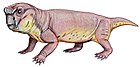
Kannemeyeria
| Kannemeyeria Temporal range: Anisian
~ | |
|---|---|

| |
| Skull of Kannemeyeria simocephalus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | †Anomodontia |
| Clade: | †Dicynodontia |
| Family: | †Kannemeyeriidae |
| Genus: | †Kannemeyeria Seeley, 1908 |
| Type species | |
| †Kannemeyeria simocephalus (Weithofer, 1888 [originally Dicynodon])
| |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Genus Synonymy
Species Synonymy
| |
Kannemeyeria is a genus of kannemeyeriid dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Africa and South America.[1] The generic name is given in honor of Dr. Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer, the South African fossil collector who discovered the original specimen.[2] It is one of the first representatives of the family, and hence one of the first large herbivores of the Triassic.
Description

Kannemeyeria was about 3 metres (9.8 ft) in length, about the size of an ox. Although it had a large head, it was lightweight due to the size of the eye sockets and nasal cavity. It also had limb girdles which formed massive plates of bone that helped support its heavily built body.[3] Despite the large size, Kannemeyeria may have been prey to large thecodonts like Erythrosuchus.[4]
Kannemeyeria was well-adapted to living as a herbivore; it had a powerful beak and strong jaw muscles built for shearing plant material.[3] Kannemeyeria had a massive head with unusually large openings for the eyes, nostrils and jaw muscles. It evidently tore up roots, stripped leaves from the vegetation with its horny break and ground them up with its toothless jaws.[5]
Distribution

Kannemeyeria is known from the Subzone B of Burgersdorp Formation of South Africa, the Ntawere Formation of Zambia, the Omingonde Formation of Namibia, the Lifua member of Manda Formation of Tanzania, and the Quebrada de los Fósiles Formation of Argentina.[6][7]
Classification

Below is a cladogram from Kammerer et al. (2013):[8]
| Kannemeyeriiformes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ^ "Kannemeyeria". Fossilworks. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Kannemeyeria". Paleofile. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ a b Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 191. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- ^ "Kannemeyeria". Prehistoric Wildlife. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Cloudsley-Thompson, John L. (2005). Ecology and Behaviour of Mesozoic Reptiles (2005 ed.). Springer. pp. 113–114. ISBN 978-3540224211. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Chinsamy-Turan, Anusuya (2011). Forerunners of Mammals: Radiation • Histology • Biology. Indiana University Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-253-00533-5. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Kammerer, C. F.; Ordoñez, M. D. (2021). "Dicynodonts (Therapsida: Anomodontia) of South America". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. In press. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2021.103171.
- ^ Kammerer, C. F.; Fröbisch, J. R.; Angielczyk, K. D. (2013). Farke, Andrew A (ed.). "On the Validity and Phylogenetic Position of Eubrachiosaurus browni, a Kannemeyeriiform Dicynodont (Anomodontia) from Triassic North America". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e64203. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...864203K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064203. PMC 3669350. PMID 23741307.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)