Andersonville Prison
Andersonville National Historic Site | |
 Reconstruction of a section of the stockade wall | |
| Location | Macon / Sumter counties, Georgia, USA |
|---|---|
| Nearest city | Andersonville, Georgia, Americus, Georgia |
| Area | 514 acres (208 ha)[3] |
| Built | April 1864 |
| Visitation | 1,436,759 (2011)[4] |
| NRHP reference No. | 70000070[1][2] |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | October 16, 1970 |
| Designated NHS | October 16, 1970 |
The Andersonville National Historic Site, located near Andersonville, Georgia, preserves the former Camp Sumter (also known as Andersonville Prison), a Confederate prisoner-of-war camp during the American Civil War. Most of the site lies in southwestern Macon County, adjacent to the east side of the town of Andersonville. As well as the former prison, the site also contains the Andersonville National Cemetery and the National Prisoner of War Museum.
Of the approximately 45,000 Union prisoners held at Camp Sumter during the war, nearly 13,000 died of starvation, malnutrition, diarrhea or communicable diseases.[5]
Conditions

Legend | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Areas of the prison as labelled by Ransom:Column-generating template families<div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
{| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead. |
The prison, which opened in February 1864,[6] originally covered about 16.5 acres (67,000 m2) of land enclosed by a 15-foot (4.6 m) high stockade. In June 1864 it was enlarged to 26.5 acres (107,000 m2). The stockade was in the shape of a rectangle 1,620 feet (490 m) by 779 feet (237 m). There were two entrances on the west side of the stockade, known as "north entrance" and "south entrance".[7]
A prisoner described his entry into the prison camp:
As we entered the place, a spectacle met our eyes that almost froze our blood with horror, and made our hearts fail within us. Before us were forms that had once been active and erect;—stalwart men, now nothing but mere walking skeletons, covered with filth and vermin. Many of our men, in the heat and intensity of their feeling, exclaimed with earnestness. "Can this be hell?" "God protect us!" and all thought that He alone could bring them out alive from so terrible a place. In the center of the whole was a swamp, occupying about three or four acres of the narrowed limits, and a part of this marshy place had been used by the prisoners as a sink, and excrement covered the ground, the scent arising from which was suffocating. The ground allotted to our ninety was near the edge of this plague-spot, and how we were to live through the warm summer weather in the midst of such fearful surroundings, was more than we cared to think of just then.[8]
Further descriptions of the camp can be found in the diary of Ransom Chadwick, a member of the 85th New York Infantry Regiment. Chadwick and his regimental mates were taken to the Andersonville Prison, arriving on April 30, 1864.[9]
Father Peter Whelan arrived on 16 June 1864 to muster the resources of the church and help provide relief to the prisoners.
At Andersonville, a light fence known as "the dead line" was erected approximately 19 feet (5.8 m) inside the stockade wall. It demarcated a no-man's land that kept prisoners away from the stockade wall, which was made of rough-hewn logs about 16 feet (4.9 m) high.[10] Anyone crossing or even touching this "dead line" was shot without warning by sentries in the pigeon roosts.

At this time in the war, Andersonville Prison was frequently undersupplied with food. This applied both to prisoners and the Confederate personnel within the fort. However, it is clear that the prisoners received much less than the guards who were not emaciated like the prisoners were and did not die from scurvy (vitamin C deficiency), probably the main cause of mortality (along with diarrhea caused by living in filth and drinking water from a creek filled at all times with fecal material from thousands of sick and dying men). Even when sufficient quantities were available, the supplies were of poor quality and poorly prepared. Although the prison was surrounded by forest, very little wood was allowed to the prisoners. This and the lack of utensils made it almost impossible for the prisoners to cook the main food they received, poorly milled corn flour. During the summer of 1864 Union prisoners suffered greatly from hunger, exposure and disease. Within seven months, about a third of them died from what was diagnosed as dysentery and scurvy and were buried in mass graves, the standard practice by Confederate prison authorities at Andersonville. In 1864 the Confederate Surgeon General asked Joseph Jones, an expert on infectious disease, to investigate the high mortality rate at the camp. He concluded that it was due to "scorbutic dysentery" (bloody diarrhea caused by vitamin C deficiency). Drisdelle claims that hookworm disease, a condition not recognized or known during the Civil War was the major cause of much of the mortality.[11] However, the signs and symptoms reported by the prisoners are identical with those of scurvy and rampant diarrhea, not of hookworm infestation.
