SPMAP1
This sandbox is in the article namespace. Either move this page into your userspace, or remove the {{User sandbox}} template.
| SPMAP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SPMAP1, chromosome 17 open reading frame 98, sperm microtubule associated protein 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1919465; HomoloGene: 19140; GeneCards: SPMAP1; OMA:SPMAP1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C17orf98 is a protein which in humans is coded by the gene c17orf98. The protein is derived from Homo sapiens chromosome 17[5]. The C17orf98 gene consists of a 552 basepair sequence. Its mRNA has three exons and no alternative splice sites. The protein has 154 amino acids, with no abnormal amino acid levels[6]. C17orf98 has a domain of unknown function (DUF4542) superfamily and is 17.6kDal in weight[7][8].
C17orf98 does not belong to any other families nor does it have any isoforms[9]. The protein has orthologs with high percent similarity in mammals and reptiles. The protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the metazoan kingdom, culminating with the sponge family.[10].

Like most proteins, C17orf98 is known to be highly expressed in the testes[11]. The protein has also been known to have elevated levels in cancer[12]. The protein has been shown to be expressed in proximity to or within intermediate filaments and the nucleolus[13]. Additionally, c17orf98 has transcription factors which are also active in hematopoietic cells, the immune system, the cardiovascular system, among others[14]. The gene is over-expressed in many cancer types, including kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma[15].
Gene
Background
GeneCards determined that C17orf98 has five enhancer sequences. The role of the se sequences may provide insight into the function of C17orf98. Four of the five enhancers are active in the thymus. All five enhancers are active in the H1 hESC. Additionally, all five enhancers are active in iPS DF 19.11 derived from foreskin fibroblasts [16]. C17orf98 has 11 Alu repeats[17]. C17orf98 gene has six sites on the sequence of possible O-GlcNAc sites[18]. C17orf98 does not have any alternative splice sites[19]. C17orf98 does not have any miRNA binding sites[20].

Transcription factors analysis The 5' UTR sequence of C17orf98 is highly conserved in primates. No non-mammalian 5'UTR mathces were able to be determined[21][22].

Variants
SNPs
Protein
Structure
C17orf98 is a 17.6kDal protein[23]. There are no positive or negative charge clusters. There are no transmembrane components. The isoelectric point pI/Mw: 9.80 / 17564.67[24].
There are no N-terminal signal peptides. There are no transmembrane domains. Cleavage motifs were not found. There are no ER membrane retention signals, nor peroxisomal targeting signal. SKL2 is not present, thus a secondary peroxisome signal is not present. There are no vacuolar targeting signals. There are no RNA binding motifs are actinin type actin binding motifs. There are no N-myristoylation pattern or prenylation pattern[25]. The results of the k-NN prediction is cytoplasmic localization[26]. C17orf98 is not a signal peptide[27]. The protein is a soluble[28].
Kinase finder at Cuckoo determined kinase binding sites for c17orf98. There are many serine, threonine, and tyrosine binding sites[29].The lack of transmembrane domains is affirmed by Enzim, who also notes the entropy of the model as 17.0158. Additionally, the entropy of the best path is 17.0158[30]. Serine and threonine kinase binding sites are the most prevalent above the statistically significant threshold.


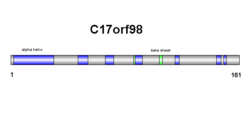
The c17orf98 protein is 17.6 kDal in weight. It is hydrophobic and soluble. Thus, it does not insert in the membrane. Additionally, there are no transmembrane domains in the protein sequence. There are no localization signals in the protein. The protein has five alpha helix regions, and two beta sheet regions.
Binding Sites
phosphorylation sites
Amino Acid Sequence
Homo Sapiens
MAYLSECRLRLEKGFILDGVAVSTAARAYGRSRPKLWSAIPPYNAQQDYHARSYFQ SHVVPPLLRVVPPLLRKTDQDHGGTGRDGWIVDYIHIFGQGQRYLNRRNWAGTGHS LQQVTGHDHYNADLKPIDGFNGRFGYRRNTPALRQSTSVFGEVTHFPLF
Associated Proteins
There are no known associated proteins[31] [32] [33] [34].
Expression
Protein abundance in Homo sapiens whole organism is quite low. No data is available for other species. The gene has a 0.44 percent abundance[35]. There are Geo Profile derived factors affecting to expression of c17orf98[36].
Cellular Expression
C17orf98 protein has been found to be expressed in the intermediate filaments and the nucleoli[37]. A C17orf98 antibody is available from Sigma-Aldrich[38]. Additionally, C17orf98 localizes in the cytoplasm. Distantly related c17orf98 ortholgs in organsisms such as Macrostomum lignano and Amphimedon queenslandica exhibit nuclear expression[39]. Nuclear localization signals are present in distantly related organisms in non-conserved sites.
Tissue
Like most proteins, C17orf98 protein is highly expressed in the testes[40]. The protein is expressed on adult tissues as well as fetal tissue. The protein has been found to be mildly expressed in connective tissue[41].
Cancer
Protein expression is elevated in many cancer patients. Specifically, protein expression has been shown to be high on colorectal, breast, prostate, and lung[42]. C17orf98 is expressed in papillary thryoid cancer as well[43]. Additionally, mutations were found in c17orf98 in endometrial, stomach, coloratura, and kidney cancer[44]. C17orf98 expression is elevated in cancer patients with BRCA. In Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma patients, c17orf98 expression dramatically decreased compared to the non cancerous state[45]. In 80% of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma patients, at least one gene duplication c17orf98 was present[46].
Evolution
C17orf98 is a slow mutating protein. It resembles Cytochrome C in its rate of amino acid changes, as determined by the molecular clock equations[47].

