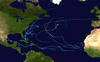
1967 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1967 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | June 10, 1967 |
| Last system dissipated | October 31, 1967 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Beulah |
| • Maximum winds | 160 mph (260 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 923 mbar (hPa; 27.26 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 29 |
| Total storms | 8 |
| Hurricanes | 5 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 1 |
| Total fatalities | 79 |
| Total damage | $207 million (1967 USD) |
The 1967 Atlantic hurricane season featured the bulk of its activity in September and October, although weaker tropical depressions were observed from June to October. The first depression originated on June 10, and the final storm – Heidi – lost tropical characteristics on October 31. Hurricane Beulah – the strongest storm of the season – was also the most damaging, causing 59 deaths and $207 million in damage (1967 USD) along its 16 day path. Beulah formed on September 5 and soon after crossed southern Martinique into the Caribbean Sea. On the island, it dropped dropped 18.7 in (475 mm) of rainfall in Les Anses-d'Arlet, causing severe flooding. Widespread evacuations occurred along the southern coast of the Dominican Republic due to fears of a repeat of Hurricane Inez from the previous year. After brushing the south coast of Hispaniola, the hurricane weakened and re-intensified, striking the Yucatán Peninsula and later near the United States/Mexico border. There, it caused severe river flooding, killing 34 people in the two countries.
Hurricanes Arlene and Chloe, as well as several tropical depressions, originated from tropical waves that left the coast of Africa. Chloe lasted for 15 days, eventually dissipating over France after wrecking a ship offshore northern Spain, killing 14 people. Hurricane Doria co-existed with Beulah and Chloe, taking an unusual trajectory over the eastern United States; it killed three people in a boating accident offshore New Jersey. In late September, Tropical Storm Edith was a minimal storm that moved through the Lesser Antilles without serious impact. Hurricane Fern killed three people when it struck Mexico north of Tampico. Tropical Storm Ginger existed in the far eastern Atlantic in early October, and Hurricane Heidi stalled over the northern Atlantic Ocean at the end of the month.
Season summary

The season began on June 1, which was the date when the National Hurricane Center (NHC) activated radar stations across the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico.[1] The season ended on November 30, which ended the conventional delimitation of the time period when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin.[2] At the end of the season, NHC director Gordon Dunn retired and was replaced by Robert Simpson.[3] For the first time in 1967, the NHC tracked weaker, developing tropical disturbances, observing that 90% of systems do not develop. Tropical cyclogenesis – the process in which a tropical cyclone develops – resulted mainly from tropical waves, the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), and decaying frontal systems. There were 30 tropical waves that exited the west coast of Africa at Dakar, Senegal, of which 14 became tropical depressions. Another 20 tropical disturbances originated offshore the Mid-Atlantic states, and 7 disturbances derived from cold-core lows.[4]
The first named storm – Arlene – did not form until August 28 and became a hurricane on September 2. At the time, only seven known seasons began later, although 1967 would the most active among these late starting seasons. The latency was caused by a stronger than normal ridge across the Atlantic Ocean, which suppressed convective activity across the basin and prevented the formation of strong low pressure areas.[5] From June to October, the NHC tracked 29 tropical depressions, which is an area of disturbed weather that has a closed circulation and maximum sustained winds of less than 39 mph (63 km/h). It was the first year that the NHC tracked the weaker depressions. Operationally, the agency followed and numbered 23 depressions, and discovered in a post-season analysis that another six systems became depressions. Eight depressions attained gale-force winds and were named from a sequential list, and six storms intensified to hurricane-strength – 74 mph (119 km/h).[4]
Storms
Hurricane Arlene
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 28 – September 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 982 mbar (hPa) |
