Instruments used in general surgery
Appearance
This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: Style/formatting issues. Capitalization of instruments and classes. Could do with a lead section. Links sh. (October 2013) |
Surgical instruments can vary widely by the field of surgery that they are used in. In general instruments can be divided into five classes by function:
- Cutting and dissecting instruments:
- Scalpels, scissors, and saws are the most traditional
- Elevators can be both cutting and lifting/retracting
- Although the term dissection is broad energy devices such as diathermy/cautery are often used as more modern alternatives.
- Grasping or holding instruments:
- Classically this included forceps and clamps predominantly
- Roughly forceps can be divided in traumatic (tissue crushing) and atraumatic (tissue preserving, such as Debakey's)
- Numerous examples are available for different purposes by field
- Hemostatic instruments:
- This includes instruments utilized for the cessation of bleeding
- Artery forceps are a classic example in which bleeding is halted by direct clamping of a vessel
- Sutures are often used, aided by a needle holder
- Cautery and related instruments are used with increasing frequency in high resource countries
- Retractors:
- Surgery is often considered to be largely about exposure
- A multitude of retractors exist to aid in exposing the bodies cavities accessed during surgery
- These can broadly be hand held (often by a junior assistant) or self retaining
- Elevators can be both cutting and lifting/retracting
- Tissue unifying instruments and materials:
- This would include instruments that aid in tissue unification (such as needle holders or staple applicators)
- And the materials themselves
Instruments used in surgery are:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11]
| Instrument class | Image | Uses | Specific instruments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Articulator | 
|
Galotti articulator | ||
| Bone chisel | 
|
Cutting instrument | ||
| Pin cutter | 
|
To cut the pins after they are used to place bone in correct place | ||
| Bone distractor | 
|
Clamps and distractors | ||
| llizarov apparatus | 
|
Accessories and implants | ||
| Intramedullary kinetic bone distractor | Clamps and distractors | |||
| Bone drill | To drill inside the bone | |||
| Elevator | Accessories and implants | |||
| Bone mallet | Accessories | |||
| Bone rasp | Cutting instruments | |||
| Bone saw | Cutting instruments | |||
| Bone skid | ||||
| Bone splint | ||||
| Bone button | ||||
| Caliper | To measure | Castroviejo caliper | ||
| Cannula | 
|
Accessories and implants | Spackmann Cannula | |
| Cautery | 
|
To cauterize and seal vessels and bone, using electricity | ||
| Curette | 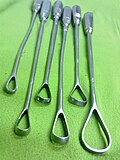
|
for scraping or debriding biological tissue or debris in a biopsy, excision, or cleaning procedure Cutting instrument | ||
| Depressor | ||||
| Dilator | 
|
Accessories and implants | ||
| Dissecting knife | cutting instrument | |||
| surgical Pinzette | 
|
Grasping/holding | ||
| Dermatome | 
|
To take off a top layer of skin to implant over another area. | ||
| Forceps, Dissecting | 
|
Grasping/holding. Usually used in skin closure or small wounds | Adson | |
| Forceps, Tissue | 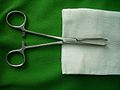
|
Grasping/holding tissue | Allis | |
| Penatrating towel clamp | 
|
Used to secure towels or reduce bone fragments | Backhaus penetating towel clamp | |
| Acanthulus or Acanthabolos | Thorn removal | |||
| Bone forceps | Grasping/holding | |||
| Carmalt forceps | haemostatic forceps | kalabasa | ||
| Cushing forceps | grasping/holding | Non-toothed dissecting forceps | ||
| Dandy forceps | haemostatic forceps | |||
| DeBakey forceps | 
|
grasping/holding | Non-toothed dissecting forceps designed for use on blood vessels, organs, or deilcate tissue | |
| Doyen intestinal clamp | clamps and distractors | Non-crushing clamp designed for use on the intestines | ||
| Epilation forceps | ||||
| Tiberio forceps | haemostatic forceps | |||
| Kelly forceps | 
|
hemostatic forceps | ||
| Kocher forceps | 
|
hemostatic forceps | ||
| Mosquito forceps | 
|
hemostatic forceps | ||
| Hook | retractor | |||
| Nerve hook | retractor | |||
| Obstetrical hook | retractor | |||
| Skin hook | retractor | |||
| Lancet (scalpel) | 
|
cutting | ||
| Lythotome | ||||
| Lythotript | ||||
| Mallet | ||||
| Partsch mallet | ||||
| Mammotome | 
|
|||
| Needle holder | 
|
grasping/holding | Castroviejo Crilewood Mayo-Hegar Olsen-Hegar | |
| Occluder | ||||
| Osteotome | 
|
cutting | ||
| Epker osteotome | cutting | |||
| Periosteal elevator | 
|
cutting and lifting | ||
| Joseph elevator | cutting | |||
| Molt periosteal elevator | cutting | |||
| Obweg periosteal elevator | cutting | |||
| Septum elevator | cutting | |||
| Tessier periosteal elevator | cutting | |||
| Periodontal probe | ||||
| Probe Dental explorer | ||||
| Retractor | 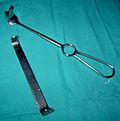
|
retractor | ||
| Deaver retractor | 
|
Deep wound retraction | ||
