Macrauchenia
| Macrauchenia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Holotype skeleton of M. patachonica (larger) and Phenacodus primaevus (smaller) at American Museum of Natural History | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Litopterna |
| Family: | †Macraucheniidae |
| Subfamily: | †Macraucheniinae |
| Genus: | †Macrauchenia Owen, 1838 |
| Type species | |
| Macrauchenia patachonica Owen, 1838
| |
| Species | |
| |
| |
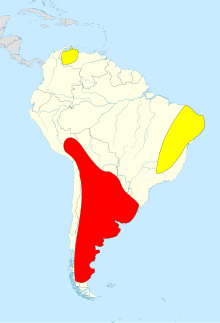
| Map showing the distribution of Macrauchenia in red, and Xenorhinotherium in yellow, inferred from fossil finds | |
Macrauchenia ("long llama", based on the now-superseded Latin term for llamas, Auchenia, from Greek "big neck") was a large, long-necked and long-limbed, three-toed native South American mammal in the order Litopterna.[1] The genus gives its name to its family, the Macraucheniidae or "robust litopterns". Like other litopterns, it is most closely related to even-toed ungulates (Perissodactyla), from which litopterns diverged approximately 66 million years ago. The oldest fossils in the genus date to the late Miocene, around seven million years ago, and M. patachonica disappears from the fossil record during the late Pleistocene, around 20,000-10,000 years ago. M. patachonica is one of the last and best known member of the family and is known primarily from the Luján Formation in Argentina, but is known from localities across southern South America. Another genus of macraucheniid Xenorhinotherium was present in northeast Brazil and Venezuela during the Late Pleistocene. The type specimen was discovered by Charles Darwin during the voyage of the Beagle. In life, Macrauchenia may have resembled a humpless camel, though the two taxa are not closely related.[2] It fed on plants in a variety of environments across what is now South America. Among the species described, M. patachonica and M. ullomensis are considered valid; M. boliviensis is considered a nomen dubium; and M. antiqua (or M. antiquus) has been moved to the genus Promacrauchenia.
Taxonomy

Macrauchenia fossils were first collected on 9 February 1834 at Port St Julian in Patagonia (Argentina) by Charles Darwin, when HMS Beagle was surveying the port.[3] As a non-expert he tentatively identified the leg bones and fragments of spine he found as "some large animal, I fancy a Mastodon". In 1837, soon after the Beagle's return, the anatomist Richard Owen identified the bones, including vertebrae from the back and neck, as from a gigantic creature resembling a llama or camel, which Owen named Macrauchenia patachonica.[4] In naming it, Owen noted the original Greek terms µακρος (makros, large or long), and αυχην (auchèn, neck) as used by Illiger as the basis of Auchenia as a generic name for the llama, Vicugna and so on.[5] The find was one of the discoveries leading to the inception of Darwin's theory. Since then, more Macrauchenia fossils have been found, mainly in Patagonia, but also in Bolivia, Chile and Venezuela.
The related genus Cramauchenia was named by Florentino Ameghino as a deliberate anagram of Macrauchenia.
