ZP3
Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 3, also known as zona pellucida glycoprotein 3 (Zp-3) or the sperm receptor, is a ZP module-containing protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP3 gene.[5] ZP3 is the glycoprotein in the zona pellucida most important for inducting the acrosome reaction of sperm cells at the beginning of fertilization.[6]
Function
The zona pellucida (ZP) is a specialized extracellular matrix that surrounds the oocyte and early embryo. It is composed of three or four glycoproteins (ZP1-4) with various functions during oogenesis, fertilization and preimplantation development. The protein encoded by this gene is a major structural component of the ZP and functions in primary binding and stimulation of the sperm acrosome reaction. The nascent protein contains a N-terminal signal peptide sequence, a conserved "ZP domain" module, a consensus furin cleavage site (CFCS), a polymerization-blocking external hydrophobic patch (EHP), and a C-terminal transmembrane domain. Cleavage at the CFCS separates the mature protein from the EHP, allowing it to incorporate into nascent ZP filaments. A variation in the last exon of this gene has previously served as the basis for an additional ZP3 locus; however, sequence and literature review reveals that there is only one full-length ZP3 locus in the human genome. Another locus encoding a bipartite transcript designated POMZP3 contains a duplication of the last four exons of ZP3, including the above described variation, and maps closely to this gene.[5]
Orthologs of these genes are found throughout Vertebrata. The western clawed frog appears to have two orthologs, and the sea lamprey has seven.[7]
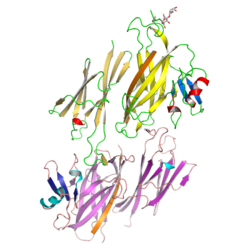
3D Structure
X-ray crystallographic studies of the N-terminal half of mammalian ZP3 (PDB: 3D4C, 3D4G, 3EF7, 5OSQ)[8] as well as its full-length avian homolog (PDB: 3NK3, 3NK4)[9] revealed that the protein's ZP module consists of two immunoglobulin-like domains, ZP-N and ZP-C. The latter, which contains EHP as well as a ZP3-specific subdomain, interacts with the ZP-N domain of a second molecule to generate an antiparallel homodimeric arrangement required for protein secretion.[9]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000188372 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000004948 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: zona pellucida glycoprotein 3 (sperm receptor)".
- ^ Litscher, E. S.; Williams, Z.; Wassarman, P. M. (2009). "Zona pellucida glycoprotein ZP3 and fertilization in mammals". Molecular Reproduction and Development. 76 (10): 933–941. doi:10.1002/mrd.21046. PMID 19504560. S2CID 21186053.
- ^ "EggNOG Database | Orthology predictions and functional annnotaion". eggnogdb.embl.de. Archived from the original on 4 March 2019. Retrieved 5 March 2019.
- ^ Monné M, Han L, Schwend T, Burendahl S, Jovine L (2008). "Crystal structure of the ZP-N domain of ZP3 reveals the core fold of animal egg coats". Nature. 456 (7222): 653–7. Bibcode:2008Natur.456..653M. doi:10.1038/nature07599. hdl:11563/8930. PMID 19052627. S2CID 4430083. PDB: 3D4C, 3D4G, 3EF7
- ^ a b Han L, Monné M, Okumura H, Schwend T, Cherry AL, Flot D, Matsuda T, Jovine L (2010). "Insights into egg coat assembly and egg-sperm interaction from the X-ray structure of full-length ZP3". Cell. 143 (3): 404–15. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.041. PMID 20970175. S2CID 18583237. PDB: 3NK3, 3NK4
Further reading
- Bansal P, Chakrabarti K, Gupta SK (2009). "Functional activity of human ZP3 primary sperm receptor resides toward its C-terminus". Biol. Reprod. 81 (1): 7–15. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.108.074716. PMID 19246320.
- Bleil JD, Wassarman PM (1980). "Mammalian sperm-egg interaction: identification of a glycoprotein in mouse egg zonae pellucidae possessing receptor activity for sperm". Cell. 20 (3): 873–82. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(80)90334-7. PMID 7418009. S2CID 29105880.
- Caballero-Campo P, Chirinos M, Fan XJ, et al. (2006). "Biological effects of recombinant human zona pellucida proteins on sperm function". Biol. Reprod. 74 (4): 760–8. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.105.047522. PMID 16407501.
- Chamberlin ME, Dean J (1990). "Human homolog of the mouse sperm receptor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (16): 6014–8. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.6014C. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.16.6014. PMC 54462. PMID 2385582.
- Chiu PC, Wong BS, Chung MK, et al. (2008). "Effects of native human zona pellucida glycoproteins 3 and 4 on acrosome reaction and zona pellucida binding of human spermatozoa". Biol. Reprod. 79 (5): 869–77. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.108.069344. PMID 18667750.
- Choudhury S, Ganguly A, Chakrabarti K, et al. (2009). "DNA vaccine encoding chimeric protein encompassing epitopes of human ZP3 and ZP4: immunogenicity and characterization of antibodies". J. Reprod. Immunol. 79 (2): 137–47. doi:10.1016/j.jri.2008.09.002. PMID 19004505.
