Lake Mamry
| Lake Mamry | |
|---|---|
 Lake Dargin, part of Lake Mamry | |
| Location | Masurian Lake District |
| Coordinates | 54°6′47″N 21°42′2.1″E / 54.11306°N 21.700583°E |
| Type | Glacial lake |
| Primary outflows | Angrapa |
| Basin countries | Poland |
| Surface area | 104 km2 (40 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 44 m (144 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 116 metres (381 ft) |
| Islands | 33 (7 in Mamry proper) |
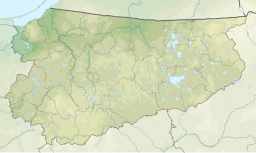
Mamry (German: Mauersee, Lithuanian: Mauras) is a lake in the Masurian Lake District of Poland's Warmia-Mazury Province. It is the second largest lake in Poland, with an area of 104 square kilometres (40 sq mi). The lake's maximum depth is 44 metres (144 ft) with an average depth of 11 metres (36 ft).
It actually comprises six connected lakes: Mamry, Kirsajty, Kisajno, Dargin, Święcajty and Dobskie.[1] Mamry features 33 islands, totaling 213 hectares (530 acres), some of which are ornithological reserves.[2]
Masurian Canal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lake Mamry is a popular tourist destination. It is connected to the Pregolya and the Baltic Sea by the disused Masurian Canal.[3] The largest town on the lake shore is Giżycko.
The lake bottom is diversified, with numerous depressions and shallows, while the northern part is considerably deeper, and the bottom is overgrown with raised vegetation and underwater meadows with horsetails. The shores of the lake are mostly low and marshy, partly overgrown with forest.
History
In the past, the lakes of the Mamry complex formed separate bodies of water connected by streams. The water level in the lakes rose in the 16th–17th centuries by several meters. The following factors contributed to the rise of the water level in the Mamry complex: the dam on the Węgorapa River (the mill), movements of the earth crust - post-glacial rebound in the northern part of the complex by one millimetre (0.039 in) a year. The former road to the church from Kal to Węgielsztyn, some Masurian settlements and cemeteries were under water.

References
- ^ NadJezioro (2019-09-16). "Mamry Lake - The Land of the Great Masurian Lakes". Jeziora Polski. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ^ Zalewski, Marcin; Ulrich, Werner (November 2006). "Dispersal as a key element of community structure: the case of ground beetles on lake islands". Diversity & Distributions. 12 (6): 767–775. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4642.2006.00283.x. ISSN 1366-9516. S2CID 86276672.
- ^ Marszelewski, Włodzimierz; Adamczyk, Alicja (2004). "Changes in the area of the Mazurian Lakes in the light of the cartographic materials at the scale 1:25000". Limnological Review. ISSN 1642-5952.