Donbas strategic offensive (August 1943)
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (March 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Donbas strategic offensive | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Eastern Front | |||||||
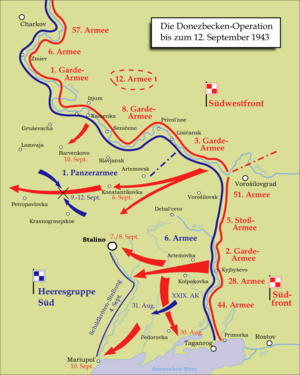 Map of the Donbas offensive (in German) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Fyodor Tolbukhin Rodion Malinovsky |
Erich von Manstein Karl-Adolf Hollidt Eberhard von Mackensen | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
Southern Front Southwestern Front | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
1,053,000 men[1] 1,257 tanks and assault guns[1] 21,000 guns and mortars[1] 1,400 combat aircraft[1] | Around 400,000 men | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
273,522 men[1]
814 guns and mortars[1] 327 aircraft[1] |
28,940 men (German claim) (11 August – 20 September)[2]
| ||||||
The Donbas strategic offensive was a strategic operation of the Soviet Red Army on the Eastern Front of World War II with the goal of the liberation the Donetsk Basin, or Donbas.
Situation Prior to the Offensive
German
With the battle of Kursk raging to the north, and significant reserves pulled from both 1st Panzer and Sixth Armies to allow for such a grand offensive, the German situation in the Donbas area was not particularly solid. 1st Panzer Army under von Mackensen had no Panzer divisions at its disposal, and instead had nine infantry divisions that had been thinning significantly for Manstein's push on the southern portion of the Kursk salient. Likewise, Sixth Army, who had only just be reconstructed from its annihilation at Stalingrad, was allotted eight infantry and one GebirgsJager division.[3]
The troops that manned this sector of the front were not as well-equipped as their northern counterparts, and some Luftwaffe field divisions were included in the order of battle for Sixth and First Panzer Armies. To make matters worse, replacements had not kept up with growing loses on the Eastern front as a whole, and this sector was no different. A previous Soviet offensive in the area had been beaten back with the assistance of SS and regular Panzer divisions, but these had since been removed to address more pressing matters to the north; in particular the battles surrounding Kharkov.[4] Therefore, on the 16th of August, when the Red Army struck, the German forces in this area would be hard pressed to hold the line without the assistance of either the river Donets or strong armored support to push back the Soviet onslaught.
Soviet
After the failed offensive just weeks earlier, Stavka ordered the Southwest and South fronts to reconsider their attack, and make preparations for a renewed offensive later in August. Similar to the offensive in July, the Russians intended to surround the bulk of the Sixth army closing the gap around the city of Stalino. From the north, the 8th and 3rd Guard armies were to strike southward toward Debal'cevo, whilst 44th, 28th, 2nd Guard, and 5th Shock armies were to push generally westward and keep up the pressure on Sixth army's weak units.
The main concern from Southern Front's commander, FI Tolbuchin, was the relative weakness of his units after July's failed attacks. For this, he was granted a slight delay of two days after Southwest Front had begun its offensive against First Panzer Army. This respite would allow the Germans to detect the intentions of the Soviet plans, was considered necessary to prevent a disaster.[5]
The course of the operation
The Donbas operation began on August 13, 1943 with the offensive of the right wing of the Southwestern Front. These troops forced the Donets river and advancing along the right bank of the river, helped the Steppe Front with the liberation of Kharkiv.
On August 16, the Southern Front troops went on the offensive and broke through the German defense on the Mius River. On August 30, Taganrog was liberated in combination with a naval operation. The XXIX Army Corps was encircled but succeeded to break out, be it with heavy casualties.
As Army Group South was threatened with dismemberment and destruction, Hitler finally allowed Manstein to withdraw across the Dnieper on 15 September.
On September 1, German troops had already begun to retreat on the entire front in the Donbas. On September 5, 1943, Soviet troops liberated Horlivka and Artemivsk, and on September 8, the largest Donbas city, Stalino (now Donetsk).
During the withdrawal, Manstein ordered scorched earth actions, and Soviet partisans hampered the retreating German Army.
Pursuing the enemy, the troops of the South-Western Front on September 22 chased the Germans behind the Dnieper at Dnipropetrovsk (Dnipro) and Zaporizhzhia, while troops of the Southern Front on the same day reached the Molochna River. This ended the Donbas operation.[6]
Results
As a result of the Soviet victory, the German Army had been forced to fall back more than 300 kilometers to the Panther–Wotan line along the Dnieper, which was still under construction.
Furthermore, the contribution of the important economic region no longer benefited Nazi Germany, and by 1944 the Soviet Union had restarted its industrial operations in the region. As a byproduct of the Soviet offensive, the German forces was also forced to retreat from the Kuban Bridgehead, as the Soviets advanced towards the Perekop Isthmus, which they took in November 1943.
Postwar assessment
In 1949, Erich von Manstein was tried for war crimes in Ukraine, found guilty on 9 of 17 charges, and sentenced to 18 years in prison. He was released in 1953 due to health problems and support of Konrad Adenauer, Winston Churchill, and others.[7]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Frieser et al. 2007, p. 351.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 25 May 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Schramm, Percy (2002). War Diary of the High Command of the Wehrmacht Vol. 3. Bonn. p. 732.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Manstein, Erich von (1976). Lost Victories. Munich. p. 517.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Wassilewski, AM (1977). A Matter of Whole Life. Berlin (East). p. 314.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Erich von Manstein: Verlorene Siege. Bernard & Graefe Verlag für Wehrwesen, München 1976, ISBN 3-7637-5051-7.
- ^ Melvin, Mungo (2010). Manstein: Hitler's Greatest General. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-297-84561-4.
Bibliography
- Frieser, Karl-Heinz; Schmider, Klaus; Schönherr, Klaus; Schreiber, Gerhard; Ungváry, Kristián; Wegner, Bernd (2007). Die Ostfront 1943/44 – Der Krieg im Osten und an den Nebenfronten [The Eastern Front 1943–1944: The War in the East and on the Neighbouring Fronts] (in German). Vol. VIII. München: Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt. ISBN 978-3-421-06235-2.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