Following a series of weak tropical depressions emerging from the west coast of Africa, the ITCZ became more active at the end of August. A tropical wave exited the coast of Africa on August 24, and by the next day, a Pan American flight observed a circulation with falling pressures. Based on the system's organization on satellite imagery, the NHC assessed that Tropical Depression Five developed late on August 28 about 740 mi (1,190 km) west of Cabo Verde. Steered by a strong ridge to the northeast, the nascent system tracked northwestward. After two ships reported gale-force winds, the NHC began issuing advisories on Tropical Storm Arlene at 08:00 UTC on August 30.[4][5] That day, the Hurricane Hunters observed winds of 70 mph (110 km/h),[5] although the storm was well below hurricane intensity at that time;[6] this was due to Arlene's interaction with the strong ridge.[5]
Arlene failed to intensify much for several days while passing through the Mid-Atlantic upper-level trough, although the wind speeds gradually increased. On September 2, Arlene turned to the north due to an approaching trough moving eastward from the Northeastern United States. Around that time, it passed about 500 mi (800 km) east of Bermuda. The storm's convection wrapped around the center and organized further as Arlene progressed northward. Turning to the northeast, the storm attained hurricane status early on September 3. Later that day, the Hurricane Hunters recorded maximum sustained winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 982 mbar (29.0 inHg), which would be Arlene's peak intensity. On the next day, the cyclone weakened to a tropical storm due to stronger wind shear, and Arlene slowed its forward motion due to a ridge to the north. Soon after, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, and was absorbed by the trough late on September 4 to the southeast of Newfoundland.[5][6]
Hurricane Chloe
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 5 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 mph (175 km/h) (1-min); 958 mbar (hPa) |
On September 4, a tropical wave exited the west coast of Africa, and by 00:00 UTC the following day, the system organized into Tropical Depression Eight between Cabo Verde and Senegal.[4][6] Soon after, the depression moved through Cabo Verde, and it continued northwestward due to a passing mid-latitude trough. On September 8, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Chloe, and it quickly intensified thereafter. The Hurricane Hunters observed winds of 86 mph (138 km/h) on September 9, indicating that Chloe attained hurricane status while the storm was turning sharply westward. Interaction with Hurricane Doria to the west turned Chloe more toward the northwest on September 11. Two days later, Chloe reached peak winds of 110 mph (175 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 958 mbar (28.3 inHg).[5][6]
After maintaining peak winds for about 36 hours, Chloe began weakening while still over the open waters of the east-central Atlantic Ocean. The Westerlies turned Chloe east-northeastward on September 17, and the storm was last observed by the Hurricane Hunters southeast of Newfoundland on the next day. On September 21, Chloe reached the coastline of France near Bordeaux as an extratropical cyclone, although it was unknown when the cyclone lost its tropical characteristics. It quickly dissipated over central France.[5] Off the northern coast of A Coruña, Spain, high waves from Chloe sank the Fiete Schulze – a German cargo ship attempting to circumnavigate the world. Of the 42 person crew, 14 people drowned, and the others were rescued and brought to a West German hospital, sparking fear of kidnapping from the East German government.[5][7]
Hurricane Beulah
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 5 – September 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 160 mph (260 km/h) (1-min); 923 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave exited the coast of Africa on August 28. Moving westward, it organized into Tropical Depression Seven at 12:00 UTC on September 5, while located about 170 mi (270 km) northeast of Barbados. On September 7, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Beulah, which crossed into the Caribbean Sea that day. After continued strengthening, Beulah became a hurricane on September 8, and two days later reached an initial peak of 150 mph (240 km/h) winds to the southwest of Puerto Rico. An anticyclone over the Bahamas turned the hurricane westward, as changing upper-level conditions from a passing trough to the north, as well as land interaction with Hispaniola, greatly weakened Beulah. The cyclone had winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) when it struck the Barahona peninsula in southern Dominican Republic on September 11. The track shifted to the southwest and weakened further to a tropical storm.[5]
