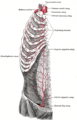
Superior thoracic aperture
| Superior thoracic aperture | |
|---|---|
 The thorax from in front. (Superior thoracic aperture visible at top.) | |
 Superior thoracic aperture seen from above | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | apertura thoracis superior |
| TA98 | A02.3.04.003 |
| TA2 | 1098 |
| FMA | 7566 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The superior thoracic aperture, also known as the thoracic outlet, or thoracic inlet refers to the opening at the top of the thoracic cavity.[1] It is also clinically referred to as the thoracic outlet, in the case of thoracic outlet syndrome. A lower thoracic opening is the inferior thoracic aperture.
Structure
The superior thoracic aperture is essentially a hole surrounded by a bony ring, through which several vital structures pass. It is bounded by: the first thoracic vertebra (T1) posteriorly; the first pair of ribs laterally, forming lateral C-shaped curves posterior to anterior; and the costal cartilage of the first rib and the superior border of the manubrium anteriorly.
Dimensions
The adult thoracic outlet is around 6.5 cm antero-posteriorly and 11 cm transversely. Because of the obliquity of the first pair of ribs, the aperture slopes antero-inferiorly.
Relations
The clavicle articulates with the manubrium to form the anterior border of the thoracic outlet. Above the superior thoracic outlet is the root of the neck, and the superior mediastinum is inferiorly related. The brachial plexus is a superolateral relation of the thoracic outlet. The brachial plexus emerges between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, superior to the first rib, and passes obliquely and inferiorly, underneath the clavicle, into the shoulder and then the arm. Impingement of the plexus in the region of the scalenes, ribs, and clavicles is responsible for thoracic outlet syndrome.
Function
Structures that pass through the thoracic inlet include:
- trachea
- oesophagus
- thoracic duct
- apices of the lungs
- nerves
- vessels
- arteries
- left and right common carotid arteries
- left subclavian arteries
- veins
- arteries
- lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels
This is not an exhaustive list. There are several other minor, but important, vessels and nerves passing through, and an abnormally large thyroid gland may extend inferiorly through the thoracic inlet into the superior mediastinum.
The oesophagus lies against the body of the T1 vertebra, separated from it by the prevertebral fascia, and the trachea lies in front of the oesophagus, in the midline, and may touch the manubrium. The apices of the lungs lie to either side of the oesophagus and trachea, and is separated from them by the other vessels and nerves listed above. Furthermore, they extend slightly superior past the level of the inlet (e.g. the horizontal plane of the first rib).
Additional images
-
Vasculature entering at top. (Note: internal mammary is now known as internal thoracic artery.)
References
- ^ Knipe, Henry. "Superior thoracic aperture | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- McMinn, RMH (Ed) (1994) Last's Anatomy: Regional and applied (9th Ed). London: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-04662-X
- Moore Clinically Oriented Anatomy: Moore, Dalley, Agur - South Asian Edition (7th Ed.): Wolters Kluwer (India) Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi. ISBN 978-81-8473-912-1