The water supply from Stockade Creek became polluted when too many Union prisoners were housed by the Confederate authorities within the prison walls. Part of the creek was used as a sink and the men were forced to wash themselves in the creek.
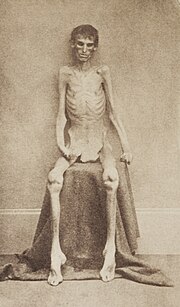
The guards, disease, starvation and exposure were not all that prisoners had to deal with. A group of prisoners, calling themselves the Andersonville Raiders, attacked their fellow inmates to steal food, jewelry, money and clothing. They were armed mostly with clubs and killed to get what they wanted. Another group rose up, organized by Peter "Big Pete" Aubrey, to stop the larceny, calling themselves "Regulators". They caught nearly all of the Raiders, who were then tried by the Regulators' judge, Peter McCullough, and jury, selected from a group of new prisoners. This jury, upon finding the Raiders guilty, set punishment that included running the gauntlet, being sent to the stocks, ball and chain and, in six cases, hanging.[12]
The conditions were so poor that in July 1864 Captain Wirz paroled five Union soldiers to deliver a petition signed by the majority of Andersonville's prisoners asking that the Union reinstate prisoner exchanges. The request in the petition was denied and the Union soldiers, who had sworn to do so, returned to report this to their comrades.[13]
In the latter part of the summer of 1864 the Confederacy offered to unconditionally release prisoners if the Union would send ships (Andersonville is inland, with access possible only via rail and road) to retrieve them. In the autumn of 1864, after the capture of Atlanta, all the prisoners who were well enough to be moved were sent to Millen, Georgia, and Florence, South Carolina. At Millen, better arrangements prevailed, and after General William Tecumseh Sherman began his march to the sea, the prisoners were returned to Andersonville, where conditions were somewhat improved.
During the war, 45,000 prisoners were received at Andersonville prison, and of these nearly 13,000 died.[5] The nature of the deaths and the reasons for them are a continuing source of controversy among historians. Some contend that they were a result of deliberate Confederate war crimes toward Union prisoners and others that they were the result of disease promoted by severe overcrowding, the shortage of food in the Confederate States, the incompetence of the prison officials, and the refusal of Union authorities to reinstate the prisoner exchange, thus overfilling the stockade.[14]
A young Union prisoner, Dorence Atwater, had been chosen to record the names and numbers of the dead at Andersonville for the use of the Confederacy and the federal government after the war ended. He believed the federal government would never see the list, and was right in this assumption, as it turned out. He sat next to Henry Wirz, who was in charge of the prison pen, and secretly kept his own list among other papers. When Atwater was released, he put the list in his bag and took it through the lines without being caught. It was published by the New York Tribune when Horace Greeley, the owner, learned that the federal government had refused and given Atwater much grief. It was Atwater's opinion that Andersonville was indeed trying to make soldiers unfit to fight.[15]
Andersonville's decrepit conditions were chronicled in the diary of P.O.W. Newell Burch. Burch of the 154th New York Volunteer Infantry, was captured on the first day of the Battle of Gettysburg and imprisoned at Belle Isle and then Andersonville. He is credited with being the longest held Union prisoner of war during the Civil War, a total of 661 days in Confederate hands.[16] His diary is in the collection of the Dunn County Historical Society in Menomonie, Wisconsin, and a mimeographed copy is in the Wisconsin Historical Society archives.[17]
Aftermath
Andersonville Prison was liberated in May 1865.[18]

After the war Henry Wirz, commandant of the inner stockade at Camp Sumter, was tried by a military tribunal on charges of conspiracy and murder. The trial was presided over by Union General Lew Wallace and featured chief Judge Advocate General (JAG) prosecutor Norton Parker Chipman.[citation needed]