- Dell A, Chalabi S, Easton RL, et al. (2003). "Murine and human zona pellucida 3 derived from mouse eggs express identical O-glycans". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (26): 15631–6. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10015631D. doi:10.1073/pnas.2635507100. PMC 307619. PMID 14673092.
- Florman HM, Wassarman PM (1985). "O-linked oligosaccharides of mouse egg ZP3 account for its sperm receptor activity". Cell. 41 (1): 313–24. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(85)90084-4. PMC 7133279. PMID 2986849.
- Furlong LI, Harris JD, Vazquez-Levin MH (2005). "Binding of recombinant human proacrosin/acrosin to zona pellucida (ZP) glycoproteins. I. Studies with recombinant human ZPA, ZPB, and ZPC". Fertil. Steril. 83 (6): 1780–90. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2004.12.042. PMID 15950651.
- Gook DA, Edgar DH, Borg J, Martic M (2008). "Detection of zona pellucida proteins during human folliculogenesis". Hum. Reprod. 23 (2): 394–402. doi:10.1093/humrep/dem373. PMID 18033806.
- Han L, Monné M, Okumura H, Schwend T, Cherry AL, Flot D, Matsuda T, Jovine L (2010). "Insights into egg coat assembly and egg-sperm interaction from the X-ray structure of full-length ZP3". Cell. 143 (3): 404–15. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.041. PMID 20970175. S2CID 18583237. PDB: 3NK3 PDB: 3NK4
- Jovine L, Qi H, Williams Z, Litscher E, Wassarman PM (2002). "The ZP domain is a conserved module for polymerization of extracellular proteins". Nat. Cell Biol. 4 (6): 457–61. doi:10.1038/ncb802. PMID 12021773. S2CID 11575790.
- Jovine L, Qi H, Williams Z, Litscher ES, Wassarman PM (2004). "A duplicated motif controls assembly of zona pellucida domain proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (16): 5922–7. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.5922J. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401600101. PMC 395899. PMID 15079052.
- Kiefer SM, Saling P (2002). "Proteolytic processing of human zona pellucida proteins". Biol. Reprod. 66 (2): 407–14. doi:10.1095/biolreprod66.2.407. PMID 11804956.
- Monné M, Han L, Schwend T, Burendahl S, Jovine L (2008). "Crystal structure of the ZP-N domain of ZP3 reveals the core fold of animal egg coats". Nature. 456 (7222): 653–7. Bibcode:2008Natur.456..653M. doi:10.1038/nature07599. hdl:11563/8930. PMID 19052627. S2CID 4430083. PDB: 3D4C PDB: 3D4G PDB: 3EF7
- Ni Y, Li K, Xu W, et al. (2007). "Acrosome reaction induced by recombinant human zona pellucida 3 peptides rhuZP3a22 approximately 176 and rhuZP3b177 approximately 348 and their mechanism". J. Androl. 28 (3): 381–8. doi:10.2164/jandrol.106.001289. PMID 17192598.
- Qi H, Williams Z, Wassarman PM (2002). "Secretion and assembly of zona pellucida glycoproteins by growing mouse oocytes microinjected with epitope-tagged cDNAs for mZP2 and mZP3". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (2): 530–41. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-09-0440. PMC 65647. PMID 11854410.
- Rankin T, Dean J (2000). "The zona pellucida: using molecular genetics to study the mammalian egg coat". Rev. Reprod. 5 (2): 114–21. doi:10.1530/ror.0.0050114. PMID 10864856.
- Törmälä RM, Jääskeläinen M, Lakkakorpi J, et al. (2008). "Zona pellucida components are present in human fetal ovary before follicle formation" (PDF). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 289 (1–2): 10–5. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2008.01.029. PMID 18502569. S2CID 3455166.
- van Duin M, Polman JE, Verkoelen CC, Bunschoten H, Meyerink JH, Olijve W, Aitken RJ (December 1992). "Cloning and characterization of the human sperm receptor ligand ZP3: evidence for a second polymorphic allele with a different frequency in the Caucasian and Japanese populations". Genomics. 14 (4): 1064–70. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80130-2. PMID 1478648.
- Wassarman PM, Jovine L, Litscher ES (2001). "A profile of fertilization in mammals". Nat. Cell Biol. 3 (2): E59–64. doi:10.1038/35055178. PMID 11175768. S2CID 6172791.
- Zhao M, Boja ES, Hoodbhoy T, et al. (2004). "Mass spectrometry analysis of recombinant human ZP3 expressed in glycosylation-deficient CHO cells". Biochemistry. 43 (38): 12090–104. doi:10.1021/bi048958k. PMID 15379548.
- Zhao M, Gold L, Ginsberg AM, et al. (2002). "Conserved furin cleavage site not essential for secretion and integration of ZP3 into the extracellular egg coat of transgenic mice". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (9): 3111–20. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.9.3111-3120.2002. PMC 133755. PMID 11940668.
External links
- ZP3+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.