Cinoxate
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
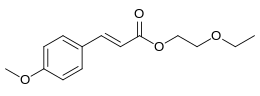
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Ethoxyethyl (2E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
2-Ethoxyethyl p-methoxycinnamate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.901 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H18O4 | |
| Molar mass | 250.294 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.102 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K) |
| Boiling point | 184 to 187 °C (363 to 369 °F; 457 to 460 K) at 2 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cinoxate is an organic compound used as an ingredient in some types of sunscreens. It is an ester formed from methoxycinnamic acid and 2-ethoxyethanol. It is a slightly yellow viscous liquid that is insoluble in water, but miscible with alcohols, esters, and vegetable oils.
It was approved as UV filter in the USA by the FDA in 1961, but it is not commonly used in cosmetic formulations anymore.[2]
See also
- Amiloxate, another methoxycinnamate-based sunscreen
- Octyl methoxycinnamate, another methoxycinnamate-based sunscreen
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2312.
- ^ Pantelic, Molly N.; Wong, Nikita; Kwa, Michael; Lim, Henry W. (24 February 2023). "Ultraviolet filters in the United States and European Union: A review of safety and implications for the future of US sunscreens". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 88 (3): 632–646. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.11.039.