A number of former prisoners testified on conditions at Andersonville, many accusing Wirz of specific acts of cruelty, for some of which Wirz was not even present in the camp. The court also considered official correspondence from captured Confederate records. Perhaps the most damaging was a letter to the Confederate surgeon general by Dr. James Jones, who in 1864 was sent by Richmond to investigate conditions at Camp Sumter.[19] Jones had been appalled by what he found and his graphically detailed report to his superiors all but closed the case for the prosecution. Wirz presented evidence that he pleaded to Confederate authorities to try to get more food and tried to improve the conditions for the prisoners inside.[citation needed]
Wirz was found guilty and was sentenced to death, and on November 10, 1865, he was hanged. Wirz was the only Confederate official to be tried and convicted of war crimes resulting from the Civil War (but see reference to Champ Ferguson). The revelation of the prisoners' sufferings was one of the factors that shaped public opinion in the North regarding the South after the close of the Civil War.[citation needed]
In 1890 the Grand Army of the Republic, Department of Georgia, bought the site of Andersonville Prison through membership and subscriptions.[20] In 1910 the site was donated to the federal government by the Woman's Relief Corps[21] (auxiliary to the Grand Army of the Republic).[22]
National Prisoner of War Museum
The National Prisoner of War Museum opened in 1998 as a memorial to all American prisoners of war. Exhibits use art, photographs, displays and video presentations to focus on the capture, living conditions, hardships and experiences of American prisoners of war in all periods. The museum also serves as the park's visitor center.[23]
Andersonville National Cemetery

The cemetery is the final resting place for the Union prisoners who died while being held at Camp Sumter/Andersonville as POWs. The prisoners' burial ground at Camp Sumter has been made a national cemetery. It contains 13,714 graves, of which 921 are marked "unknown".[citation needed]
As a National Cemetery, it is also used as a burial place for more recent veterans and their dependents.[24]
Andersonville National Historic Site
Visitors can walk the 26.5 acres (10.7 ha) site of Camp Sumter, which has been outlined with double rows of white posts. Two sections of the stockade wall have been reconstructed, the north gate and the northeast corner.
Depictions in popular culture
- Andersonville is a novel by MacKinlay Kantor concerning the Andersonville prison. Published in 1955, it won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction the following year.
- The 1959 play The Andersonville Trial (presented on PBS in 1971) depicts the 1865 trial of Andersonville commandant Henry Wirz.
- The 1996 TV Movie Andersonville directed by John Frankenheimer, tells the story of the notorious Confederate prison camp.[25]
- Escape from Andersonville: A Novel of the Civil War. Macmillan. 2008. p. 352. ISBN 0-312-36373-7. Retrieved 2011-08-14.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - The 2009 historical novel by Max R. Terman, Hiram's Honor: Reliving Private Terman's Civil War (Hillsboro, KS: TESA Books, ISBN 0-615-27812-4).[26]
See also
- Libby Prison
- Salisbury Prison
- Florence Stockade
- Camp Lawton
- Dix-Hill Cartel – the agreement reached in July 1862 to regulate prisoner of war exchanges
- Immortal Six Hundred
- Prisoner-of-war camp
References
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. April 15, 2008.
- ^ Horrors of Andersonvile James K. Polk
- ^ "Listing of acreage – December 31, 2011" (XLSX). Land Resource Division, National Park Service. Retrieved 2012-03-30. (National Park Service Acreage Reports)
- ^ "NPS Annual Recreation Visits Report". National Park Service. Retrieved 2012-03-30.
- ^ a b "Camp Sumter / Andersonville Prison". National Park Service. Retrieved 2013-02-14.
- ^ "Andersonville Civil War Prison Historical Background". 2009-11-06.
- ^ Pamphlet Andersonville, National Park Service
- ^ Kellogg, Robert H. Life and Death in Rebel Prisons. Hartford, CT: L. Stebbins, 1865.
- ^ "Ransom Chadwick: An Inventory of His Andersonville Prison Diary at the Minnesota Historical Society". Mnhs.org. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ Andersonville, Giving Up the Ghost, A Collection of Prisoners' Diaries, Letters and Memoirs by William Stryple
- ^ Drisdelle R. Parasites. Tales of Humanity's Most Unwelcome Guests. Univ. of California Publishers, 2010. p. 86. ISBN 978-0-520-25938-6.