Paralogs
There are no known Homo sapiens paralogs for C17orf98[48].
Orthologs
The protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the metazoan kingdom. It's most distant relative is in the sponge family. There is no known ortholog in ctenophores, nematodes, bacteria, fungus, plants, or zebrafish[49]. Interestingly, there are only two fish with the c17orf 98 gene. Model organisms such as C. elegans, and Drosophila melanogaster, do not have the gene.
C17orf98 Orthologs[50]
| Sequence # | Genus and Species | Common Name | Accession # | Protein Length | MYA Div | Seq Id | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Homo sapiens | Human | NP_001073934 | 154 | 0 | 100% | na |
| 2 | Camelus ferus | Wild Bactrian Camel | XP_006176436 | 154 | 96 | 83% | 2.00E-94 |
| 3 | Pteropus alecto | Black Flying Fox | XP_006924784 | 154 | 96 | 81% | 1.00E-92 |
| 4 | Lipotes vexilifer | Yangtze River Dolphin | XP_007465208 | 154 | 96 | 81% | 6.00E-89 |
| 5 | Condylura cristat | Star Nosed Mole | XP_004684322 | 154 | 96 | 75% | 5.00E-78 |
| 6 | Myotis brandtii | Brandt's Bat | EPQ05064 | 171 | 96 | 78% | 6.00E-78 |
| 7 | Marmata marmata marmata | Alpine Marmot | XP_015362150.1 | 154 | 90 | 81% | 3.00E-94 |
| 8 | Octodon degus | Chilean Rodent | XP_004633931 | 153 | 90 | 73% | 1.00E-76 |
| 9 | Alligator sinensis | Chinese Alligator | XP_006022630 | 154 | 312 | 63% | 8.00E-68 |
| 10 | Anolis carolinensis | Lizard | XP_003222553 | 154 | 312 | 62% | 6.00E-67 |
| 11 | Xenopus laevis | African Clawed Frog | XP_018090228 | 244 | 352 | 51% | 4.00E-38 |
| 12 | Rhincodon typus | Whale Shark | XP_020388051.1 | 164 | 476 | 53% | 5.00E-52 |
| 13 | Acanthaster planci | Starfish | XP_022086463 | 209 | 684 | 48% | 1.00E-37 |
| 14 | Mizuhopecten yessoensis | Scallop | XP_021340301 | 275 | 797 | 45% | 5.00E-06 |
| 15 | Lottia gigantea | Sea Snail | XP_009063876 | 173 | 797 | 45% | 2.00E-37 |
| 16 | Lingula anatine | Lamp Shell | XP_013388744.1 | 211 | 797 | 43% | 2.00E-35 |
| 17 | Biomphalaria glabrata | Freshwater Snail | XP_013088317 | 198 | 797 | 41% | 6.00E-15 |
| 18 | Nematostella vectensis | Sea Anemone | XP_001629616 | 173 | 824 | 48% | 2.00E-35 |
| 19 | Stylophora pistillata | Coral | XP_022795125 | 226 | 824 | 46% | 3.00E-38 |
| 20 | Macrostonum lignano | Flatworm | PAA73615 | 235 | 824 | 36% | 4.00E-25 |
| 21 | Amphimedon queenslandica | Sponge | XP_003389909 | 275 | 951.8 | 32% | 2.00E-12 |
C17orf98
This article, SPMAP1, has recently been created via the Articles for creation process. Please check to see if the reviewer has accidentally left this template after accepting the draft and take appropriate action as necessary.
Reviewer tools: Inform author |
- ^ a b c ENSG00000276913 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000275489, ENSG00000276913 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000018543 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Zody, M.C., et al. (2006). DNA sequence of human chromosome 17 and analysis of rearrangement in the human lineage. Nature, 440(787), 1045-11049
- ^ PSORT II entry on c17orf98 https://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html
- ^ NCBI Conserved Domains entry C17orf98
- ^ ENMBL-EBI SAPS entry on c17orf98 https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/services/web/toolresult.ebi?jobId=saps-I20180419-1415
- ^ https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
- ^ https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastp&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome
- ^ Human protein atlas entry on c17orf98 https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000275489-C17orf98/tissue
- ^ Human protein atlas entry on c17orf98 https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000275489-C17orf98/tissue
- ^ Human protein atlas entry on c17orf98 https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000275489-C17orf98/tissue
- ^ Genomatix El Derado etnry on c17orf98 https://www.genomatix.de/cgibin/eldorado/eldorado.pl?s=0c99e39acf1f2c9dd47191b5b7f412b;SHOW_ANNOTATION=C17 orf98;ELDORADO_VERSION=E33R1705