| Gelpi retractor | self-retaining retractor. Used for superficial wound exposure | |||
| Weitlaner retractor | self-retaining retractor. Used for superficial wound exposure | |||
| USA-Army/Navy retractor | retractor | |||
| O'Connor-O'Sullivan | retractor | |||
| Mathieu Retractor | retractor | |||
| Jackson Tracheal Hook | retractor | |||
| Crile Retractor | retractor | |||
| Meyerding Finger Retractor | retractor | |||
| Little Retractor | retractor | |||
| Love Nerve Retractor | retractor | |||
| Green Retractor | retractor | |||
| Goelet Retractor | retractor | |||
| Cushing Vein Retractor | retractor | |||
| Langenbeck Retractor | retractor | |||
| Richardson Retractor | retractor | |||
| Richardson-Eastmann Retractor | retractor | |||
| Kelly Retractor | retractor | |||
| Parker Retractor | retractor | |||
| Parker-Mott Retractor | retractor | |||
| Roux Retractor | retractor | |||
| Mayo-Collins Retractor | retractor | |||
| Ribbon Retractor | retractor | |||
| Alm Retractor | retractor | |||
| Self Retaining Retractors | West, Travers and Norfolk & Norwich | |||
| Weitlaner Retractor | ||||
| Beckman-Weitlaner Retractor | ||||
| Beckman-Eaton Retractor | ||||
| Beckman Retractor | ||||
| Adson Retractor | ||||
| Rib spreader | ||||
| Rongeur | cutting instrument | |||
| Ultrasonic scalpel | cutting | |||
| Laser scalpel | 
|
cutting | ||
| Scissors | 
|
cutting | ||
| Iris scissors | cutting | |||
| Kiene scissors | cutting | |||
| Metzenbaum scissors | 
|
To dissect delicate tissue | cutting | |
| Mayo scissors | 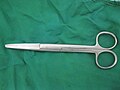
|
To cut suture, bandages, or dressings | cutting | |
| Tenotomy scissors | cutting | |||
| Spatula | ||||
| Speculum | 
|
To retract the walls of the vagina | Graves vaginal speculum | |
| Mouth speculum | retractor | |||
| Rectal speculum | retractor | |||
| Sim's vaginal speculum | 
|
To retract the walls of the vagina | ||
| Cusco's vaginal speculum | 
|
retractor | ||
| Sponge bowl | accessories and implants | |||
| Sterilization tray | accessories and implants | |||
| Sternal saw | cutting | |||
| Suction tube and Yankeur suction tip | 
|
accessories and implants | ||
| Surgical elevator | 
|
|||
| Surgical hook | 
|
retractor | ||
| Surgical blade #15 | 
|
Used to cut vessels or make small incisions | ||
| Surgical mesh | 
|
accessories and implants | ||
| Surgical needle | 
|
accessories and implants | ||
| Surgical snare | ||||
| Surgical sponge | ||||
| Curettes | 
|
|||
| GIA stapler | 
|
Used to make a gastrointestinal anastamosis | Linear stapler | |
| Surgical tray | ||||
| Suture | 
|
|||
| Tongue depressor | 
|
|||
| Tonsillotome | ||||
| Towel clamp | 
|
clamp | ||
| Towel forceps | clamp | |||
| Backhaus towel forceps | 
|
|||
| Lorna towel clamp | Non-penatrating towel clamp | |||
| Tracheotome | ||||
| Tissue expander | accessories and implant | |||
| Subcutaneous inflatable balloon expander | accessories and implants | |||
| Trephine | 
|
cutting instrument | ||
| Trocar |  |
Access instrument. Used to create an opening into a space without opening the abdominal cavity. A camera then inserted through one to view the inside of the space while instruments are inserted through the others to manipulate the organs. | ||
| Ultrasonic energy device | Surgical device using electrical energy that's converted to mechanical ultrasound energy typically used to dissect tissue but also seals small vessels and tissue bundles. | |||
| Vessel Sealing Device |  |
Vessel sealing device used to weld vessels together prior to cutting. These devices used bipolar radio frequency energy to create heat that welds the tissue. | Advanced Bipolar Energy |
References
- ^ "ilizarov.com (English)". Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2008-06-04.
- ^ Children with Tracheostomies Resource Guide, by Marilyn K. Kertoy, p. 15 (Google book search)
- ^ Rob Toreki (1 December 2004). "Cannulas". The Glassware Gallery. Interactive Learning ←Paradigms Incorporated.
- ^ "Practical approach to nephrostomy". Archived from the original on 2005-11-03. Retrieved 2008-06-04.
- ^ See Mr R McElroy for details of various operations and the unintended effects of chemical cauterization
- ^ Ring, Malvin (July 2001). "How a Dentist's Name Became a Synonym for a Life-saving Device: The Story of Dr. Charles Stent". Journal of the History of Dentistry. 49 (2): 77–80. PMID 11484317. Archived from the original on 2005-04-28. Retrieved 2008-04-01.
- ^ How do they get the hole through a hypodermic needle?
- ^ Bonfils-Roberts, E (May 1972). "The Rib Spreader: A Chapter in the History of Thoracic Surgery" (PDF). Chest. 61 (5): 469–474. doi:10.1378/chest.61.5.469. ISSN 0012-3692. PMID 4558402. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-12-17. Retrieved 2008-04-22.
- ^ "General Instrument Sourcebook - KMedic" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2011-02-10.
- ^ Bailey & Love’s SHORT PRACTICE OF SURGERY (23rd ed.). ISBN 0-340-75949-6.
- ^ Gould, George M. (1934). Gould's Pocket Pronouncing Medical Dictionary (10th (rev) ed.). P. Blakiston's Son & Co., Inc.
