of state is a relation between the energy density and the pressure. This has been found through lattice computations, and compared to both perturbation theory and string theory. This is still a matter of active research. Response functions such as the specific heat and various quark number susceptibilities are currently being computed.
Flow
The equation of state is an important input into the flow equations. The speed of sound is currently under investigation in lattice computations. The mean free path of quarks and gluons has been computed using perturbation theory as well as string theory. Lattice computations have been slower here, although the first computations of transport coefficients have recently been concluded. These indicate that the mean free time of quarks and gluons in the QGP may be comparable to the average interparticle spacing: hence the QGP is a liquid as far as its flow properties go. This is very much an active field of research, and these conclusions may evolve rapidly. The incorporation of dissipative phenomena into hydrodynamics is another recent development that is still in an active stage.
Excitation spectrum
Does the QGP really contain (almost) free quarks and gluons? The study of thermodynamic and flow properties would indicate that this is an over-simplification. Many ideas are currently being evolved and will be put to test in the near future. It has been hypothesized recently that some mesons built from heavy quarks do not dissolve until the temperature reaches about 350 MeV. This has led to speculation that many other kinds of bound states may exist in the plasma. Some static properties of the plasma (similar to the Debye screening length) constrain the excitation spectrum.
Glasma hypothesis
Since 2008, there is a discussion about a hypothetical precursor state of the Quark–gluon plasma, the so-called "Glasma", where the dressed particles are condensed into some kind of glassy (or amorphous) state, below the genuine transition between the confined state and the plasma liquid.[16] This would be analogous to the formation of metallic glasses, or amorphous alloys of them, below the genuine onset of the liquid metallic state.
Experimental situation
Those forms of the QGP that are easiest to compute are not those that are easiest to verify experimentally. While the balance of evidence points towards the QGP being the origin of the detailed properties of the fireball produced at SPS (CERN), in the RHIC and at LHC, this is the main barrier which prevents experimentalists from declaring a sighting of the QGP.[17]
The important classes of experimental observations are
- Single particle spectra (photons and dileptons)
- Strangeness production
- Photon and muon rates (and J/ψ melting)
- Elliptic flow
- Jet quenching
- Fluctuations
- Hanbury Brown and Twiss effect and Bose–Einstein correlations
In short, a quark–gluon plasma flows like a splat of liquid, and because it's not "transparent" with respect to quarks, it can attenuate jets emitted by collisions. Furthermore, once formed, a ball of quark–gluon plasma, like any hot object, transfers heat internally by radiation. However, unlike in everyday objects, there is enough energy available that gluons (particles mediating the strong force) collide and produce an excess of the heavy (i.e. high-energy) strange quarks. Whereas, if the QGP didn't exist and there was a pure collision, the same energy would be converted into even heavier quarks such as charm quarks or bottom quarks.
Formation of quark matter
In April 2005, formation of quark matter was tentatively confirmed by results obtained at Brookhaven National Laboratory's Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). The consensus of the four RHIC research groups was that they had created a quark–gluon liquid of very low viscosity. However, contrary to what was at that time still the widespread assumption, it is yet unknown from theoretical predictions whether the QCD "plasma", especially close to the transition temperature, should behave like a gas or liquid. Authors favoring the weakly interacting interpretation derive their assumptions from the lattice QCD calculation, where the entropy density of quark–gluon plasma approaches the weakly interacting limit. However, since both energy density and correlation shows significant deviation from the weakly interacting limit, it has been pointed out by many authors that there is in fact no reason to assume a QCD "plasma" close to the transition point should be weakly interacting, like electromagnetic plasma (see, e.g.,[18]). That being said, systematically improvable perturbative QCD quasiparticle models do a very good job of reproducing the lattice data for thermodynamical observables (pressure, entropy, quark susceptibility), including the aforementioned "significant deviation from the weakly interacting limit", down to temperatures on the order of 2 to 3 times the critical temperature for the transition.[19][20][21]
See also
- Hadrons (that is mesons and baryons) and confinement
- Hadronization
- List of plasma (physics) articles
- Neutron stars
- Plasma physics
- QCD matter
- Quantum electrodynamics
- Quantum chromodynamics
- Quantum hydrodynamics
- Relativistic plasma
- Relativistic nuclear collision
- Strangeness production
- Strange matter
- Color-glass condensate
References
- ^ Bohr, Henrik; Nielsen, H. B. (1977). "Hadron production from a boiling quark soup: quark model predicting particle ratios in hadronic collisions". Nuclear Physics B. 128 (2): 275. Bibcode:1977NuPhB.128..275B. doi:10.1016/0550-3213(77)90032-3.