On September 13, Beulah began a steady track to the northwest while passing south of Jamaica. On the next day, it re-intensified into a hurricane due to favorable conditions, strengthening to a major hurricane by September 15. Beulah weakened slightly before making landfall on Cozumel and later the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula. Emerging into the Gulf of Mexico with much of its former intensity, the hurricane restrengthened over the warm waters, attaining peak winds of 160 mph (260 km/h) early on September 20, making it a Category 5 on the Saffir-Simpson scale. At the same time, Hurricane Hunters reported a minimum pressure of 923 mbar (27.3 inHg), the second-lowest aircraft reading at the time after Hurricane Hattie in 1961. Beulah weakened slightly before making its final landfall around 12:00 UTC on September 20, just south of the United States/Mexico border. It weakened quickly over land and stalled near Alice, Texas, before turning to the southwest and dissipating over Nuevo León on September 22.[5]
On Martinique, Beulah dropped 18.7 in (475 mm) of rainfall in Les Anses-d'Arlet.[8] Flooding rains damaged roads, bridges, and houses on Martinique and neighboring Saint Lucia. In the Lesser Antilles, Beulah caused $7.5 million in damage and 17 deaths. The storm caused minor damage and one death in southern Puerto Rico. After the severe impacts of Hurricane Inez a year prior, about 200,000 people evacuated the southern coast of the Dominican Republic. There, Beulah left heavy damage to roads, bridges, and the banana and coffee crops, but the evacuations led to a low death toll of two in the nation. Minor water damage occurred along Haiti's southern Tiburon Peninsula. On Cozumel, Beulah's strong winds destroyed 40% of the houses and heavily damaged many hotels, severely impacting the tourism industry. Along the northern Yucatán Peninsula, the winds wrecked a clock tower in Tizimín, killing five.[5] Beulah dropped heavy rainfall in southern Texas and northeastern Mexico, peaking at 27.38 in (695 mm) in Pettus, Texas.[9] The rains caused record river flooding, with a peak crest of 53.4 ft (16.3 m) along the San Antonio River at Goliad. In northeastern Mexico, Beulah killed 19 people and left 100,000 people homeless. In Texas, damage reached $200 million, and there were 15 deaths, 5 of whom related to a tornado outbreak.[5]
Hurricane Doria
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 8 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 973 mbar (hPa) |
A decaying cold front led to Tropical Depression Nine developing on September 8 off the east coast of Florida. It drifted to the west-southwest before turning sharply to the northeast on September 9. That day it intensified into Tropical Storm Doria, becoming a hurricane on September 10 while 200 mi (320 km) east of the Florida–Georgia border. It briefly weakened to a tropical storm on September 11, but by the next day had already re-strengthened into a hurricane. Doria attained peak winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) on September 13, after which a ridge over New England turned the storm westward. On September 16, the hurricane weakened to tropical storm status to the south of New Jersey. Later that day, Doria made landfall near Virginia Beach, Virginia, and it later turned southward, re-emerging into the Atlantic Ocean east of Cape Lookout as a tropical depression. It crossed over its former path before turning eastward, dissipating on September 21 southwest of Bermuda. Doria left $150,000 in minor coastal damage and killed three people when capsizing a boat offshore Ocean City, New Jersey.[5][6]
Tropical Storm Edith
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 26 – October 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min); 1000 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical disturbance moved westward from the African coast on September 20. On September 26, satellite imagery and ship observations indicated that a tropical depression about 830 mi (1,340 km) east of Barbados.[4][5] At 21:00 UTC, the NHC issued their first advisory, naming the system Edith.[10] A nearby ship reported 16 ft (4.9 m) waves on September 27, potentially indicating stronger winds during periods without meteorological observations,[11] although unfavorable conditions prevented initial development.[12] It was not until 12:00 UTC that Edith attained tropical storm force winds. Twelve hours later, the storm reached peak winds of 60 mph (95 km/h),[6] a trend that spurred hurricane watches from Dominica northward through the Leeward Islands.[13] The storm failed to intensify due to its proximity to a cold upper-level trough and releasing too much latent heat. On September 30, Edith passed over Dominica as a weakened tropical storm and dissipated the next day over the eastern Caribbean Sea. It caused gusty winds and minor damage during its passage through the Lesser Antilles.[5]
Hurricane Fern