- ^ "Andersonville: Prisoner of War Camp-Reading 2". Cr.nps.gov. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ Prof. Linder. "Scopes Trial Home Page - UMKC School of Law". Law2.umkc.edu. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ Marvel, William, Andersonville: The Last Depot, University of North Carolina Press, 1994.
- ^ Safranski, Debby Burnett, Angel of Andersonville, Prince of Tahiti: The Extraordinary Life of Dorence Atwater, Alling-Porterfield Publishing House, 2008.
- ^ Andreas, A.T., Proprietor (1881). History of Northern Wisconsin, An Account of Its Settlement, Growth, Development and Resources; an Extensive Sketch of its Counties, Cities, Towns and Villages. Chicago: The Western Historical Company via USGenWeb. p. 283.
{{cite book}}: line feed character in|title=at position 141 (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Plate: front view: Object Description". Wisconsin Decorative Arts Database, Wisconsin Historical Society. Retrieved April 9, 2013.
- ^ "Andersonville: Earlier War Crimes "Abuse" Trial | Strike-The-Root: A Journal Of Liberty". Strike-The-Root. 2004-05-11. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ A Perfect Picture of Hell: Eyewitness Accounts by Civil War Prisoners from the 12th Iowa, copyright 2001, University of Iowa Press
- ^ Roster and History of the Department of Georgia (States of Georgia and South Carolina) Grand Army of the Republic, Atlanta, Georgia: Syl. Lester & Co. Printers, 1894, 5.
- ^ "Andersonville National Historic Site - Park Statistics (U.S. National Park Service)". nps.gov. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "WRC National Woman's Relief Corps, Auxiliary to the Grand Army of the Republic, Inc". suvcw.org. Archived from the original on 9 June 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Andersonville National Historic Site - National Prisoner of War Museum (U.S. National Park Service)". nps.gov. Archived from the original on 30 May 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Andersonville National Historic Site. Burial Guidelines and Qualifications. Accessed July 21, 2013.
- ^ "Andersonville (TV 1996) - IMDb". imdb.com. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "Andersonville's Whirlpool of Death". Clevelandcivilwarroundtable.com. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
Further reading
- Chipman, Norton P. The Horrors of Andersonville Rebel Prison. San Francisco: Bancroft, 1891.
- Cloyd, Benjamin G. Haunted by Atrocity: Civil War Prisons in American Memory. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2010.
- Genoways, Ted & Hugh H. Genoways (eds.). A Perfect Picture of Hell: Eyewitness Accounts by Civil War Prisoners from the 12th Iowa. Iowa City: University of Iowa Press, 2001.
- McElroy, John. Andersonville: A Story of Rebel Military Prisons Toledo: D.R. Locke, 1879.
- Ransom, John. Andersonville Diary. Auburn, NY: Author, 1881.
- Rhodes, James, History of the United States from the Compromise of 1850, vol. V. New York: Macmillan, 1904.
- Spencer, Ambrose, A Narrative of Andersonville. New York: Harper, 1866.
- Stevenson, R. Randolph. The Southern Side, or Andersonville Prison. Baltimore: Turnbull, 1876.
- Voorhees, Alfred H. The Andersonville Prison Diary of Alfred H. Voorhees. 1864.
External links
- Andersonville National Historic Site at NPS.gov – official site
- Andersonville Civil War Prison Historical Background
- "Andersonville: Prisoner of War Camp", a National Park Service Teaching with Historic Places (TwHP) lesson plan
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Andersonville Prison
- Andersonville Civil War Prison
- Slide show of visit to Andersonville
- "WWW Guide to Civil War Prisons" (2004)
- "The Rebel Prison Pen at Andersonville, Georgia" 1874 newspaper transcript by a former prison guard
- Andersonville National Cemetery at Find a Grave
- American Civil War museums in Georgia (U.S. state)
- American Civil War prison camps
- American Civil War cemeteries
- Cemeteries on the National Register of Historic Places in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Defunct prisons in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Historic districts in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Military and war museums in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Museums in Macon County, Georgia
- National Historic Sites in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Prison museums in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Protected areas of Sumter County, Georgia
- Military monuments and memorials in the United States
- War crimes in the United States
- Institutions accredited by the American Alliance of Museums
- Protected areas of Macon County, Georgia