- ^ Eleanor Imster. "LHC creates liquid from Big Bang | Human World". EarthSky. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ "Quark-gluon plasma goes liquid". physicsworld.com. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ "A New State of Matter - Experiments". Newstate-matter.web.cern.ch. 2000-02-04. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ "RHIC | Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider". Bnl.gov. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ a b http://www.bnl.gov/rhic/news2/news.asp?a=1074&t=pr 'Perfect' Liquid Hot Enough to be Quark Soup
- ^ http://web.archive.org/web/20060213023750/http://aliceinfo.cern.ch:80/index.html. Archived from the original on February 13, 2006. Retrieved July 12, 2005.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ http://web.archive.org/web/20101107090326/http://press.web.cern.ch:80/press/PressReleases/Releases2010/PR20.10E.html. Archived from the original on November 7, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Hot stuff: CERN physicists create record-breaking subatomic soup : News blog". Blogs.nature.com. 2012-08-13. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ http://web.archive.org/web/20050212185849/http://theory.tifr.res.in:80/~sgupta/ilgti/infocenter/. Archived from the original on February 12, 2005. Retrieved May 20, 2005.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ WA Zajc (2008). "The fluid nature of quark-gluon plasma". Nuclear Physics A. 805: 283c–294c. arXiv:0802.3552. Bibcode:2008NuPhA.805..283Z. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2008.02.285.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Plümer, M.; Raha, S.; Weiner, R. M. (1984). "How free is the quark-gluon plasma". Nucl. Phys. A. 418: 549–557. Bibcode:1984NuPhA.418..549P. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(84)90575-X.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Plümer, M.; Raha, S.; Weiner, R. M. (1984). "Effect of confinement on the sound velocity in a quark-gluon plasma". Phys. Lett. B. 139 (3): 198–202. Bibcode:1984PhLB..139..198P. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(84)91244-9.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ http://arxiv.org/PS_cache/hep-lat/pdf/9503/9503010v1.pdf
- ^ "[1101.3937] The Quark-Gluon Plasma". Arxiv.org. 2011-01-20. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2011.05.014. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ "[0806.1356] From Glasma to Quark Gluon Plasma in heavy ion collisions". Arxiv.org. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ^ http://www.bnl.gov/npp/docs/Hunting%20the%20QGP.pdf
- ^ Miklos Gyulassy (2004). "The QGP Discovered at RHIC". arXiv:nucl-th/0403032.
{{cite arXiv}}:|class=ignored (help) - ^ Andersen; Leganger; Strickland; Su (2011). "NNLO hard-thermal-loop thermodynamics for QCD". Physics Letters B. 696 (5): 468. arXiv:1009.4644. Bibcode:2011PhLB..696..468A. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2010.12.070.
- ^ Andersen; Michael Strickland; Nan Su (2010). "Gluon Thermodynamics at Intermediate Coupling". Physical Review Letters. 104 (12). arXiv:0911.0676. Bibcode:2010PhRvL.104l2003A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.122003.
- ^ Blaizot; Iancu; Rebhan (2003). "Thermodynamics of the high-temperature quark-gluon plasma". arXiv:hep-ph/0303185.
{{cite arXiv}}:|class=ignored (help)
External links
- The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory
- The Alice Experiment at CERN
- The Indian Lattice Gauge Theory Initiative
- Quark matter reviews: 2004 theory, 2004 experiment
- Quark-Gluon Plasma reviews: 2011 theory
- Lattice reviews: 2003, 2005
- BBC article mentioning Brookhaven results (2005)
- Physics News Update article on the quark-gluon liquid, with links to preprints
- Read for free : "Hadrons and Quark-Gluon Plasma" by Jean Letessier and Johann Rafelski Cambridge University Press (2002) ISBN 0-521-38536-9, Cambridge, UK;