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 1 – October 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 987 mbar (hPa) |
Toward the end of September, a powerful cold front moved through the Gulf of Mexico and stalled over the Bay of Campeche. Convection persisted across the region as the surface pressure dropped.[5] Satellite imagery suggested that Tropical Depression Fourteen developed on October 1 about 140 mi (220 km) northwest of Ciudad del Carmen.[4][14] As the system organized more, it tracked northward, although a ridge to the north steered the nascent system to the west. On October 2, the British ship Plainsman observed gale force winds, prompting the NHC to upgrade the depression to Tropical Storm Fern.[5] A small system, the storm intensified further to hurricane status on October 3, reaching peak winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 987 mbar (29.1 inHg).[6] Upwelling and cold air left in the wake of Hurricane Beulah caused Fern to weaken slightly as it approached the Gulf Coast of Mexico. Around 06:00 UTC on October 4, Fern made landfall about 30 mi (50 km) north of Tampico, Tamaulipas, possibly having weakened to a tropical storm. It rapidly weakened over land, dissipating by 18:00 UTC.[5][6]
Fern's landfall was accompanied by an area of heavy rainfall that extended into the mountainous areas of Veracruz.[15] The rains caused additional flooding along the Pánuco River, which became swollen during Hurricane Beulah two weeks prior. Three people drowned in the floodwaters. Damage was minor related to Fern.[5] Along the lower Texas coast, the threat from Fern spurred high tide and small craft warnings from the National Weather Service. Additional members of the Texas National Guard, in place after Beulah, were activated due to the threat from Fern.[16]
Tropical Storm Ginger
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 5 – October 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); 1002 mbar (hPa) |
An area of convection developed off the west coast of Africa following the westward passage of Tropical Depression Sixteen. On October 5, it is estimated that Tropical Depression Seventeen developed from this system,[4] based on the convective appearance on satellite imagery. Three ships reported 40 to 45 mph (64 to 72 km/h) winds on October 6,[5] which was the basis for the NHC upgrading it to Tropical Storm Ginger, in conjunction with data from Cabo Verde.[17] At the time, the storm was located about 400 mi (645 km) north-northwest of Dakar, Senegal, well east of 35° W where the NHC began issuing formal tropical cyclone advisories. Instead, the Rota, Spain Naval Fleet Station issued gale warnings in relation to the storm.[17][18] Later on October 6, it was estimated that Ginger reached peak winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 1,002 mbar (29.6 inHg). On October 7, the storm curved west-southwestward and quickly weakened into a tropical depression. Ginger dissipated on October 8 to the north of Cabo Verde.[6]
Hurricane Heidi
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 19 – October 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min); 981 mbar (hPa) |
An area of convection persisted on October 16 between the Lesser Antilles and Cabo Verde. It moved west-northwestward for several days, developing into Tropical Depression Twenty-Two on October 19 about 500 mi (800 km) northeast of the Lesser Antilles.[4][5] The S.S. Sunrana moved through the storm on October 20, reporting winds of 58 mph (93 km/h). At the time, the system was not named due to the lack of a warm thermal core,[5] although it was later assessed as a tropical storm as of 18:00 UTC that day.[6] On October 21, the Hurricane Hunters observed a weak circulation with winds of only 35 mph (56 km/h). At the same time, the storm was located along the edge of a baroclinic zone, which limited strengthening. Curving northeastward due to an approaching trough, the storm intensified more on October 22, as a ship reported winds of 70 mph (110 km/h). That day, data from the Hurricane Hunters observed a warm core,[5] and the NHC classified the system as Tropical Storm Heidi. The storm was more of a hybrid storm initially,[19] with the strongest winds near the center, spurring gale warnings for Bermuda.[20] However, winds there only reached about 15 mph (24 km/h) during the storm's passage.[21]