Evolution


It is likely that Macrauchenia evolved from earlier litopterns Theosodon or Promacrauchenia, or a similar species. Litopterna was one of the five (four in some classifications) ancient orders of endemic South American mammals collectively called Meridungulates. Their relationships with other mammal groups outside South America have been poorly understood, as their early evolutionary history would have been in Western Gondwana, and outside of South America this area is now Antarctica. When South America separated from Antarctica in the Eocene,[6] meridungulate orders survived in South America in isolation. Most flourished in the Paleogene and then diminished. Formerly, North American paleontologists considered them inferior to Northern Hemisphere taxa and to have been outcompeted to extinction in the Great American Biotic Interchange after the establishment of the Central American land bridge. However, more recent evidence shows that three of the meridungulate orders declined long before, just as happened to early mammal groups elsewhere.[7] Litopterns and notoungulates continued, evolving into a variety of more derived forms. While toxodontid notoungulates expanded into North America during the GABI, litopterns remained confined to South America. Macrauchenia was among the last surviving meridungulates, along with litopterns such as Neocaliphrium and the large notungulates Toxodon and Mixotoxodon. These last endemic South American hoofed animals died out at the end of the Lujanian (10,000-20,000 years ago).[8]
Sequencing of mitochondrial DNA extracted from an M. patachonica fossil from a cave in southern Chile indicates that Macrauchenia (and by inference, Litopterna) is the sister group to Perissodactyla, with an estimated divergence date of sixty-six million years ago.[9][10] Analysis of collagen sequences obtained from Macrauchenia and Toxodon reached a similar conclusion and extended membership in the sister group clade to notoungulates.[11][12]
Description


Macrauchenia had a somewhat camel-like body, with sturdy legs, a long neck and a relatively small head. Its feet, however, more closely resembled those of a modern rhinoceros, with one central toe and two side toes on each foot. It was a large animal, with a body length of around 3 metres (9.8 ft) and a weight up to 1,042.8 kg (2,299 lb), about the size of a black rhinoceros.[13][14]
One striking characteristic of Macrauchenia is the openings for the nostrils on top of the head, above and between the eyes. Increasingly retracted nostrils are an evolutionary trend in later litopterns. Because mammals with trunks show the nostrils in a similar position, a popular hypothesis is that Macrauchenia had a trunk similar to a tapir or an inflated snout like that of the saiga antelope, perhaps to keep dust out of the nostrils.[13] However, a 2018 study comparing the skulls of tapirs and various other herbivorous extant and extinct mammal species instead saw similarities with the skulls of moose, suggesting that Macrauchenia and other macraucheniids, such as Huayqueriana did not possess trunks.[15] However, pictographs depicting various extinct megafauna dated to around 12,600 to 11,800 years ago from the Serranía de La Lindosa rock formation of Guaviare, Colombia showed what appears to be a possible trunked macraucheniid, presumably Xenorhinotherium.[16][17]
The snout of Macrauchenia is completely enclosed by bone, and the animal has an elongated neck that allowed it to reach upward; no living mammal with a proboscis has these features. An alternative hypothesis is that these litopterns were high browsers on tough and thorny vegetation, and retracted nostrils allowed them to reach leaves without being impaled in the nose. Sauropod dinosaurs (reconstructed as high browsers on conifer needles and cycads) have similar snouts, and living giraffes and gerenuks, high browsers on thorny vegetation, have more retracted nostrils than related taxa with other feeding habits.[7]
One insight into Macrauchenia's habits is that its ankle joints and shin bones may indicate that it was adapted to have unusually good mobility, being able to rapidly change direction when it ran at high speed.[18]
Macrauchenia is known, like its relative Theosodon, to have had a full set of 44 teeth.[citation needed]
Paleobiology

Macrauchenia was a herbivore, likely living on leaves from trees or grasses. Carbon isotope analysis of M. patachonica's tooth enamel, as well as analysis of its hypsodonty index (low in this case; i.e., it was brachydont), body size and relative muzzle width suggests that it was a mixed feeder, combining browsing on C3 foliage with grazing on C4 grasses.[19] A dental microwear, occusal enamel, and carbon isotope analysis of Macrauchenia and Xenorhinotherium found that both were grazers on C3 grasses.[20]
The genus was widespread, found in environments that ranged from dry to humid, from southern Chile to northeastern Brazil and the coast of Venezuela. Fossils of M. ullomensis have been found in Bolivia at altitudes up to 4000 meters. Habits and diet may have varied depending on the environment, but in plant feeders an elongated neck is usually an adaptation to allow high browsing on trees and shrubs. As the genus was not confined to forest, it was probably able to exploit more marginal environments by mixing high browsing with low browsing and grazing. A site in northern Chile preserved the remains of five subadults associated together, which suggests Macrauchenia may have lived in small herds or family groups.[7]

When Macrauchenia first arose, it could have been preyed upon by the largest of native South American mammal predators, the sabertoothed sparassodontid Thylacosmilus. The largest phorusrhacid birds may also have been able to prey on juveniles. After the GABI, the primary predator on adults would have been the very large sabertoothed cat Smilodon populator[21] and giant short-faced bears. Dire wolves and jaguars may also have hunted Macrauchenia, particularly juveniles.
