Javan short-tailed gymnure
| Javan short-tailed gymnure | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Erinaceidae |
| Genus: | Hylomys |
| Species: | H. suillus[1]
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hylomys suillus[1] S. Müller, 1840
| |
| |
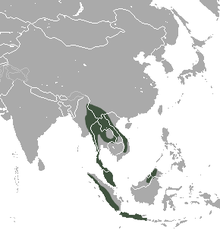
| Short-tailed gymnure range, including H. suillus and all current species that were formerly a part of the species | |
The Javan short-tailed gymnure (Hylomys suillus) is a small mammal from the family of the Erinaceidae. The scientific name of the species is first published by Salomon Müller in 1840. This species used to include the dorsalis, maxi, and peguensis subspecies, but these have now been elevated to species of their own: the Bornean short-tailed gymnure, Max's short-tailed gymnure, and the northern short-tailed gymnure.[3] In addition, two new species were created from two other populations of H. suillus.[3] The range of this species is now limited to Java.[3]
Description
The upperparts of the short-tailed gymnure are reddish brown to dark brown, with a grey tinge. The underparts are light grey, with white-tipped hairs. It resembles a large shrew, with a long snout and a very short hairless tail. It also has rounded, leathery ears.[4] The head and body length is 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 in) and the tail length measures 2–3 cm (0.79–1.18 in)[5]
Habits and habitat
The short-tailed gymnure is active both during day and at night. It lives in hilly and montane forests up to 3,000 m (9,800 ft), and sometimes in humid lowland forests. It feeds mainly on insects on the ground but also sometimes takes fruit. It normally does not live any longer than 2 years.[5]
Distribution
The species lives on the Indonesian island of Java.[3]
References
- ^ Hutterer, R. (2005). Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 218. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Chiozza, F. (2016). "Hylomys suillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40611A115175083.
- ^ a b c d Hinckley, A.; Camacho-Sanchez, M.; et al. (2023). "An integrative taxonomic revision of lesser gymnures (Eulipotyphla: Hylomys) reveals five new species and emerging patterns of local endemism in Tropical East Asia". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society: zlad177. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad177.
- ^ Feldhamer, George; et al. (2015). Mammalogy: Adaptation, Diversity, Ecology (fourth ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 285. ISBN 978-1-4214-1588-8.
- ^ a b Shepherd, Chris R.; Shepherd, Loretta Ann (2012). A Naturalist's Guide to the Mammals of Southeast Asia. Wiltshire: John BeauFoy Publishing. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-906780-71-5.
External links


