Necrosis
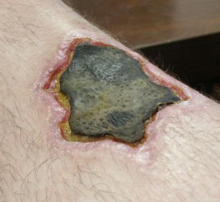
Necrosis (from the Greek νεκρός, "dead", νέκρωσις, "death, the stage of dying, the act of killing") is the premature death of cells and living tissue. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma. This is in contrast to apoptosis, which is a naturally occurring cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal.
Cells that die due to necrosis do not usually send the same chemical signals to the immune system that cells undergoing apoptosis do. This prevents nearby phagocytes from locating and engulfing the dead cells, leading to a build-up of dead tissue and cell debris at or near the site of the cell death. For this reason, it is often necessary to remove necrotic tissue surgically, a process known as debridement.
Classification

There are seven distinctive morphologic patterns of necrosis:
- Coagulative necrosis is typically seen in hypoxic (low-oxygen) environments, such as an infarction. Cell outlines remain after cell death and can be observed by light microscopy. Hypoxic infarcts in the brain however result in Liquefactive necrosis.
- Liquefactive necrosis (or colliquative necrosis) is usually associated with cellular destruction and pus formation (e.g., pneumonia). This is typical of bacterial or, sometimes, fungal infections because of their ability to stimulate an inflammatory reaction. Ischemia (restriction of blood supply) in the brain produces liquefactive, rather than coagulative necrosis due to the lack of any substantial supportive stroma.
- Gummatous necrosis is restricted to necrosis involving spirochaetal infections (e.g., syphilis).
- Haemorrhagic necrosis is due to blockage of the venous drainage of an organ or tissue (e.g., in testicular torsion).
- Caseous necrosis is a specific form of coagulation necrosis typically caused by mycobacteria (e.g., tuberculosis), fungi, and some foreign substances. It can be considered a combination of coagulative and liquefactive necrosis.
- Fatty necrosis results from the action of lipases on fatty tissues (e.g., acute pancreatitis, breast tissue necrosis).
- Fibrinoid necrosis is caused by immune-mediated vascular damage. It is marked by deposition of fibrin-like proteinaceous material in arterial walls, which appears smudgy and eosinophilic on light microscopy.
Arachnogenic necrosis
In the US, both brown recluse Spider bites and yellow sac spider bites (genus Loxosceles) have been proven to consistently cause necrosis.[1] Other spiders of the same genus, such as the Chilean recluse in South America, have similarly been shown to cause necrosis in other countries.[2][3]
The belief that, in the US, only brown recluse have necrotic venom, is held by many. However, the yellow sac spider, which is also found across the US, has necrotic venom as well. Often a doctor will diagnose a yellow sac spider bite as a brown recluse bite. This does not cause much harm, as the venom is essentially similar and therefor has a similar treatment, the venom itself varying only in strength (the yellow sac spider bite is not deadly, and will spread to about two handspans surrounding the bite and then stop). The unfortunate side effect of this prognosis is people believing that brown recluse live in places they do not, such as California where the climate cannot foster brown recluse. [4][5]
A few other spiders commonly suspected (but not all conclusively proven) of having necrotic venom include:
Causes
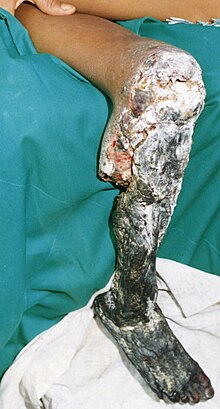
Cellular necrosis can be induced by a number of external sources, including injury, infection, cancer, infarction, poisons, ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species), and inflammation. For example, an infarction (blockage of blood flow to muscular tissue) causes necrosis of muscle tissue due to lack of oxygen to the affected cell, such as occurs in a myocardial infarction -- a heart attack. Certain spider (brown recluse) and snake (rattlesnake, Bothrops) venoms can cause necrosis of the tissue near the bite wound, as can a Group A streptococcus infection (one of the "flesh-eating" bacteria).[citation needed]
Necrotic tissue does not undergo the same chemical reactions that normally dying apoptotic tissue does. The sudden failure of one part of the cell triggers a cascade of events. In addition to the lack of chemical signals to the immune system, cells undergoing necrosis can release harmful chemicals into the surrounding tissue. In particular, cells contain small organelles called lysosomes, which are capable of digesting cellular material. Damage to the lysosome membrane can trigger release of the contained enzymes, destroying other parts of the cell. Worse, when these enzymes are released from the non-dead cell, they can trigger a chain reaction of further cell death. If a sufficient amount of contiguous tissue necrotizes, it is termed gangrene. Proper care and treatment of wounds or animal bites plays a key role in preventing this type of widespread necrosis. During a surgical biopsy, this necrosis chain-reaction is halted by fixation or freezing.[citation needed]
Necrosis typically begins with cell swelling, chromatin digestion, and disruption of the plasma membrane and organelle membranes. Late necrosis is characterized by extensive DNA hydrolysis, vacuolation of the endoplasmic reticulum, organelle breakdown, and cell lysis. The release of intracellular content after plasma membrane rupture is the cause of inflammation in necrosis.[citation needed]
Treatment
Treatment of necrosis typically involves two distinct processes. Usually, the underlying cause of the necrosis must be treated before the dead tissue itself can be dealt with. For example, a snake or spider bite victim will receive anti-venom to halt the spread of the toxins, while an infected patient will receive antibiotics.
Even after the initial cause of the necrosis has been halted, the necrotic tissue will remain in the body. The body's immune response to apoptosis, the automatic breaking down and recycling of the cell material, is not triggered by necrotic cell death.
The standard therapy of necrosis (wounds, bedsores, burns, etc.) is surgical removal of necrotic tissue. Depending on the severity of the necrosis, this may range from removal of small patches of skin, to complete amputation of affected limbs or organs. Chemical removal, via an enzymatic debriding agent, is another option. In select cases, special maggot therapy has been utilized with good results.
In plants
If calcium is deficient, pectin cannot be synthesized, and therefore the cell walls cannot be bonded and thus an impediment of the meristems. This will lead to necrosis of stem and root tips and leaf edges.[7]
See also
- Avascular necrosis
- Gangrene
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Box jellyfish
References
- ^ Atkins J, Wingo C, Sodeman W (1957). "Probable cause of necrotic spider bite in the Midwest". Science. 126 (3263): 73. doi:10.1126/science.126.3263.73. PMID 13442644.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Maynor ML, Moon RE, Klitzman B, Fracica PJ, Canada A (1997). "Brown recluse spider envenomation: a prospective trial of hyperbaric oxygen therapy". Acad Emerg Med. 4 (3): 184–92. doi:10.1111/j.1553-2712.1997.tb03738.x. PMID 9063544.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Maynor ML, Abt JL, Osborne PD (1992). "Brown Recluse Spider Bites: Beneficial Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen". J. Hyperbaric Med. 7 (2): 89–102. ISSN 0884-1225. Retrieved 2008-07-25.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ http://entomology.wsu.edu/insectoftheweek/archive/yellowsacspider.html
- ^ http://lancaster.unl.edu/pest/resources/SacSpiders.shtml
- ^ Vetter R, Isbister G (2004). "Do hobo spider bites cause dermonecrotic injuries?". Ann Emerg Med. 44 (6): 605–7. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2004.03.016. PMID 15573036.
- ^ Capon, Brian Botany for Gardeners, p. 178, Timber Press, 2010, 3rd edition.
External links
- Life In The Fast Lane: toxicology Conundrum #018
- Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections". Retrieved 2008-07-25.