It is presumed that Macrauchenia dealt with its predators primarily by outrunning them, or, failing that, kicking them with its long, powerful legs. The large size of adults would have limited their vulnerability to most predators. Its potential ability to twist and turn at high speed could have enabled it to evade pursuers; both Thylacosmilus and S. populator were ambush hunters likely unable to run down prey over distance if the prey evaded the first attack.
Distribution
Fossils of Macrauchenia have been found in:[22]
- Miocene
- Pliocene
- Pleistocene
References
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ "BBC - Science & Nature - Wildfacts - Macrauchenia". Retrieved 2009-06-15.
- ^ ed. Keynes, R. D. (2001). "Charles Darwin's Beagle Diary". Cambridge University Press. p. 214. Retrieved 2008-12-19.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "Darwin Correspondence Project - Letter 238 — Darwin, C. R. to Henslow, J. S., Mar 1834". Archived from the original on 2009-01-16. Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ^ Owen 1838, p. 35
- ^ "Tectonic history: into the deep freeze". Discovering Antarctica. Retrieved 2019-07-10.
- ^ a b c Croft, Darin (2016). Horned Armadillos and Rafting Monkeys; the Fascinating Fossil Mammals of South America. Indiana University Press.
- ^ Alberto L. Cione, Eduardo P. Tonni, Leopoldo Soibelzon: The Broken Zig-Zag: Late Cenozoic large mammal and tortoise extinction in South America. In: Revista del Museo Argentino de Ciencias Naturales. 5, 1, 2003, ISSN 1514-5158, S. 1–19, online Archived 2011-07-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Westbury, M.; Baleka, S.; Barlow, A.; Hartmann, S.; Paijmans, J. L. A.; Kramarz, A.; Forasiepi, A. M.; Bond, M.; Gelfo, J. N.; Reguero, M. A.; López-Mendoza, P.; Taglioretti, M.; Scaglia, F.; Rinderknecht, A.; Jones, W.; Mena, F.; Billet, G.; de Muizon, C.; Aguilar, J. L.; MacPhee, R. D. E.; Hofreiter, M. (2017-06-27). "A mitogenomic timetree for Darwin's enigmatic South American mammal Macrauchenia patachonica". Nature Communications. 8: 15951. Bibcode:2017NatCo...815951W. doi:10.1038/ncomms15951. PMC 5490259. PMID 28654082.
- ^ Strickland, A. (June 27, 2017). "DNA solves ancient animal riddle that Darwin couldn't". CNN. Retrieved June 27, 2017.
- ^ Welker, F.; Collins, M. J.; Thomas, J. A.; Wadsley, M.; Brace, S.; Cappellini, E.; Turvey, S. T.; Reguero, M.; Gelfo, J. N.; Kramarz, A.; Burger, J.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Ashford, D. A.; Ashton, P. D.; Rowsell, K.; Porter, D. M.; Kessler, B.; Fischer, R.; Baessmann, C.; Kaspar, S.; Olsen, J. V.; Kiley, P.; Elliott, J. A.; Kelstrup, C. D.; Mullin, V.; Hofreiter, M.; Willerslev, E.; Hublin, J.-J.; Orlando, L.; Barnes, I.; MacPhee, R. D. E. (2015-03-18). "Ancient proteins resolve the evolutionary history of Darwin's South American ungulates". Nature. 522 (7554): 81–84. Bibcode:2015Natur.522...81W. doi:10.1038/nature14249. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 25799987.