The NHC initially anticipated that Heidi would become extratropical within two days.[22] Early on October 23, the agency upgraded the storm to hurricane status about 105 mi (175 mi) southeast of Bermuda. Heidi moved quickly eastward with the approaching trough until October 25, when a building ridge caused the hurricane to move slowly northeastward in an area of light wind shear. Early on October 26, Heidi attained peak winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) about halfway between Bermuda and the Azores.[5][6] By the next day, the hurricane had become much larger, with characteristics of an extratropical storm despite maintaining the warm thermal core.[23] After stalling on October 29, Heidi turned westward and weakened to tropical storm status.[6] Another approaching trough turned the storm back to the northeast on October 31.[24] Later that day, Heidi started losing tropical characteristics,[25] transitioning into an extratropical cyclone by November 1. Later that day, the remnants of Heidi were absorbed into the prevailing weather conditions of the north Atlantic Ocean.[5][6]
Other storms

On June 10, the first tropical depression of the season developed in the western Caribbean Sea. It moved northwestward, dissipating over the eastern Yucatán Peninsula on June 12. At the same time that the previous system developed, Tropical Depression Two originated north of the Lesser Antilles. This system moved northward and passed just east of Bermuda on June 11. After turning to the northeast, the depression dissipated on June 13. On June 18, Tropical Depression Four also developed north of the Lesser Antilles, taking a similar trajectory to the north-northwest, and dissipating on June 20 east of Bermuda.[6][4]
Satellite imagery and ship data indicated that Tropical Depression Three formed on June 14 to the northeast of the northeastern Bahamas,[5] associated with an upper-level low. With a ridge to the northeast, the depression moved northwestward toward the southeastern United States.[26] Conditions were not favorable for strengthening, with cool air and minimal outflow, although the winds approached gale-force.[5] An approaching cold front turned the system to the northeast on June 18.[26] That day, the depression moved ashore just southwest of Wilmington, North Carolina, and soon lost tropical characteristics.[5] The remnants continued to the northeast, transitioning into an extratropical storm that passed just east of Massachusetts on June 19. On the next day, the system was absorbed by the front, and continued to the northeast into Nova Scotia by June 22. The system dropped locally heavy rainfall, peaking at 8.86 in (225 mm) in North Wilkesboro, North Carolina.[26] In South Carolina, the rains caused flooding near Myrtle Beach, concurrent with 2.5 ft (0.76 m) above-normal tides, which caused $15,000 in damage, mostly to crops. Farther north, the rains were beneficial,[5] with totals as high as 6.71 in (170 mm) in Saco, Maine.[26]
There were two short-lived, unnumbered depressions in July that emerged off the coast of Africa, and both were unnumbered. The first was observed on July 5 near the coast of Guinea-Bissau; moving westward, it was last noted on July 9. The other depression emerged from Senegal on July 21 and dissipated south of Cabo Verde on the next day.[4][6] Another series of unnumbered tropical depressions exited the coast of Africa in August. On August 3, a tropical depression formed just off the coast of Mauritania and moved southwestward through Cabo Verde the next day. It was last noted on August 6. A depression was first noted over eastern Senegal on August 10, exiting the African coast the next day. It continued on a westward trajectory, passing south of Cabo Verde, and dissipated on August 16. On the same day, another depression emerged from Mauritania and passed through northern Cabo Verde, dissipating on August 19. The final in the series of four depressions was first noted on August 20 near the Mauritania/Western Sahara border. The system moved southwestward through Cabo Verde, dissipating on August 24.[4][6] Tropical Depression Six exited the west coast of Africa on August 30, and soon after moved through Cabo Verde. It was last noted on September 4.[4]
A series of tropical waves in late August to early September became hurricanes Arlene, Beulah, and Chloe, and the wave between the latter two emerged from Africa on August 30 as Tropical Depression Six. It crossed through Cabo Verde on September 1, dissipating three days later over the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Tropical Depression Ten took a similar trajectory, exiting Senegal on September 18 and progressing westward near Cabo Verde. It lasted longer than other depressions in the season, dissipating on September 26 east of the Lesser Antilles. Tropical Depression Thirteen exited western Africa near Guinea on September 22, which moved westward until September 27. It turned northwestward that day and dissipated on September 30. Tropical Depression Eleven formed on September 25 and crossed Cabo Verde two days later, dissipating on September 28.[4][6]
