Duty cycle
In engineering, the duty cycle of a machine or system is the time that it spends in an active state as a fraction of the total time under consideration.[1]
The term is often used pertaining to electrical devices, e.g., switching power supplies. A 60% duty cycle means the power is on 60% of the time and off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second – or for say, irrigation pumps, days – depending on how long the device's period is. Here one period is the length of time it takes for the device to go through a complete on/off cycle. The term "duty cycle" has no agreed meaning for aperiodic devices.
Definition
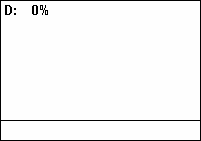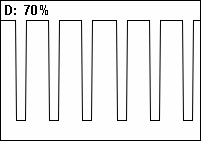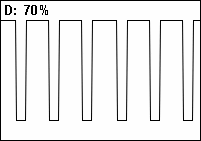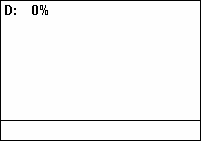
In a periodic event, duty cycle is the ratio of the duration of the event to the total period.
- duty cycle [2]
where
- is the duration that the function is active
- is the period of the function.
Examples
Electrical machines
A motor runs for one out of 100 seconds, or 1/100 of the time, and therefore its duty cycle is 1/100, or 1 percent.[3]
Electronics
In an ideal pulse train (one having rectangular pulses), the duty cycle is the pulse duration divided by the pulse period.[4] For example, a pulse train in which the pulse duration is 1 μs and the pulse period is 4 μs has a duty cycle of 25%. The pulse duration is normally calculated for positive pulses unless "negative duty cycle" is specified.
The duty cycle of a non-rectangular waveform, such as a sine or triangle wave, is defined as the time that the waveform spends above zero volts as a fraction of the period.[5]
Digital signal processing
In a continuously variable slope delta (CVSD) modulation converter, the mean proportion of binary "1" digits at the converter output in which each "1" indicates a run of a specified number of consecutive bits of the same polarity in the digital output signal.
Electronic music
Music synthesizers vary the duty cycle of their audio-frequency oscillators to obtain a subtle effect on the tone colors. This technique is known as pulse-width modulation (PWM).
Welding
In equipment such as a welding power supply, the maximum duty cycle is defined as the percentage of time in a 10 minute period that it can be operated continuously before overheating.[6] Duty cycle is the percentage of time that a device or signal is ON, compared to its period.
Printers and copiers
In the printer / copier industry, the duty cycle specification refers to the rated throughput (that is, printed pages) of a device per month.
References
- ^ "Definition: duty cycle", Institute for Telecommunication Sciences, Boulder, Colorado, accessed 2011-03-23; from Federal Standard 1037C, "Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunication Terms", 1996
- ^ "555 timer", Doctronics, accessed 2011-03-23
- ^ "Electric Motors", Machine Design, accessed 2011-03-23
- ^ "Clock Positive Duty Cycle", Aubrax, accessed 2011-03-23
- ^ MAX038 High-Frequency Function Generator Data Sheet 19-0266; Rev 7; 8/07, Maxim Integrated Products, Inc., accessed 2011-03-23
- ^ "What does the term duty cycle mean?", ZENA, Inc. welding systems