- ^ Buckley, M. (2015-04-01). "Ancient collagen reveals evolutionary history of the endemic South American 'ungulates'". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 282 (1806): 20142671. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.2671. PMC 4426609. PMID 25833851.
- ^ a b Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 248. ISBN 978-1-84028-152-1.
- ^ http://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/handle/10915/16838?show=full (in Spanish)
- ^ Moyano, S.R.; Giannini, N.P. (2018-10-10). "Cranial characters associated with the proboscis postnatal-development in Tapirus (Perissodactyla: Tapiridae) and comparisons with other extant and fossil hoofed mammals". Zoologischer Anzeiger. 277 (7554): 143–147. doi:10.1016/j.jcz.2018.08.005. ISSN 0044-5231.
- ^ Morcote-Ríos, Gaspar; Aceituno, Francisco Javier; Iriarte, José; Robinson, Mark; Chaparro-Cárdenas, Jeison L. (2020-04-29). "Colonisation and early peopling of the Colombian Amazon during the Late Pleistocene and the Early Holocene: New evidence from La Serranía La Lindosa". Quaternary International. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2020.04.026. ISSN 1040-6182.
- ^ "12,000-Year-Old Rock Drawings of Ice Age Megafauna Discovered in Colombian Amazon | Archaeology | Sci-News.com". Breaking Science News | Sci-News.com. Retrieved 2020-12-04.
- ^ Fariña, Richard A.; Blanco, R. Ernesto; Christiansen, Per (2005). "Swerving as the escape strategy of Macrauchenia patachonica Owen (Mammalia; Litopterna)". Ameghiniana. 42 (4): 752–760.
- ^ MacFadden, B. J.; Shockey, B. J. (Winter 1997). "Ancient feeding ecology and niche differentiation of Pleistocene mammalian herbivores from Tarija, Bolivia: morphological and isotopic evidence". Paleobiology. 23 (1): 77–100. doi:10.1017/S0094837300016651. JSTOR 2401158.
- ^ de Oliveira, Karoliny; Araújo, Thaísa; Rotti, Alline; Mothé, Dimila; Rivals, Florent; Avilla, Leonardo S. (March 2020). "Fantastic beasts and what they ate: Revealing feeding habits and ecological niche of late Quaternary Macraucheniidae from South America". Quaternary Science Reviews. 231: 106178. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106178.
- ^ Anton, Mauricio. "Sabertooth". Indiana University Press. Retrieved 2019-07-10.
- ^ Macrauchenia at Fossilworks.org
Further reading
- Barry Cox, Colin Harrison, R.J.G. Savage, and Brian Gardiner. (1999): The Simon & Schuster Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Creatures: A Visual Who's Who of Prehistoric Life. Simon & Schuster.
- Jayne Parsons. (2001): Dinosaur Encyclopedia. DK.
- Owen, Richard (1838). "Description of Parts of the Skeleton of Macrauchenia patachonica". In Darwin, C. R. (ed.). Fossil Mammalia Part 1 No. 1. The zoology of the voyage of H.M.S. Beagle. London: Smith Elder and Co.
External links
- Litopterns
- Messinian first appearances
- Pleistocene genus extinctions
- Miocene mammals of South America
- Pliocene mammals of South America
- Pleistocene mammals of South America
- Lujanian
- Ensenadan
- Uquian
- Chapadmalalan
- Montehermosan
- Huayquerian
- Neogene Argentina
- Cerro Azul Formation
- Pleistocene Argentina
- Pleistocene Bolivia
- Pleistocene Brazil
- Pleistocene Chile
- Pleistocene Paraguay
- Pleistocene Peru
- Pleistocene Uruguay
- Pleistocene Venezuela
- Fossils of Argentina
- Fossils of Bolivia
- Fossils of Brazil
- Fossils of Chile
- Fossils of Paraguay
- Fossils of Peru
- Fossils of Uruguay
- Fossils of Venezuela
- Fossil taxa described in 1838
- Taxa named by Richard Owen