On October 3, Tropical Depression Sixteen exited the west coast of Africa near The Gambia, dissipating two days later after passing south of Cabo Verde. Tropical Depression Fifteen existed briefly on October 4 to the southeast of Bermuda. Short-lived Tropical Depression Eighteen formed near the Bahamas on October 8, dissipating the next day after moving northeastward. Tropical Depression Nineteen spawned on October 12 north of Hispaniola and moved northwestward through the Turks and Caicos Islands. After turning to the northeast, it dissipated on October 14. On the next day, Tropical Depression Twenty-One originated between the Lesser Antilles and Cabo Verde, which moved westward and dissipated on October 17. Tropical Depression Twenty briefly existed on October 16, which moved northwestward to the southwest of Bermuda. The final system of the season was Tropical Depression Twenty-Three, which formed northeast of the Bahamas on October 26. It tracked eastward before looping back to the northwest, dissipating on October 29 about 130 mi (215 km) southwest of Bermuda.[4][6]
Storm names
The following names were used for named storms (tropical storms and hurricanes) that formed in the North Atlantic in 1967. Storms were named Chloe, Doria, Fern, Ginger and Heidi for the first time in 1967. At the end of the season, the name Beulah was retired and replaced with Beth in 1971. Names that were not assigned are marked in gray.
|
|
Contemporaneous seasons
- 1967 Pacific hurricane season
- 1967 Pacific typhoon season
- 1966–67/1967–68 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
Notes
- ^ "Hurricane Season Opens Thursday". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. Associated Press. May 31, 1967. Retrieved May 22, 2011.
- ^ "Weathermen Brace for Hurricane Season". The News and Courier. Associated Press. May 28, 1967.
- ^ Russell Pfost; Pablo Santos (August 15, 2013). "History of the National Weather Service Forecast Office Miami, Florida". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Bob Simpson; Neil Frank; David Shideler; H. M. Johnson (April 1968). "Atlantic Tropical Disturbances, 1967" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. 96 (4). Retrieved August 24, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac Arnold L. Sugg; Joseph M. Pelissier (April 1968). "The Hurricane Season of 1967" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. 96 (4). Retrieved September 2, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "MV Fiete Schulze (+1967)". Wreck Site. Retrieved August 26, 2013.
- ^ 1967 Beulah: Ouragan. Pluies extrêmes aux Antilles (Report) (in French). Météo-France. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ David M. Roth (March 6, 2013). Hurricane Beulah - September 8-24, 1967 (Report). Weather Prediction Center. Retrieved August 26, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Edith (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. September 26, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Edith (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. September 27, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Edith (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. September 26, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Edith (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. September 28, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Fern (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 2, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Fern (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 4, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ "Hurricane Fern Aiming at Mexico". Spokane Daily Chronicle. Associated Press. October 3, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ a b Bob Simpson (October 6, 1967). Tropical Storm Ginger Forms Near African Coast (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Ginger (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Heidi (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 22, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Bureau Marine/Aviation/Military Advisory for Tropical Storm Heidi (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 22, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ "Hurricane No Threat to Land". Ocala Star-Banner. Associated Press. October 23, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Heidi (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 22, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Heidi (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 27, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Heidi (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 31, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Heidi (GIF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. October 31, 1967. Retrieved August 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c d David M. Roth (March 6, 2013). Tropical Depression Three - June 15-22, 1967 (Report). Weather Prediction Center. Retrieved August 24, 2016.