2-Methylpyridine
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
2-picoline
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.313 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H7N | |||
| Molar mass | 93.13 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Faintly yellow-green clear liquid | ||
| Density | 0.943 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −70 °C (−94 °F; 203 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 128 to 129 °C (262 to 264 °F; 401 to 402 K) | ||
| Miscible | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
2-Methylpyridine, or 2-picoline, is the compound described with formula C6H7N. 2-Picoline is a colorless liquid that has an unpleasant odor similar to pyridine. Pyridines including 2-picoline are most crudely prepared by the reaction of acetylene and hydrogen cyanide.
Synthesis
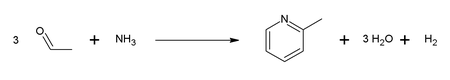
2-Picoline was the first pyridine compound reported to be isolated in pure form. It was isolated from coal tar in 1846 by T. Anderson.[1] It is now mainly produced by two principal routes, the condensation of acetaldehyde, formaldehyde, and ammonia and the cyclization of nitriles and acetylene. One example of such reaction is the combination of acetaldehyde and ammonia:
Approximately 8000 t/a was produced worldwide in 1989.[2]
Uses
The principal application of 2-picoline is as a precursor of 2-vinylpyridine. The formation of 2-vinylpyridine is achieved by the addition of aqueous formaldehyde to 2-picoline, followed by a dehydration of the resulting alcohol:
The copolymerization of 2-vinylpyridine, butadiene and styrene is used as an adhesive for textile tire cord. 2-Picoline is also a precursor to the agrichemical, nitrapyrin, which prevents loss of ammonia from fertilizers.[2]
2-Picoline is a versatile building block and can be used as a precursor to a variety of derivatives. For example, oxidation by potassium permanganate affords picolinic acid:[2]
- α-picoline is used in production of amprolium, and Butoprozine.
Environmental Behavior
Like other pyridine derivatives, 2-methylpyridine is often reported as an environmental contaminant associated with facilities processing oil shale or coal, and has also been found at legacy wood treatment sites. Owing to high water solubility, 2-methylpyridine has significant potential for mobility in the environment, which may promote water contamination. The compound is, however, readily degradable by certain microorganisms, such as Arthrobacter sp. strain R1 (ATTC strain number 49987), which was isolated from an aquifer contaminated with a complex mixture of pyridine derivatives.[3] Arthrobacter and closely related Actinobacteria are often found associated with degradation of pyridine derivatives and other nitrogen heterocyclic compounds. 2-methypyridine and 4-methypyridine are more readily degraded and exhibit less volatilization loss from environmental samples than does 3-methypyridine.[4]
References
- ^ Anderson, T. (1846). "On the constitution and properties of Picoline, a new organic base from Coal Tar" (Free full text at Google Books). Edinburgh New Phil. J. XLI: 146–156, 291–300.
- ^ a b c Shinkichi Shimizu, Nanao Watanabe, Toshiaki Kataoka, Takayuki Shoji, Nobuyuki Abe, Sinji Morishita, Hisao Ichimura. (2002). "Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ O'Loughlin, E. J., G.K. Sims, and S.J. Traina. 1999. Biodegradation of 2-methyl, 2-ethyl, and 2-hydroxypyridine by an Arthrobacter sp. isolated from subsurface sediment. Biodegradation 10:93-104.
- ^ Sims, G.K.; L.E. Sommers (1985). "Biodegradation of pyridine derivatives in soil suspensions". Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 5: 503–509. doi:10.1002/etc.5620050601.
- Eric F. V. Scriven, Ramiah Murugan. 'Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives', Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, (2005). doi:10.1002/0471238961.1625180919031809.a01.pub2