- ^ TissGDB entry on c17orf98 https://bioinfo.uth.edu/TissGDB/gene_search_result.cgi?page=page&type=quick_search&quick_search=388381
- ^ http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C17orf98
- ^ Genomatix El Derado etnry on c17orf98 https://www.genomatix.de/cgibin/eldorado/eldorado.pl?s=0c99e39acf1f2c9dd47191b5b7f412b;SHOW _ANNOTATION=C17orf98;ELDORADO_VERSION=E33R1705
- ^ YinOyang entry on c17orf98 http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/YinOYang/
- ^ Acieview entry on c17orf98 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/IEB/Research/Acembly/av.cgi?db=human&term=c17orf98&submit=Go
- ^ Target Scan entry on c17orf98 http://www.targetscan.org/cgibin/targetscan/vert_71/view_gene.cgi?rs=ENST00000398575.4&taxid=9606&showc nc=0&shownc=0&shownc_nc=&showncf1=&showncf2=&subset=1
- ^ ClustalW entry on c17orf98 5’ UTR https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/
- ^ NCBI Blast entry on c17orf98 5’ UTR https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastn&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blastho me
- ^ ENMBL-EBI SAPS entry on c17orf98 https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/services/web/toolresult.ebi?jobId=saps-I20180419-1415
- ^ ExPASy pI/mW entry on c17orf98 https://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/compute_pi/pi_tool
- ^ PSort II entry on C17orf98 https://psort.hgc.jp/cgi-bin/runpsort.pl
- ^ PSort II entry on C17orf98 https://psort.hgc.jp/cgi-bin/runpsort.pl
- ^ DTU Bioinformatics entry on c17orf98 http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/cgi-bin/webface2.fcgi?jobid=5AD7D62200000C8DFA04286C&wait=20
- ^ Expasy Sosui entry on C17orf98 http://harrier.nagahama-i-bio.ac.jp/sosui/cgi-bin/adv_sosui.cgi
- ^ Bio Cockoo GPS entry on C17orf98 http://gps.biocu
- ^ Enzim entry on c17orf98 http://www.enzim.hu/hmmtop/html/submit.html
- ^ BioGrid entry on c17orf98 https://thebiogrid.org/132666/summary/homo-sapiens/c17orf98.html
- ^ MINT entry on c17orf98 https://mint.bio.uniroma2.it/index.php/results-interactions/?id=c17orf98
- ^ STRING entry on C17orf98 https://string-db.org/cgi/network.pl?taskId=V780xrKjRDdJ
- ^ PSICQUIC View entry on c17orf98 http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/webservices/psicquic/view/results.xhtml?conversationContext=3
- ^ pax-db entry on c17orf98 https://pax-db.org/protein/1858623#
- ^ NCBI GeoProfiles entry on c17orf98 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geoprofiles/?term=c17orf98
- ^ Human Protein Atlas (sigma) entry on c17orf98 https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000275489‐C17orf98/cell
- ^ Sigma Aldrich entry on c17orf98 https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/hpa051696?lang=en®ion=US
- ^ PSORT II entry on c17orf98 amino acid sequence https://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html
- ^ Protein Atlas entry on c17orf98 https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000275489-C17orf98/cell
- ^ NCBI Unigene entry on c17orf98 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/clust.cgi?UGID=169593&TAXID=9606&SEARCH=c17orf98
- ^ Human Protein Atlas (sigma) entry on c17orf98 https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000275489-C17orf98/cell
- ^ NCBI GeoProfiles entry on c17orf98 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geoprofiles
- ^ Phosphosite entry on c17orf98 https://www.phosphosite.org/proteinAction.action?id=5156341&showAllSites=true
- ^ TissGDB entry on c17orf98 https://bioinfo.uth.edu/TissGDB/gene_search_result.cgi?page=page&type=quick_search&quick_search=388381
- ^ TissGDB entry on c17orf98 https://bioinfo.uth.edu/TissGDB/gene_search_result.cgi?page=page&type=quick_search&quick_search=388381
- ^ https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/the-molecular-clock-and-estimating-species-divergence-41971
- ^ Blast entry on c17orf98 https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE=Proteins
- ^ https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastp&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome
- ^ https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastp&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome





